Size and Shape Dependent Young Modulus and Vibrational Frequency of Nanomaterials
Full text
Figure
![Fig. 1: Size and shape dependence of Young modulus of TiO2 using eqs. (4-6). The experimental data[1] are shown by for TiO2 (spherical)](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/8582867.861458/5.612.147.390.512.685/size-shape-dependence-young-modulus-using-experimental-spherical.webp)
![Fig.5: Size and shape dependence of Young modulus of Cu using eqs. (4-6). The experimental data [5] are shown by for Cu nanowire at 0K and .are the theoretical results obtained by Aoet al](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/8582867.861458/6.612.165.400.523.686/dependence-young-modulus-experimental-nanowire-theoretical-results-obtained.webp)
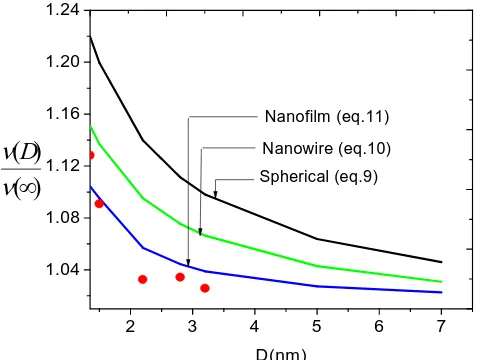
Related documents
As described in the section Production of recombinant antibody fragments by Escherichia coli , this micro-organ- ism has shown to be a potential expression host for anti-
In the case of thermal pads, high pressures are needed to achieve an adequate interface, thus, a paste and pad of similar bulk thermal conductivity may have very different
Project mainly accommodate the formation of insulating bricks using agricultural by product .In this chaptered are briefly introduced about status of rice husk, pigeon pea ,
Further research is required to assess other modes of monitoring and other types of technology; however, current data indicate that face-to-face technologies can likely be used
Routing can be posed as an optimization problem by using the above mapping from packet loss probability to video distortion where the objective is to minimize
• Small 18 µL sample size mode • User-definable high/low flagging • Automated quality assurance • Compact benchtop design • Zero routine maintenance. Clinical
The students’ improvement in each session was observed through tasks and homework. At the end of the first session, the students were assigned to do little research in the
No cytotoxicity was observed for any of MC hydrogels, gold NP (Conc: 1.00 mM), or leptin- embedded MC–gold NP hydrogels incubated with mouse embryonal fibroblast 3T3-L1 cells