Each self-renewing tissue organizes the turnover of cells in its own way; but wherever the process depends on stem cells, the same fundamental questions arise. What is special about the niche in which stem cells live, and what mechanisms regulate its extent and location? What are the signals that control stem-cell proliferation and dictate whether a daughter of a stem cell shall remain a stem cell or become committed to differentiation? How are some stem-cell progeny directed towards one path-way of differentiation, and others to another? How are the various cell types guided to their proper positions? In the intestine, it is becoming possible to give a specific and coherent answer to all of these general questions. Mutations in the genes that govern the renewal process can be identified and interpreted through the disruptions they cause in normal tissue architecture, and analysis of these mutants has clarified many of the underlying mechanisms.
In this review, we try to describe both the new answers that have been revealed by studies of the intes-tinal stem-cell system, and the problems that continue to present a challenge. We begin with an outline of the pat-tern of cell renewal in the intestine. We then discuss how feedback loops involving the hedgehog, bone morpho-genetic protein (BMP), Wnt and Eph/ephrin pathways define and localize the stem-cell niche. We shall see how Wnt and Notch signals function together to maintain stem cells, control proliferation and govern cell fate deci-sions. Finally, we consider how insights from the intes-tine illuminate the behaviour of other stem-cell systems, and in particular their dependence on combinatorial control by Wnt and Notch.
Intestinal stem cells are confined to crypts In the lining of the mammalian intestine, dividing cells are confined to the crypts of Lieberkühn — finger-like invaginations of the epithelium into the underlying con-nective tissue. In the small intestine, the progeny of these dividing cells migrate upwards from the depths of the crypts onto the surfaces of the villi — relatively large finger-like protrusions into the gut lumen — where no further division occurs and all the cells seem to be fully differentiated. Here the cells are exposed to the gut con-tents and finally sloughed from the villus tips (FIG. 1a). The renewal process operates continually (although with a strong diurnal rhythm1), with cells taking two to seven
days to make the journey from the site of their final divi-sion cycle in the crypt to the point of their exfoliation from the villus tip2. The differentiated cells generated in
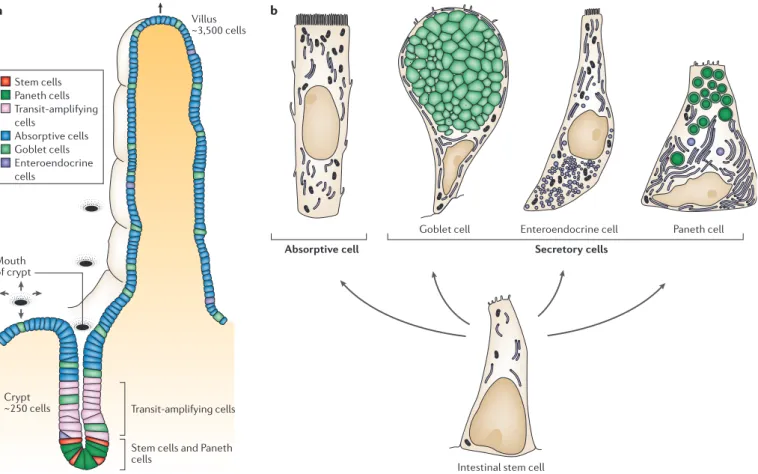
this process are of four distinct types: absorptive, goblet, enteroendocrine and Paneth cells. Absorptive cells, also known as columnar cells or enterocytes, are the major-ity cell type; the other three classes are all secretory (FIG. 1b).
This pattern of cell migration and epithelial renewal was first demonstrated by experiments in which a pulse of tritiated thymidine was used to label a cohort of dividing cells and follow their fate: this method provided evidence that all cells of the gut epithelium originate from stem cells in the crypts3. The same
work indicated that these stem cells are pluripotent; each can give rise to all the differentiated cell types. This result has been confirmed by clonal analysis4–6,
which also revealed that several such stem cells exist in each crypt7.
Vertebrate Development Laboratory, Cancer Research UK London Research Institute, 44 Lincoln’s Inn Fields, London WC2A 3PX, UK. Correspondence to J.L. e-mail:
julian.lewis@cancer.org.uk doi:10.1038/nrg1840 Niche
The specific microenvironment that stem cells inhabit. Clonal analysis Analysis of the composition and distribution of the clones of cells that are descended from individual, heritably marked cells, in order to discover the fate of these progenitors.
