Journal of Engineering Innovation and Research, Volume: IX, Issue:3, July-September 2019 1
ISSN 2230- 9373
Volume-IX , Issue-3
July-September, 2019
Conceptual Roadmap of Sustainability for
Small Scale Organizations
Chinmay Das
Associate Professor, Mechanical Engineering Department, ABIT, Cuttack chinmaydas@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
In today’s turbulent market environment the survival of small scale organizations is at stake.
The big organizations are creating barriers for growth of small enterprises due to their
marketing and technological prowess. The failure of small scale sector will create adverse
cascading effects on employment and economy of the nation. The paper addresses some
strategic issues of sustainability for this sector.
Key Words:
Sustainability, Collaborative Network, Virtual Enterprise
INTRODUCTION
The small scale sector plays significant role in terms of employment creation, regional development, promotion of entrepreneurship culture and innovations, and introduction of products for niche markets. These organizations have certain inherent advantages like lean structure, dynamic behavior, quick adaptability to market evolution, active involvement of versatile human resources, etc. At the same time, their activities are constrained due to limited capability in technology, plant & machinery, research & development. Lack of sophisticated know-how, difficulty in diverting skilled personnel from day to day activities to undertake process reengineering initiatives also play barrier to their growth [1].
In turbulent market condition, it is really testing time for small scale organizations to survive and grow. Due to latest manufacturing technology like FMS, CIM, Distributed Manufacturing, Mass Customization techniques large scale organizations are successfully serving the low volume market segments which are traditionally catered by small enterprises. Therefore the competitive advantage developed to serve the niche market in quick time is now under severe pressure to sustain [1].
Journal of Engineering Innovation and Research, Volume: IX, Issue:3, July-September 2019 2 in developed countries maintenance and acceleration of the already high levels of resource consumption are the prime concerns. Natural resources are often viewed as limit less by the industrialized world, either due to a myopic view of the future or because of their immense faith in technology providing a substitute for the natural resource [2].
The ecological damage and its consequences on quality of life have made the awakened customers ready to pay more for products that are environment friendly. The cost of production of these products will be high if sustainability issue is not addressed properly. Here small organizations have competitive edge over large ones due to their inherent flexible structure that encourage rapid collaboration. The paper addresses some important issues on sustainable practices in the field of design, manufacture and delivery of eco-products.
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
A common definition of sustainable development is that of the UN Brundtland Commission. According to it, sustainable development is that process of development, which meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This concept suggests that, in addition to its economic performance, an organization must also account for and focus on its environmental and social performance to be truly sustainable. Another common way of saying this is “people, planet, and profit”. Sustainability is the intersection of these three concepts.
Figure.1 Sustainability as the intersection of key parts
Journal of Engineering Innovation and Research, Volume: IX, Issue:3, July-September 2019 3 Managing operations in an environmentally and socially responsible manner –“sustainable manufacturing”– is no longer just nice-to-have, but a business imperative. The organiations across the world face increased costs in materials, energy, and compliance coupled with higher expectations of customers, investors and local communities. Many businesses have already started to take important steps towards green growth –ensuring their development is economically and environmentally sustainable. Their pioneering experiences largely show that environmental improvements go hand in hand with profit-making and improved competitiveness. Unfortunately the small organizations lack adequate strength in both capacity and capability towards implementaion of sustainable practces [3].
Chinmay Das, et al suggest collaborative networking for small enterprises to implement sustainability concepts and remain productive. A collaborative network (CN) is a network consisting of a variety of entities ( e.g. organisations and people) that are largely autonomous, geographically distributed, and heterogeneous in terms of their operating environment, culture, social capital and goals, but that collaborate to better achieve common or compatible goals, and whose interactions are supported by computer network. In today’s society, collaborative networks manifest in a large variety of forms like virtual enterprises, dynamic supply chain, dynamic virtual organisations, virtual team, professional virtual communities, virtual organisation breeding environment, etc. [4].
Out of various collabortive forms virtual enterprise (VE) is suitable for small organizations. It is a temporary collaboration among compatible organisations and people connected by information & communication technology to share resources, risks, responsibilities, rewards through effective and efficient solutions to fast changing business opportunities [5].
