Amino[(1H benzimidazol 2 yl)amino]methaniminium 4 methylbenzenesulfonate
Full text
Figure

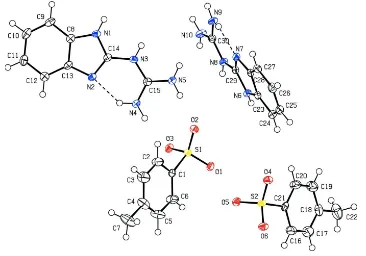

Related documents
The supramolecular structure is mainly governed by C—H N hydrogen-bonded centrosymmetric dimers, C—H O and C—H S hydrogen bonds and S and – stacking interactions
In addition, cations and anions are linked through N—H O hydrogen bonds, and the water molecule bridges two anions with two O—H O hydrogen bonds and is also the acceptor of an
In the crystal, a single strong O—H O inter- molecular hydrogen bond links the anions, forming chains along the c- axis direction.. The chains of anions are linked by the
Supramolecular tapes along [110] are formed in the crystal packing through N(amino)—H O(hydroxyl) and N(amino)—H N(pyrimidinyl) hydrogen bonds, and these are linked into layers
In the crystal, molecules are connected through N—H N hydrogen bonds and weak C—H O contacts, forming a two-dimensional network parallel to (001)..
In the crystal, uncoordinated nitrate anions and the coordi- nating water molecules are involved in O—H O and N— H O hydrogen bonds, forming a bridge between the pyrazole
In the crystal structure, intermolecular N—H O and C—H O hydrogen bonds link each molecule to two others, forming an infinite one-dimensional supramolecular structure along the
The crystal packing is stabilized by a classical N—H O hydrogen bond, several weak C—H O hydrogen bonds and a – stacking