Organizing cell renewal in the
intestine: stem cells, signals and
combinatorial control
Cécile Crosnier, Despina Stamataki and Julian Lewis
Abstract | The lining of the intestine is renewed at an extraordinary rate, outpacing all
other tissues in the vertebrate body. The renewal process is neatly organized in space, so
that the whole production line, from the ever-youthful stem cells to their dying, terminally
differentiated progeny, is laid out to view in histological sections. A flurry of recent papers
has clarified the key regulatory signals and brought us to the point where we can begin to
give a coherent account, for at least one tissue, of how these signals collaborate to
organize the architecture and behaviour of a stem-cell system.
Crypt
~250 cells Transit-amplifying cells
Stem cells and Paneth cells Mouth of crypt Villus ~3,500 cells Stem cells Paneth cells Transit-amplifying cells Absorptive cells Goblet cells Enteroendocrine cells Paneth cell Enteroendocrine cell Goblet cell
Intestinal stem cell
b a
Secretory cells Absorptive cell
From the pattern of cell migration revealed by labelling experiments with tritiated thymidine or BrdU (bromo-deoxyuridine), it seems that the stem cells must lie near the crypt base. Higher up in the crypt, cells continue to divide but are destined, with all their progeny, to move up out of the crypt and eventually to be discarded. The divisions of these cells, in transit from the stem-cell region to the villi, amplify the number of progeny that results from each division of a stem cell. Such cells are therefore called transit-amplifying cells, and in terms of prospective fate they are clearly not stem cells: all their progeny will differentiate and die. Prospective fate, however, is not the same as intrinsic potency. If the transit-amplifying cells were put back at the crypt base, could they function as stem cells? There is some indirect evidence that the answer is yes8. In terms of
potency, therefore, it is possible that some or all of the transit-amplifying cells should be classified as stem cells on a par with the stem cells at the crypt base.
Despite uncertainties about the identifying features of the stem cells (BOX 1), we shall see that a great deal is known about the mechanisms governing their location and behaviour.
How are crypts and villi made?
Stem cells are dangerous cells: they provide for renewal and repair, but disaster can ensue if they proliferate excessively or in the wrong place. How is the intestinal stem-cell niche defined, how is it created, and what keeps the stem cells in it? The most complete information comes from studies of the mouse, and we shall take this animal as our mammalian model here.
Figure 1 | The distribution of epithelial cell types in the mammalian small intestine. a | A villus with one of the crypts that contribute to renewal of its epithelium. Arrows indicate the upwards flow of cells out of the crypts. Stem cells lie near the crypt base; it is uncertain whether they are mixed with, or just above, the Paneth cells. Above the stem cells are transit-amplifying cells (dividing progenitors, some of them already partially differentiated); and above these, in the neck of the crypt and on the villus, lie post-mitotic differentiated cells (absorptive cells, goblet cells and enteroendocrine cells; see panel b). In the colon there are no villi, but the organization is otherwise similar; cells are discarded into the gut lumen after they emerge onto the exposed flat surfaces around the mouths of the crypts.
b | There are four classes of terminally differentiated cells. Absorptive cells have a brush border (a dense array of microvilli) on their apical surface. The other three classes are all secretory: goblet cells secrete mucus, and their apical cytoplasm is generally distended with mucus-filled secretory granules; enteroendocrine cells (of which there are many subtypes) are smaller and secrete various gut hormones (peptides and catecholamines); and Paneth cells secrete antibacterial proteins (lysozyme and cryptdins or defensins). Paneth cells differ from the other differentiated cell types in that they lie at the bottoms of the crypts. They seem to be absent in some vertebrate species, including zebrafish46,90, and in the mammalian large intestine. Panel a modified with permission from REF. 8 © (1998) Royal Society of London. Panel b modified with permission from REF. 3 © (1974) Wiley-Liss.
Pseudostratified Describes an epithelium that, because of the uneven positions of the cell nuclei, seems to contain several layers of cells (stratified) but is in fact composed of a single one, in which all cells make contact with the basal surface.
Villi begin to form at embryonic day 15; crypts form substantially later, around postnatal day 7 (FIG. 2). What, then, is the mechanism that organizes the for-mation of villi and crypts (or of intervillus pockets, the equivalent of crypts in some non-mammalian species)? It has long been known that the modelling of the intestinal epithelium depends on epithelial– mesenchymal interactions9, and recent data have
iden-tified the hedgehog, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and BMP signalling pathways as key mediators of these two-way communications (FIG. 3): mutations in these pathways derange the construction of crypts and villi. Moreover, within the epithelium, cells signal to one another through the Wnt, Notch and Eph/ephrin path-ways (FIG. 3): mutations that affect these pathways cause marked changes in the distribution of cell types along the crypt–villus axis. The challenge is to understand not just the action of each type of signal individually, but how the whole set of signals operates as a system to organize the crypt–villus architecture and to control the patterning and renewal of the gut epithelium.
