Raising the bar: language testing experience and second language motivation among South Korean young adolescents
Full text
Figure



Related documents
perceived intercultural competence and second language (L2) learning motivation of Chinese and Irish students in higher education in Ireland. Literature shows that the
Principal components analyses identified three motivational orientations intrinsic, instrumental mastery, and performance orientation, four sources of motivation
Figure 6 shows the profile of a student who has a very strong motivation level, especially in the Ideal L2 self and Learning experience dimensions, whereas
Using Dörnyei’s (2005) L2 Motivational Self System (L2MSS) and Kubanyiova’s (2007, 2009) model of ‘possible language teacher selves’ as main theoretical frameworks, the current
Using language learning motivation theories, Dörnyei’s (2005, 2009) L2 Motivational Self System and Dweck’s (2006) concept of mindsets, the questions are: (i) By whom and at what
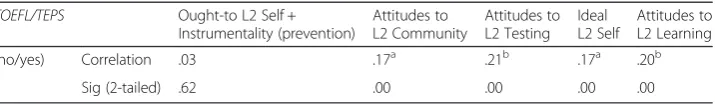
The short answer to the second research question is also ‘yes’. Out of the different types of motivation included in the questionnaire, the ideal L2 self and integrative
Motivation can affect L2 learning through its dimensions and factors, relationship of these dimensions and factors with learning, and the effect of the motivational