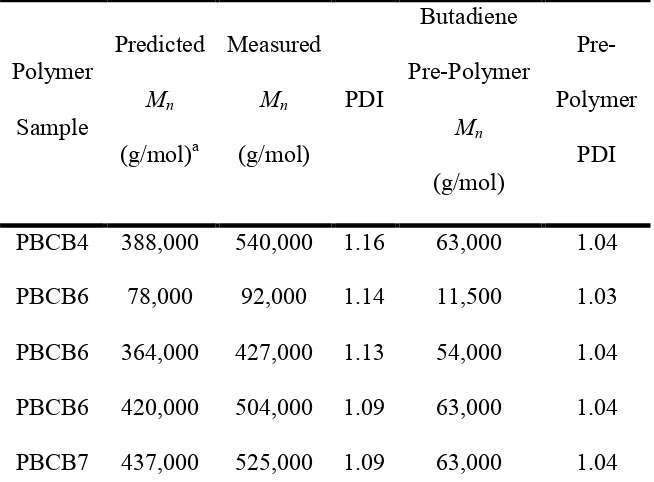
Rheology and Dynamics of Side Group Liquid Crystalline Polymers in Nematic Solvents
Full text
Figure



Outline
Related documents
This article focuses on the analysis of seasonal varia- tion of physicochemical parameters and heavy metal concentrations in both seasons (dry and raining seasons); in surface
The lack of an instrument that is useful during the child's growth, and follows the guidelines of the ICF, led to the development of the Clubfoot Assessment Protocol (CAP). The aims
Our result shows that the information in imperfect but abundant data from unambiguous attachments, as shown in Tables 2 and 3, is sufficient to resolve ambigu- ous
T h e states and the transi- tion probabilities of the Markov model were de- termined by the learning algorithm and tag out- put probabilities were estimated
The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only
At the time-points where we observed equivalent running- and AICAR-induced muscle pAMPK levels (7 and 14 days), cell proliferation, synaptic plasticity and gene expression, as well
The study involved germination of non-dormant seeds in the light and the dark at 5–30°C, the germination energy at 15, 24, and 33°C, and the primary dormancy of seeds matured during
The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are
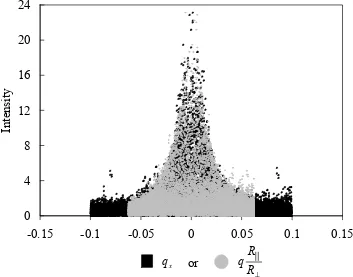


![Table 4.2. MALLS results. a The molar masses listed in this table are those calculated based on 100% attachment of the mesogen to the backbone [27]](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/310635.1032260/71.612.192.458.415.632/table-malls-results-masses-calculated-attachment-mesogen-backbone.webp)