Hedgehog demarcates villus from crypt
In the small intestine of the developing mouse, expres-sion of the two ligands Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and Indian hedgehog (Ihh) is restricted to the epithelium and becomes progressively concentrated in the intervillus regions of the epithelium as villus morphogenesis pro-ceeds. Meanwhile, expression of the receptors patched 1 (Ptch1) and patched 2 (Ptch2), and the effectors of hedgehog signalling, Gli1, Gli2 and Gli3, is restricted to the underlying mesenchyme10. Hedgehog signalling
from the gut epithelium to the mesenchyme is crucial for development of the connective-tissue coat around the gut tube11,12, but it is no less important for the
behav-iour of the epithelial cells themselves, which are power-fully affected by feedback from the mesenchymal cells. Blocking of the hedgehog signal by strong overexpression of an inhibitor, hedgehog-interacting protein (HHIP),
leads to a complete absence of villi and the persistence of a highly proliferative, and sometimes pseudostratified, intestinal epithelium, with increased activation of the Wnt pathway and a deficit of properly differentiated cells10. Partial inhibition of hedgehog signalling leads to
a milder effect: abnormally branched villi are formed on which there is ectopic epithelial proliferation and ectopic activation of the Wnt pathway10. Blocking of the
path-way with a pan-hedgehog antibody produces a similar phenotype13. Although unconditional knockouts of Shh
and Ihh individually have complex effects on embryonic development of the gut14–16, the general conclusion is that
hedgehog signalling from epithelium to mesenchyme is required for the formation of villi and the concomitant restriction of proliferation to the intervillus regions within the intestinal epithelium. This process must depend on a feedback loop in which mesenchymal cells respond directly to hedgehog from the epithelium, and deliver a signal back to the epithelium by some other signalling pathway.
In the small intestine, both SHH and IHH are pro-duced only in those sites at which proliferation persists — the intervillus pockets, and subsequently the bases of the crypts (although the pattern is different in the colon17). The suggestion, therefore, is that hedgehog
proteins diffuse outwards from these sites and exert their effect at a distance, promoting villus formation and inhibiting crypt-like behaviour in the neighbourhood of each established crypt, so as to maintain a proper spacing between one crypt and the next, as discussed below.
Hedgehog is not the only signal passing from epithe-lium to mesenchyme. PDGFA, like SHH and IHH, is made by the epithelial cells, and its receptor, PDGFRA, is expressed in the mesenchyme. PDGF signalling helps to control the behaviour of the mesenchyme and the shaping of villi, but does not, apparently, evoke signals that act back on the epithelium to regulate its proliferation or differentiation18.
BMP inhibits crypt formation
If hedgehog and PDGF signals are both delivered from the epithelium to the mesenchyme, what molecules con-vey signals from the mesenchyme back to the epithelium to control its regional differentiation? One pathway, at least, has been identified: BMP2 and BMP4 are both expressed in the mesenchyme, where they are posi-tively regulated by hedgehog signalling10; their receptor, BMPR1A, is expressed in the epithelium. The BMP antagonist noggin is expressed in the neighbourhood of the crypts, whereas activation of the BMP pathway, as indicated by the presence of phosphoSMAD1, 5 and 8, is seen most strongly in the epithelium of the villi18–20.
When the receptor is knocked out, or the antagonist noggin is overexpressed, excessive quantities of crypt-like structures develop. In the noggin overexpression mutant, these occur on the sides of the villi19; in the
mouse Bmpr1a knockout, there is also a marked increase in the number of crypts in the region within which crypts normally lie20. Similar abnormalities are seen in humans
with juvenile polyposis syndrome, which can be traced to mutations in BMPR1A or SMAD4 (a key downstream
Box 1 | Defining intestinal stem cells
It is still not clear at what point the progeny of intestinal stem cells lose stem-cell potency and become irreversibly committed to differentiation. There are, indeed, many genes that are expressed only by undifferentiated cells near the crypt base and are therefore candidates to be molecular markers of the stem-cell state24,41,55,73–76. For none of these
genes, however, is there proof that expression is restricted to stem cells only. There is similar uncertainty about another, more curious, type of proposed stem-cell marker. After a pulse of tritiated thymidine or BrdU (bromodeoxyuridine) is delivered to the juvenile gut to label cells that are in S phase, a small proportion of cells in the crypt bases are found to retain the label for long periods, up to more than 9 weeks72. It has been
suggested that these label-retaining cells are the true stem cells. If so, two interpretations are possible. The stem cells might divide only rarely, relying on proliferation in the transit-amplifying stage to boost the number of their progeny. Alternatively, they might divide at a more normal rate, but segregate their DNA strands asymmetrically, in such a way as to retain in every division, and for each chromosome, the specific strand that was initially labelled. The latter ‘immortal strand’ hypothesis has been proposed as a way in which stem cells might minimize the accumulation of mutations that are associated with DNA replication71. Wild as the idea might seem, it has received
some experimental support in the gut72, in cultured fibroblasts77, in cultured neural stem
cells78, and in the mammary gland79; but it remains contentious.
