Original Article An analysis of the chemotherapy efficacy on the survival of advanced gastric cancer patients
Full text
Figure

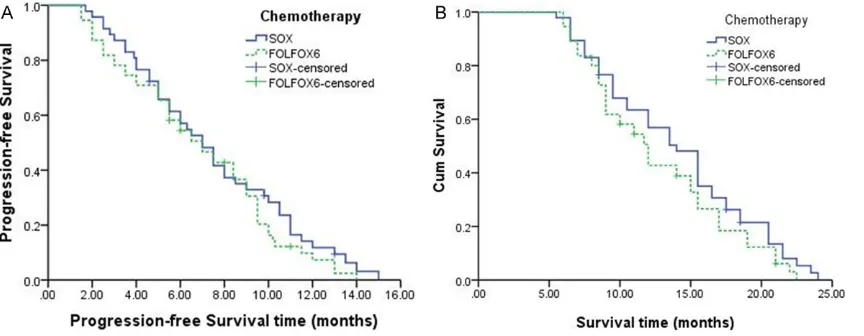

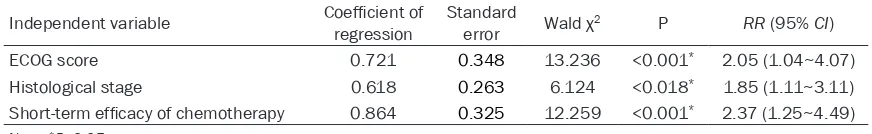
Related documents
Purpose: The objective of the present investigation was to evaluate the antibacterial properties and the biocompatibility of composite electrospun nanofibrous membranes
The GNM produced promising results from the quali- tative point of view. Since it was developed to provide a stable solution for the segmentation of images contain- ing
The study aimed to gather expert opinion on pain management in cognitively impaired hospitalised older people.. Methods: Consultant Geriatricians listed as dementia leads in
Three robotic operations, left hepatectomy with intraoperative common bile duct exploration, low anterior resection, and radical distal subtotal gastrectomy with
The purpose of our study was threefold; first, to pro- vide a review of the extant literature on DDs and vio- lent behavior; second, to describe the prevalence of recent
Graphs showing the percentage change in epithelial expression of the pro-apoptotic markers Bad and Bak; the anti-apoptotic marker Bcl-2; the death receptor Fas; the caspase
The aim of the study was to assess the presence of pathogenic microbes on treatment tables in one outpatient teaching clinic and determine a simple behavioral model for
The prevalence of anxiety, somatization disorder, alcohol abuse and eating disorders was greater in Guasca than Guatavita with a prevalence of 32.5% and 25.7% for an- xiety, 73.8%