ARCHITECTURE OF VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
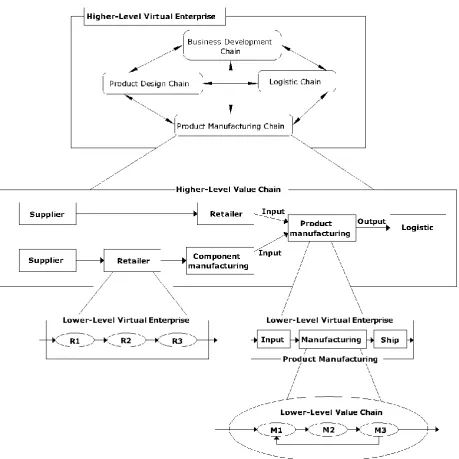
The architecture of VE is developed considering the fact that it represents a flexible, dynamic, autonomous, multilevel network. Flexibility will come by the combination of technology and people. Extensive use of ICT will give sufficient information at the right time for quick decision making. Since the collaboration among like minded partners is short term in nature, therefore it brings dynamism to the network. Any partner can join or leave the network at any time. All the members of VE maintain their individual identities while offering their core competencies for commercial exploitations. They are autonomous in nature. To satisfy above criteria the structure of VE must be multi-layered, modular, reusable and decomposable in nature. It operates in multiple levels--higher and lower levels. Each level has its own VE and Value Chains (VC).A generic VE with its basic elements is given in Figure-2 showing different levels. A brief description of the various building blocks is given here.
Industry Cluster (IC): It consists of a group of organisations located in the same geographical region and operating in a common business sector. It draws competitive advantage through some common resources like technologies & tools, labour pools, buyers & suppliers, distribution channels etc. Some sort of cooperation exists among the organisations when business opportunities arise.
Virtual Industry Cluster (VIC): In CN the member organisations share their resources and responsibilities. Collaboration will be possible only when the organisations reengineer their activities from context dependent into context independent in nature. All the sharable resources are virtualized using information, communication technologies (ICT). These likeminded organisations with compatible processes form VIC. It may not be confined to same geographical region.
Journal of Engineering Innovation and Research, Volume: IX, Issue:3, July-September 2019 4
Figure 2: The various levels of value chains and virtual enterprises
Virtual Enterprise Value Chain (VEVC): In a VEBE the organisations possessing common core competencies will form virtual enterprise value chain (VEVC) like design value chain, manufacturing value chain, logistics value chain, marketing & business development value chain, project engineering value chain etc. This value chain may not be confined to any specific geographical region. Marketing & business development value chain becomes the interface between the customers and VE during the execution of any project.
Journal of Engineering Innovation and Research, Volume: IX, Issue:3, July-September 2019 5 Support Service Providers (SSP): For smooth and speedy execution of projects VE needs services from specialized organizations like banks & lending institutions, R & D organizations, regulatory & environmental bodies, quality certification bodies, federal organizations etc.
Through VE the participating organization will always search and collaborate with compatible partners to achieve sustainability in design, manufacture and delivery of eco friendly products.
CONCLUSION
The sustainable practices will bring more profit in long term and the small organizations will
develop competitive edge over the large ones. Due to their inherent weakness small enterprises
cannot implement every sustainable practices themselves. So they will form collaborative
network like virtual enterprise to augment their capacity and capability.
REFERENCES
[1] Das, Chinmay, Innovations through virtual enterprise: A case study for MSMEs, International Journal of Engineering, Business and Enterprise Applications, Volume-1, Issue-5, June-August 2013, pp 77-80 [2] Ramakrishnan P.S., Ecology and Sustainable Development, National Book Trust, pp 14-15 [3] Satpathy, Biswajit, Sustainable Manufacturing, Seminar Presentation
[4] Das, Chinmay, Development of Architecture of Virtual Enterprise suitable for small organizations,
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, Volume-111, Issue-2, February 2014, pp 1721-1724
[5] Rout, Biswaranjan and Das, Chinmay, Sustainable Manufacturing Strategy for Socio-Economic