Adult (from P7) Neonate Early embryo (E14) Mesenchyme Epithelium Villus Crypt
effector of BMP signalling)21,22. All this evidence strongly
suggests that (in the adult at least19) BMP signalling is a
key factor, if not the key factor, that mediates the action of hedgehog, blocking the formation of ectopic crypts, and that the expression of noggin in the neighbourhood of each crypt base protects the epithelium in this region from the action of BMPs, thereby enabling proliferation to continue.
Crypts and villi: a self-organizing system? Through hedgehog and BMP, each crypt or intervillus pocket delivers a long-range signal that inhibits crypt formation in its neighbourhood. But what then sustains the crypt itself, and how does the pattern of crypts and villi arise? Crypts form by invagination of the prolif-erative intervillus pockets that lie between the villi in the fetal intestine. The mechanism of this invagination is unclear, but the origin of the initial spacing pattern of villi and intervillus pockets can be explained quite simply (FIG. 3c,d). As Gierer and Meinhardt have shown mathematically23, a tissue can pattern itself
autono-mously by means of a pair of diffusible signals — a short-range (weakly diffusible) activator and a long-short-range (more freely diffusible) inhibitor — both of which are secreted at the same time by the same cells and regulate their own production. The positive feedback that is due to the activator can give rise to self-sustaining foci of signal production, with a regular spacing between them. If the hedgehog–BMP relay provides the long-range inhibition in the intestine, what could provide the short-range activation? Evidence that we discuss below points to an obvious candidate: the Wnt signalling pathway. The epithelial cells in the crypts produce both the signal molecules — Wnt proteins — and the receptors for the so-called canonical branch of the Wnt pathway, and they respond to activation of these receptors by increasing
their production of at least one of the Wnt molecules (WNT6(REF. 24)). The noggin protein produced in the neighbourhood of the Wnt-active region (and produced perhaps in response to Wnt) would help to make the system robust by protecting the crypt or intervillus cells from inhibition.
This explanation of the origin of the pattern of crypts and villi in terms of a Gierer–Meinhardt mechanism is speculative. But the importance of Wnt signalling in the intestine is firmly established, as we now explain. Wnt signalling maintains proliferation
The Wnt signalling pathway25 was the first to be
impli-cated in the control of the gut stem-cell system, and a large body of evidence shows that activation of the Wnt pathway is the key factor that maintains the crypt cell population in a proliferative state. When the pathway is overactivated, crypts enlarge; when the pathway is blocked, they disappear.
A subset of members of the Wnt family are thought to be specifically responsible for canonical Wnt signalling, and these proteins (WNT3, WNT6 and WNT9B) are expressed only in the epithelium, where they are restricted to the crypts (at least in the small intestine24; FIG. 3). The crypt epithelial cells
also express members of the corresponding recep-tor families (frizzled 5, 6 and 7, and LRP5 and 6) and show activation of the canonical pathway, which is manifest in high levels of intranuclear β-catenin. Other Wnt family members are expressed in the villus mesen-chyme, and other frizzled molecules are expressed in the villus epithelium, but these are thought to mediate only non-canonical Wnt signalling: the villus epithelial cells do not contain intranuclear β-catenin.
Deletion of transcription factor 4 (Tcf4), the main downstream effector of the pathway in the small intestine, Figure 2 | Morphogenesis of the small intestine in the mouse. The digestive tract originates from the folding of an endodermal sheet, which undergoes remodelling to form a tube that is lined with stratified epithelium91. Until around embryonic day 14 (E14), all of the intestinal epithelial cells, which are still undifferentiated, proliferate actively. Villus morphogenesis starts at E15 and involves a reshaping of the mesenchyme (yellow) that underlies the intestinal epithelium; the mesenchyme seems to drive the formation of protrusions into the gut lumen. This process is accompanied by marked effects on the epithelial cells (red and blue cells): the epithelium becomes monolayered, and epithelial proliferation (red) becomes restricted to the intervillus pockets, and ultimately to crypts. The crypts themselves develop relatively late, beginning around postnatal day 7 (P7), by invagination of the intervillus epithelium. In some vertebrate species they never develop. In zebrafish, for example, crypts are absent, but stem cells are maintained in the intervillus pockets46,92.
