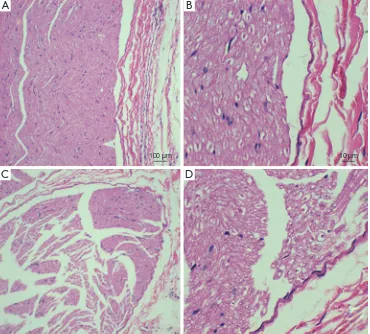
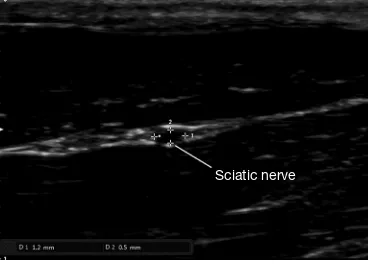
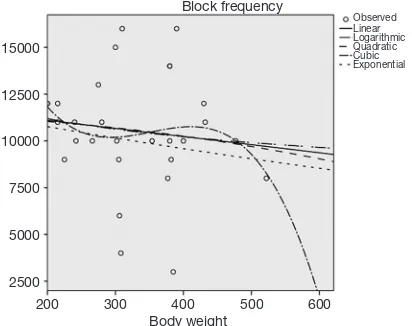
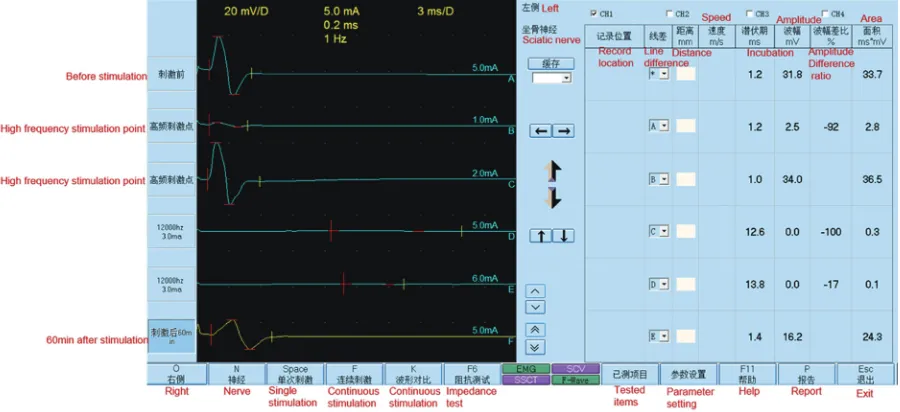
Kilohertz high frequency alternating current blocks nerve conduction without causing nerve damage in rats
Full text
Figure

Related documents
As the current Convener and Co-convener of the Physical Education and Sports Pedagogy (PESP) Special Interest Group (SIG) of the British Educational Research Association (BERA)
Since Evans reported the first case of AIHA associated with ITP, there have been sev- eral case reports of Evans' syndrome occurring simultaneously with an autoimmune thyroid disease
This is due to low pupil progress and attainment data as a result of the high proportion of pupils with special educational needs in the school.. It is pertinent that
A recent study including the pooled data of 1,485 alcohol-dependent patients from seven rando- mized, controlled trials comparing acamprosate and a placebo, directly tested the
“Human Resource Development and Society: Human Resource Development’s Role in Embedding Corporate Social. Responsibility, Sustainability and Ethics in Organizations.”
A key aim of welfare reform has been to move people into work: by offering more personalised and intensive support to help individuals find work; by incentivising employment
Key Words: Parathyroid hormone analogue, -helical struc α - ture, ovariectomized rat, bone mineral density, bone
In conclusion, the minimally invasive approach for isolated primary mitral valve operations with either parasternal or low-sternal approach provide the optimal surgical results and