A new physiology image encryption algorithm based on two dimensional coupled chaotic Map
Full text
Figure
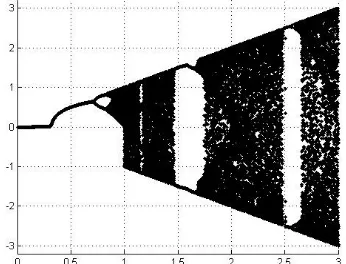
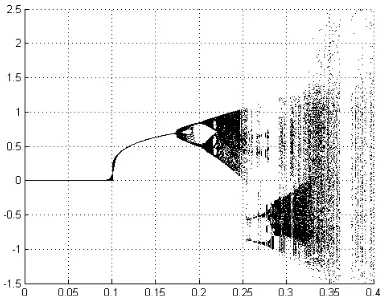


Related documents
Sea ice in Mc- Murdo Sound is atypical of Antarctic pack ice, so improved understanding of the CS-2 freeboard measurement over vary- ing snow and sea ice conditions in open water
The aims of this study were: 1) the comparison of the generic HRQoL and fatigue between chronic liver patients and healthy Dutch controls and 2) to give a profound insight in
software to obtain the section curve of refactoring, obtaining high quality of reconstruction model, through cross.. section data preprocessing in the first place, the cross
Figure 1: Typical example of estimating the background from an cluttered image sequence: (a) input frames cluttered with foreground objects, where only parts of the background
Different from the original BPN network learning algorithm, our proposed scheme lets each party encrypt her/ his input data set and upload the encrypted data to the
Figure 4 The ratio of Treg cells to Th17 cells negatively correlated with total bilirubin levels in chronic HBV-infected patients, especially in patients with ACHBLF (B) and
AHA/NHLBI: American Heart Association/National Heart Lung and Blood Institute; AUC: Area under curve; BMI: Body mass index; c-HDL: Cholesterol associated to high density
Driving need, initial event rate, fraction of events per- ceived as risky, event decay time, effect of recent events on monthly driving, effect of recent events on events per mile,