Mib Nucleus Epithelium BMP LEF/TCF RBPSUH β-Catenin* NICD β-Catenin Notch Delta APC Wnt Frizzled BMP Hedgehog pathway: SHH, IHH PDGF pathway: PDGFA Canonical Wnt pathway: WNT3, 6, 9B; frizzled 5, 6, 7; LRP5, 6 Eph/ephrin pathway: EPHB2, EPHB3 Notch pathway: NOTCH1, 2; DLL1, 4; JAG1; HES1, 6, 7 Eph/ephrin pathway: ephrin B1 BMP pathway: BMPR1A; phosphoSMAD1, 5, 8 BMP Villus Villus Villus Wnt HH Wnt HH Cell B Cell A ? Wnt HH Hedgehog pathway: PTCH1, 2; GLI1, 2, 3 BMP pathway: BMP2, 4 Mesenchyme PDGF pathway: PDGFRA BMP pathway: noggin Noggin Crypt Noggin Crypt a c b d BMP
leads to an absence of proliferating cells in the intestinal epithelium26. Villi are reduced in number, and the animal
dies soon after birth. Similarly, forced expression of the diffusible Wnt inhibitor, dickkopf homologue 1 (DKK1), leads to a loss of crypts and a decrease of villus size and numbers in adult mice27,28.
Converse effects are seen when the Wnt pathway is overactivated by mutations in adenomatous polyposis coli (Apc), β-catenin, or other Wnt pathway components, leading to the constitutive activation of downstream targets of the canonical Wnt pathway29. Therefore,
when Apc is knocked out in the adult gut epithelium, crypts become enormously enlarged within four to five days, whereas the villi become smaller, as if the normal
progression from a crypt-like proliferative state to a post-mitotic differentiated villus state has been blocked30,31.
The outward migration of cells along the villi is also reduced, implying that the mutant cells remain crypt-like not only in their proliferative behaviour but also in their affinity for the stem-cell niche30,31.
In a similar way, polyps consisting of masses of giant crypts develop in the human intestine at sites where both copies of APC have been lost or inactivated32. In
fact, loss of APC through somatic mutations seems to be the initiating event in most human colorectal can-cers. A mouse model shows similar phenomena: the
Min (ApcMin/+) mouse, carrying a germline mutation in
Apc, forms intestinal adenomas at sites where a somatic Figure 3 | Signalling pathways in the small intestine. a | Components of the hedgehog (HH), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), Wnt, Eph/ephrin and Notch pathways are expressed in different regions along the crypt–villus axis — some in the epithelium and some in the mesenchyme. The brackets list, for each indicated region, the pathway components that are expressed there. Only those molecules mentioned in the text are included. Because all these signalling pathways have essential functions in many other tissues, experiments to study their role in the gut have rested heavily on conditional mutagenesis and conditional misexpression, using gut-specific promoters. Two such promoters have been especially valuable: the villin promoter93–95, and the Cyp1A1 (cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 1) promoter96. Both of these drive expression in all cells of the gut epithelium, including the stem cells. b | A simplified diagram of the Wnt and Notch pathways, showing the functional relationships among components mentioned in the text. c | A model of how the HH, BMP and Wnt signalling pathways combine to organize the pattern of villi and crypts or intervillus pockets. Epithelial cells in each crypt or intervillus pocket form a signalling centre, which functions as a source of long-range inhibition through the HH–BMP relay, and of short-range auto-activation through Wnt signalling. HH signalling activates the expression of BMP in the mesenchyme. BMP feeds back on the intestinal epithelium to repress Wnt signalling. The expression of the BMP inhibitor noggin in the neighbourhood of the crypts counteracts the effect of BMP so that Wnt activity is maintained in the crypt epithelium. d | The logic of the gene control network corresponding to the spatial patterning mechanism that is suggested in panel c. NICD, intracellular domain of Notch.
mutation has eliminated the remaining functional allele of Apc33. Apc mutant zebrafish similarly develop
intestinal tumours34.
Wnt maintains stem cells cooperatively
Do the effects of Wnt on proliferation reflect an action on the stem cells themselves, or only on transit-amplifying cells? Because loss of Apc gives rise to polyps that can apparently grow without limit, it seems that a high level of Wnt signalling can keep cells proliferating indefinitely, or at least for a large number of cycles. If the ability to divide indefinitely is the feature that distinguishes stem cells from transit-amplifying cells, it follows that Wnt signalling can keep cells in a stem-cell state.
