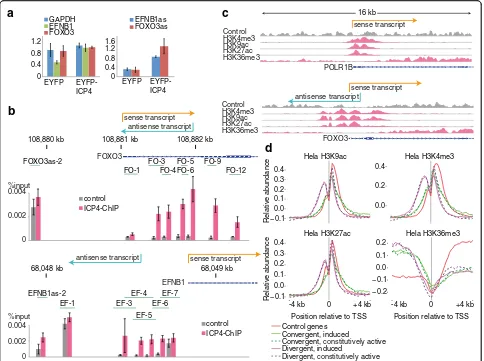
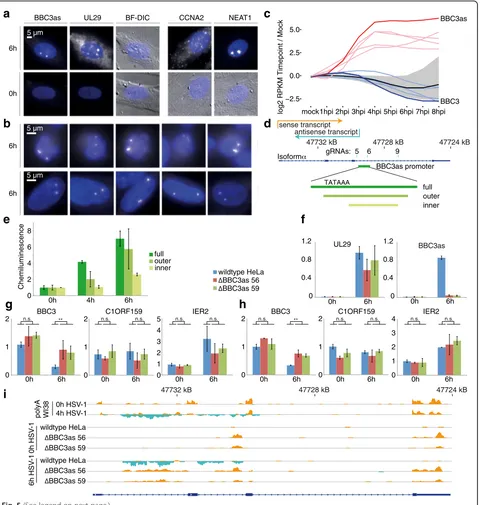
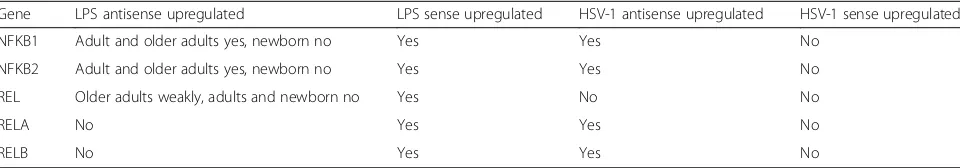
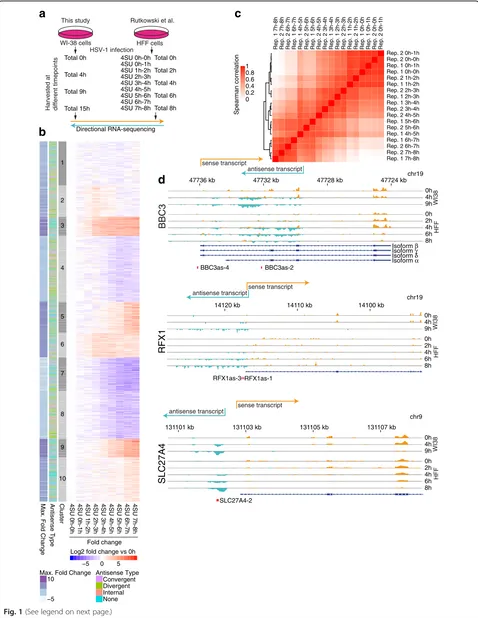
Widespread activation of antisense transcription of the host genome during herpes simplex virus 1 infection
Full text
Figure
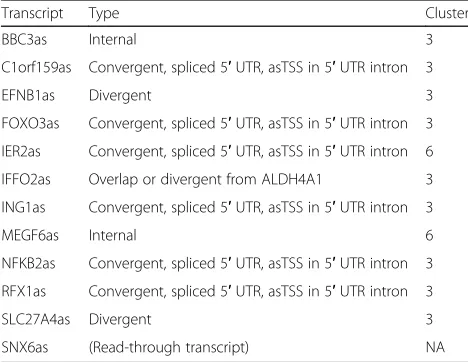
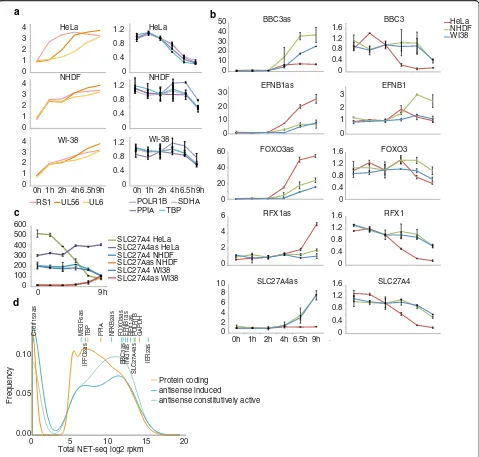
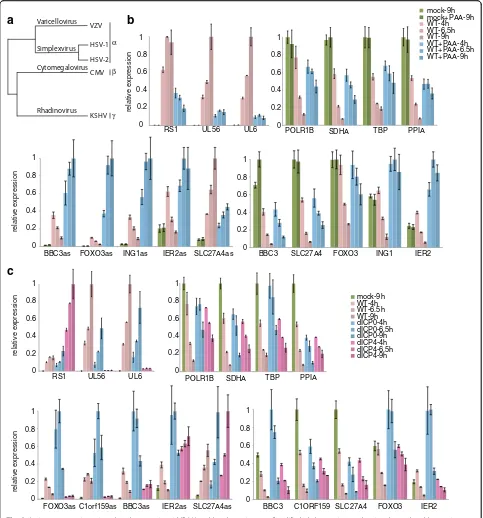
Related documents
This paper proposes an accounting methodology which estimates fore- gone C sequestration derived LUCF change in the southern New England State of Connecticut (CT). The Natural
In this study, biliary stone (in bile duct or gall-bladder) is the first common cause of obstructive jaundice (61.3%) as it obstructs flow of bile which is retained in liver
When an intruder enters the ladies compartment, the system transmits a warning signal to the receiver kept near to the officials in the train.. Once warning signal is received it
Objective: This study aimed to determine the magnitude and associated factors of surgical site infection following cesarean section at Felegehiwot referral hospital, Amhara,
Figure 3.7 Personal responsible for selecting cutting-off processes 27 Figure 3.8 Personal responsible for selecting cutting-off machines 27 Figure 3.9 Personal responsible
In this context, this chapter explores what Brazilian state and corporate determination to lead the international commodification of green energy in general – and sugar-derived
Virus expression can be enhanced by activation with cofactors such as CD3 antibodies (29) or by activation of HIV long terminal repeat (LTR)-directed viral gene expression by
In order to analyze the role of V3 domain sequences in mediating HIV entry, we introduced several amino acid substitution mutations in the GPGRA sequence of gpl60 derived from