Original Article Cyclin D1b overexpression inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in cervical cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
Full text
Figure
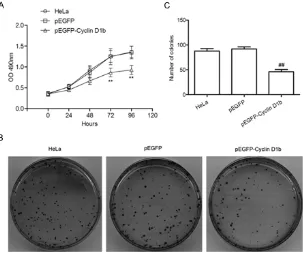

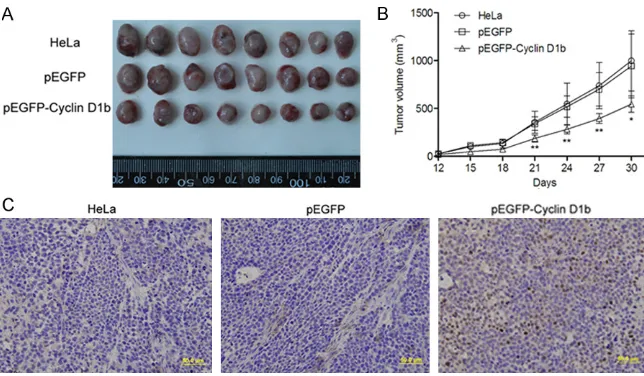
Related documents
In addition, we found that psoralen could induces cell cycle arrest at G1 phase and induce ER-stress to promote cell apoptosis, thus revealing the molecular mechanism of psoralen in
Overexpression miR-148a with miR-148a mimics (miR-148a) initiated G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis and inhibited growth of SGC7901 cells in vitro, and miR-148a could
The results showed downregulation of TSPAN13 inhibited the proliferation of HCT116 cells by inhibiting cell cycle progression at G0/G1 phase and promoting cell apoptosis, which
In conclusion, we demonstrated here that zerumbone inhibits the proliferation of SiHa cells via induction of G1 cell cycle arrest fol- lowed by apoptosis, accompanied with
Consistent with its mechanism of action, ulixertinib inhibited ERK1/2 activation and cell proliferation, and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lymphoma cell
Similar to the effects of miR-503, arcyriaflavin A inhibited cell proliferation and VEGF-A production, and induced apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in these cells mainly at 1
In conclusion, the results of the present study showed that fucoidan can induce cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and apoptosis via a mechanism related to the inhi- bition of
Several studies have demonstrated that luteolin could induce cell cycle arrest and further inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in different types of cancer cells in