A puzzling observation is that the diffusible Wnt antagonist, SFRP5 (secreted frizzled-related sequence protein 5), is also produced by some cells in the stem-cell region24. We do not know how the effects of Wnt and
its antagonist balance out as a function of distance from their source; for example, if SFRP5 is the more diffus-ible factor, the net effect could be autostimulation within the stem-cell region but inhibition outside that region, limiting the size of the stem-cell population. In any case, other evidence — from mutants and the distribution of nuclear β-catenin — indicates that the Wnt pathway is strongly activated in the stem-cell region and essential for maintaining the stem-cell character.
Therefore, it seems that the cells in the crypt stimulate one another by both making and responding to Wnt. Furthermore, if the cells respond to Wnt by making more Wnt24, crypt-like behaviour would be expected to be a
cooperative phenomenon, and cells in which the Wnt pathway is hyperactive should tend to make it hyperactive in their neighbours too. Bjerknes and Cheng have exam-ined the adenomas in Min mice35. In these Apc+/– mutants,
the bulk of the intestinal epithelium is phenotypically normal, with adenomas forming only where a somatic mutation has given rise to Apc–/– tissue. However, in the
close neighbourhood of the Apc–/– tissue, the Apc+/– cells
proliferate abnormally, forming colossal crypts that are up to ten times the normal length. This is just what would be expected if the Apc–/– cells secrete excessive quantities
of Wnt protein. Positive feedback, such that Wnt signal reception stimulates production of Wnt signal, will tend to amplify and propagate the effect. The same mechanism could help to explain the development of polyclonal ade-nomas, which are observed in both mouse Apc+/–(REF. 36)
and human APC+/–(REF. 37) mutants.
Eph/ephrin signals control cell segregation Through selective cell migration, the different catego-ries of cells in the intestinal epithelium are segregated into separate regions: the cluster of Wnt-activated cells avoids becoming diluted with differentiated cells that lack Wnt activity (Paneth cells being a special case; see below), whereas the population of differentiated cells on the villi avoids contamination with dangerously proliferative stem cells. This segregation is controlled by the level of Wnt pathway activation, through the effects of Wnt signalling on ephrin B1 and its receptors
EPHB2 and EPHB3.
Eph receptors and their ligands (ephrins) are membrane-associated proteins that mediate communica-tion between adjacent cells. Repulsion between Eph- and ephrin-expressing cells seems to be a general mechanism for creating tissue boundaries38 and for restricting and
defining paths of cell migration39. In the gut, Wnt
sig-nalling switches on expression of EphB2 and EphB3 and inhibits expression of ephrin B1 (REFS 40,41). Therefore, in the neonatal mouse, ephrin B1is expressed by the epithelial cells of the villi, and EphB2 and EphB3
by cells of the intervillus pockets41. As the intestinal
epithelium matures, ephrin B1 expression becomes confined to the crypt–villus junction and EphB3 to the Paneth cells, whereas EphB2 is mainly expressed by cells located near the base of the crypts, with the exception of Paneth cells.
Deletion of the EphB2 and EphB3 genes leads to marked changes in the arrangement of the different cell populations within the crypts: Paneth cells and proliferating cells are no longer restricted to the bottom of the crypts but are abnormally scattered along the crypt–villus axis, and cells expressing ephrin B1 become distributed throughout the crypts41. Therefore it seems
that control of EphB2 and EphB3 expression by Wnt ensures the proper segregation of proliferating (and Paneth) cells from post-mitotic cells. The importance of this mechanism is indicated by the finding that, in colorectal cancer, loss of expression of EPHB receptors is correlated with the onset of invasive behaviour42.
Wnt makes cells competent for secretory fates Wnt signalling is crucial in controlling cell proliferation in the gut epithelium. But there is more to the character of a gut epithelial cell than the simple dichotomy between proliferative and non-proliferative behaviour. What part does Wnt signalling have in guiding the choices the cells must make between different modes of terminal dif-ferentiation? Only one of the terminally differentiated cell types in the gut — the Paneth cell — shows signs of sustained Wnt pathway activation. Paneth cells reside at the base of crypts, where Wnt protein is plentiful, and Wnt signalling drives their differentiation30,43. All
the other terminally differentiated intestinal cell types — absorptive, goblet and enteroendocrine — maintain their differentiated characters in areas where canonical Wnt signalling is not active, but have those characters assigned to them while under the influence of Wnt signalling or shortly after.
