Methods of Assessment and Clinical Relevance of QT Dynamics
Full text
Figure

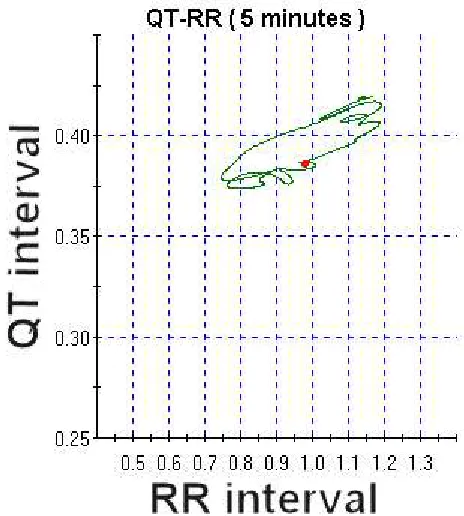
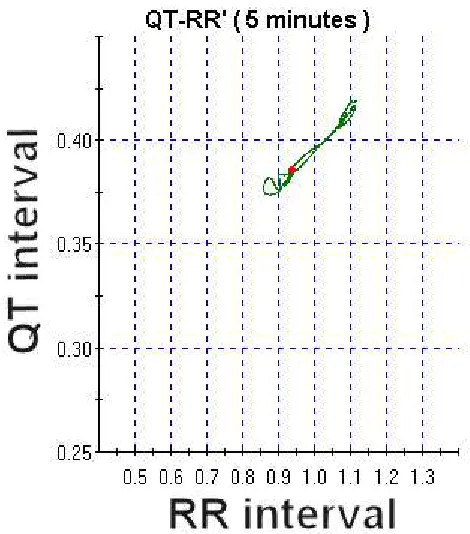

Related documents
Applying the framework, we find that the relationship between the marginal productivity of an agent with an asset and the substitution effect is key, and we get a set of
Considering the significance of assessing the effects of process variables on the recombinant proteins expres- sion, the current research work was geared towards the evaluations of
In terms of the Libyan case in particular, Hofstede’s findings are in agreement with Twati (2006), who conducted a study about the influence of societal and
Since tax revenue rises with top income shares if marginal income taxes are progressive, the negative conditional relationship can be explained by the fact that a more
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of damage to the computer or an unsuccessful installation, download and install a BIOS update only when the computer is connected to reliable external
Perz S, Küfner R, Meisinger C, Ziegler D, Englmeier KH and the KORA Study Group: The Effect of Different QT interval Corrections for Heart Rate on the QT Distributions in
Automated Profiling Demo Automation Script written in Jscript Windows Scripting Host CCS Scripting APIs Executable to be profiled - one per platform.
Figure 5 and 6 shows the denoised effect of single level PCA and proposed Iterative PCA based denoising algorithms on DT-MRI brain images with different noise variance. Denoising