Effects of Long Term Use of Flavonoids on the Absorption and Tissue Distribution of Orally Administered Doses of Trace Elements in Rats
Full text
Figure
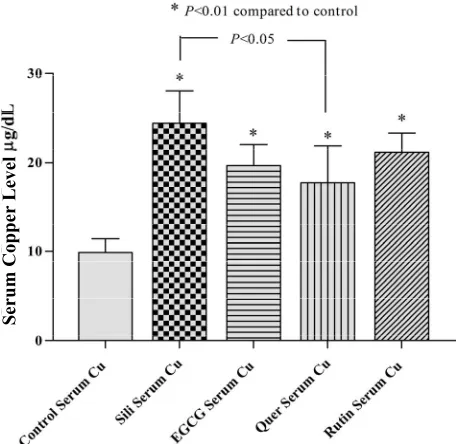


Related documents
Figure 8 shows the variation in instantaneous power loss for cases with different crowning for the duration of a meshing cycle.. Total power loss along the meshing cycle for
To test our hypothesis of domain adaptation, we trained a FCN on a subset of the IXI dataset to regress the rigid transformation parameters as described in previous experiments
Oral DNEL / Long term exposure - Systemic effects 0.75 mg/Kg bw/d (general population) DNEL / Short term exposure - Systemic effects 0.75 mg/Kg (general population) Dermal DNEL /
Mice in groups C, D and E were orally administered Mangifera indica extract (50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg and 150 mg/kg body weight, respectively) dissolved in 0.2 ml of distilled water for
perspective of the Global North, leaving the rural population of the Global South diminished and ignored (Banerjee, 2003, p. 21–22) agree that the western view and ideologies
et al.. A fourth reason comes from one opinion frequently expressed on the VRML-list mailing list, and supported by many of the par- ticipants: 3D environments must handle 2D
Despite the popularity of direct democracy in recent decades, research on the actual output effects of popular decision- making is rare. This is especially true with regard to
Two-dimensional materials (TDMs) including graphene and its derivatives, transition metal dichalcogenides (e.g. MoS 2 , WS 2 ), black phosphorus (BP), metal nanosheets