When Wnt signalling is defective, as a result of loss of Tcf4, the gut epithelial cells differentiate as practi-cally normal absorptive cells, but enteroendocrine cells fail to develop26. When Wnt signalling is blocked
by overexpression of DKK1, a more extreme effect is seen: absorptive cells still differentiate normally, but all classes of secretory cells seem to be lost27. In the
opposite circumstance, where the Wnt pathway is overactivated by the loss of Apc, there is a more general failure to differentiate, leading to reduced expression of markers of absorptive, goblet and enteroendo-crine cells, but with an overproduction of Paneth cell precursors30,31.
From all this evidence one can tentatively conclude that Wnt signalling has three basic effects: it keeps the cells dividing; it stops them from differentiating (except as Paneth cells); and it confers the potential — but not the obligation — to differentiate as a secretory cell type once the cell escapes from the influence of Wnt. Some other mechanism must guide the final choice between the various secretory and absorptive fates.
Secretory precursors exert lateral inhibition Notch and its ligands of the Delta and Serrate/Jagged subfamilies are transmembrane proteins that medi-ate communication between cells that are in contact with one another. These and other components of the Notch pathway are expressed in the epithelium of the adult intestinal crypts and for the most part not in the villus epithelium44, which suggests that Notch
signals are mainly exchanged between cells in the crypts (FIG. 3a,b).
When the Notch pathway is partially inactivated by deletion of Hes1 (hairy and enhancer of split 1) in mouse45 or by a nonsense mutation in deltaD in
zebrafish46, excessive numbers of goblet and
ente-roendocrine cells are produced. Stronger inhibition of Notch signalling by deletion of Rbpsuh (recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless)47 (which
medi-ates control of gene expression by Notch), or by use of a γ-secretase inhibitor that prevents the release of NICD
(REFS 47,48) (‘activated Notch’ — the active intracellular domain of Notch), results in a more extreme effect: the intestinal epithelium of the mouse becomes almost exclusively composed of goblet cells. Similarly in the zebrafish mutant mind bomb (mib), in which Notch is not activated49, almost all the epithelial cells adopt
a secretory character46. Increased activity of Notch
signalling has the opposite effect on intestinal cell dif-ferentiation: mice that express NICD constitutively in
the gut epithelium show a severe reduction of all three secretory cell types50.
It therefore seems that in the normal tissue, the cells that become secretory are those that escape Notch acti-vation. These cells are also the ones that express Delta proteins46, enabling them to activate Notch in their
neighbours. Notch signalling in the gut epithelium therefore seems to mediate lateral inhibition in the standard fashion: like nascent neurons in the CNS51,
cells in the gut that become committed to a secretory fate express Notch ligands and inhibit their neighbours from differentiating in the same way.
All three secretory cell types derive from a precursor expressing Math1 (mouse atonal homologue 1), which encodes a bHLH (basic helix-loop-helix) transcription factor that is also expressed in some classes of neuron52
and in sensory hair cells in the ear53. Math1 mutant
mice lack all three secretory gut cell types54 but still
generate absorptive cells. The Notch-controlled choice between an absorptive fate (MATH1-negative, receiv-ing lateral inhibition) and a secretory fate (MATH1-positive, delivering lateral inhibition) might therefore be the first of the decisions made by daughters of stem cells as they become committed to differentiation.
Crypt cells that are homozygous for a LacZ knockin mutation in Math1 form a dense cluster of LacZ -expressing cells at the base of each crypt 54. This pattern
suggests that Notch-mediated lateral inhibition has failed, and that functional MATH1 protein is required not only for cells to progress along the secretory pathway of differentiation, but also to deliver lateral inhibition to their neighbours as they do so. A possible interpretation of this result is that MATH1 is needed to drive the expression of Delta.
Cells keep on dividing after fate commitment Cells in the gut epithelium that express Math1 often seem to be still capable of dividing (as indicated by expression of Ki67, a marker of proliferative cells)54.
Therefore, commitment to a secretory fate probably precedes withdrawal from the cell cycle. This tallies with the findings of clonal analysis: single genetically marked cells in the mouse intestine can give rise to large clones that consist of nothing but secretory cells — as many as 19(REF. 6). Clones that consist entirely of absorptive cells also occur and are on average five times as big. Therefore different numbers of transit-amplifying divi-sions in the two committed sublineages could explain why absorptive cells are so strongly in the majority on the villi.
Wnt and Notch jointly maintain stem cells It might be tempting to suggest that there is a simple division of function between the Wnt and Notch path-ways, with Wnt signalling in the crypt base maintaining the stem-cell proliferative state, and Notch signalling in the transit-amplifying compartment controlling the choice between differentiating as an absorptive cell and differentiating as a secretory cell.
