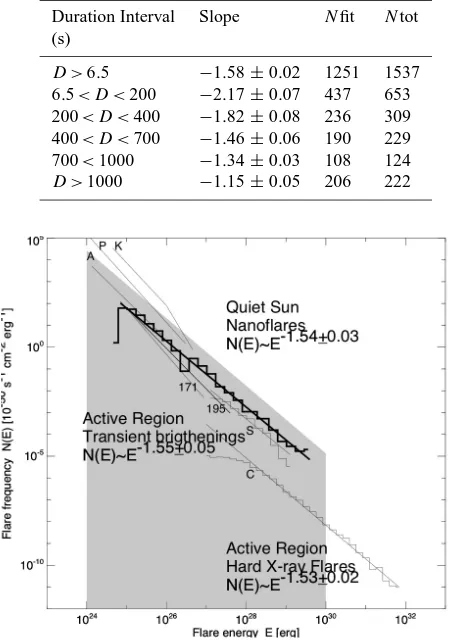
Frequency distributions: from the sun to the earth
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Montana Department of Commerce SBDC Program – Small Business Administration. Montana Procurement Technical Assistance Center (PTAC) – US Department
Slide 17 2010-08-10 Jan Kiszka © Siemens AG, Corporate Technology Managing Priorities Priority Guest A Guest A RT task Time-sharing task Guest B Time-sharing task Black-Box
Like solar flares, these coronal mass ejections release energy built up in solar magnetic fields. They usually last hours, however, while the rapid eruptions from flares typically
Keywords: coronal mass ejections, flares, radio bursts, filaments, prominences, streamers, solar magnetism, active regions, closed and open magnetic fields, pre-eruption
[3] Hamidi, Z.S., Probability of Solar Flares Turn Out to Form a Coronal Mass Ejections Events Due to the Characterization of Solar Radio Burst Type II and III.. International
We present a brief introduction to the essential physics of coronal mass ejections as well as a review of theory and models of CME initiation, solar energetic particle
[ 1 ] Fast coronal mass ejections (CMEs), X-class flares, solar energetic particle (SEP) events, and interplanetary shocks were abundantly observed during the episode of intense
The main solar phenomena responsible for the appearance of such con- ditions in the solar wind are Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) and high speed flows from Coronal Holes