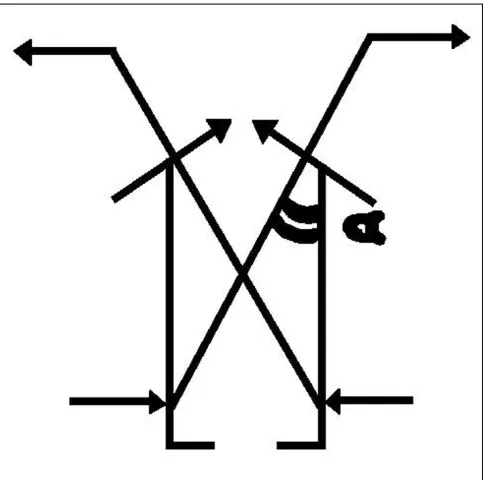
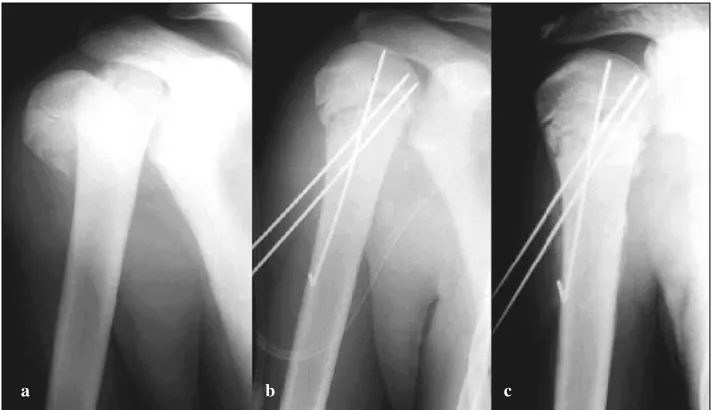
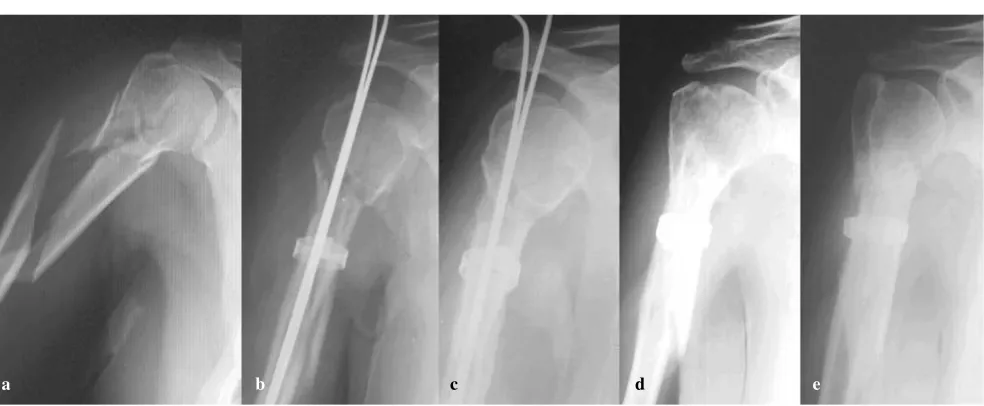
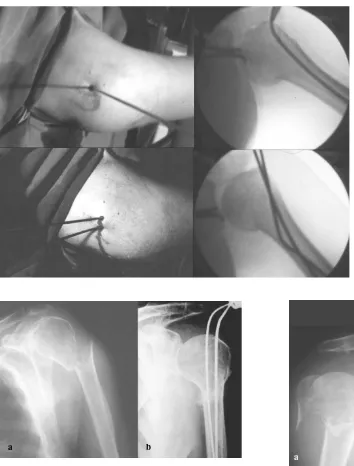
Percutaneous elastic fixation of proximal humeral fractures: operative indications, techniques, results and complications
Full text
Figure
![Fig. 1 Neer’s four-part classification (from [2] with permission)](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/941998.1592851/2.595.56.555.79.350/fig-neer-s-classification-permission.webp)

Related documents
The specific shortcomings of the original and revised VIFs discussed in this paper are perti- nent not only to the Cambodian case, but also as cautionary tales to other
For effective control of Rottboellia cochinchinensis, pre – emergence application of pendimethalin 1.5 kg ha -1 in cropped fields and post emergence spraying
G-CSF-producing gastric ASC has two poor prognos- tic factors, namely, the squamous cell component of the tumor and the G-CSF production.. Although the inci- dence of
AGREE: Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation; AHCPR: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; AHRQ: Agency for Health Care Research and Quality; AIRE: Appraisal
Iraq, not only for Germany, but for NATO, Kosovo, Afghanistan, and German foreign relations.. This paper uses a variety of sources in its analysis, including many peer
Results: Human brain microvascular endothelial cells exhibit a unique phenotype in response to shear stress com- pared to static conditions: (1) they do not elongate and align,
To date CHEK2 mutations have been associated with an increased risk of cancer at several different sites, including breast, prostate, thyroid, colon, kidney, stomach, (low-
For instance, the micro- biome associated with obesity has been found to be more efficient in harvesting energy from the diet, alter host metabolic pathways such as fatty