The truth, however, seems to be more interesting. Notch, Delta and Hes proteins are in fact chiefly expressed in the neighbourhood of the crypt base, in the stem-cell region44,55. When Notch signalling is blocked, secretory
cells are overproduced. However, this does not only occur at the expense of differentiated absorptive cells: it seems that the whole cell population of the adult intestinal crypt is converted to a secretory character and stops proliferat-ing47. Overactivation of the Wnt signalling pathway, at
least as seen in adenomas, is not sufficient to overcome this proliferation failure: when Min mice are treated with a γ-secretase inhibitor that abolishes Notch signal-ling, proliferation is blocked within the tumour tissue47.
The opposite combination of signals — overactivation of the Notch pathway along the villus epithelium, where the canonical Wnt pathway is inactive56 — is equally unable
to drive proliferation. Forced expression of NICD in the
newborn mouse does indeed increase the population of proliferating cells, but mainly in the intervillus regions, where Wnt signalling is active50.
The ultimate stem cells might respond to Wnt and Notch signalling according to different rules. As they are a small minority of the crypt population, different proliferative behaviour on their part could go unnoticed. But the simplest interpretation of the observations is that all the proliferating cells, including the stem cells, depend
Secretory cells Stem cells Lateral inhibition Amplifying divisions Stem-cell divisions Terminal differentiation Transit-amplifying cells
Lymphoid and myeloid blood cells Neuron
Glial cells
Lateral inhibition
b Central nervous system c Haemopoietic system
Secretory precursor Committed precursor (short-term stem cell) Nascent neuron Absorptive cells a Intestine Wnt pathway activated Notch pathway activated
on Notch and Wnt signals in combination to keep them in a proliferating state: neither Wnt pathway activation nor Notch pathway activation is sufficient by itself. Wnt signalling evokes Notch signalling
A Wnt pathway mutation, such as loss of Apc, is suf-ficient to give rise to a tumour that grows without limit. This suggests that the mutation, in ectopically activat-ing the Wnt pathway, has also ectopically activated the Notch pathway, as otherwise proliferation would not be expected to continue. In fact, active Wnt signalling seems able to switch on Notch activity, if we can judge from the evidence of the Min mouse: in the adenomatous tissue, expression of the Notch target gene Hes1 is increased47.
The converse does not seem to apply: there is no obvious effect on β-catenin nuclear localization when the Notch pathway is constitutively activated50 or blocked47.
These observations suggest the following model (FIG. 4a). Wnt signalling drives expression of Notch path-way components. Notch pathpath-way components mediate lateral inhibition within the Wnt-activated (Wnt+) popu-lation, so that some cells express Delta and escape Notch activation (Notch–) while others fail to express Delta and have Notch activation (Notch+) imposed on them. The (Wnt+, Notch–) cells become committed to a secretory fate and eventually stop dividing. The (Wnt+, Notch+) cells continue to divide without differentiating, generating daughters like themselves that again interact through Figure 4 | Wnt and Notch signalling cooperate to maintain stem cells. The diagrams show, in simplified form, the lineage history and sequence of cell fate choices made by the cells in three stem-cell systems: the intestine (a), the CNS (b), and the haemopoietic system (c). The differentiated cell types and the programmes of transit-amplifying divisions are different for the three tissues, but the rules of stem-cell maintenance by Wnt and Notch signalling seem to be the same. Note, however, that for haemopoietic stem cells the Notch-activating stimulus is thought to be provided by the stromal bone marrow cells that form the stem-cell niche (probably JAG1 (jagged 1)-expressing osteoblasts), rather than by adjacent haemopoietic stem cells. The transit-amplifying stages for all these systems are certainly more complex than we have indicated, and the numbers of amplifying divisions and their timing in relation to commitment to a specific
differentiated fate are uncertain. Although we show Notch signalling only in the stem-cell region, it might also be involved in later cell fate choices.
Box 2 | Notch signalling and epidermal stem cells
In the interfollicular regions of mammalian epidermis, it is the stem cells that express Notch ligands and activate Notch in their neighbours. Notch activation in these cells, far from helping to maintain the stem-cell state, actually drives cells towards terminal differentation80, and loss of Notch leads to uncontrolled proliferation81. Therefore, in respect to Notch
signalling, the epidermis behaves in an opposite way to the vertebrate gut. Wnt signalling in the epidermis has complex functions and, in contrast to what occurs in the vertebrate intestine, hedgehog signalling in the epidermis seems to be a key positive regulator of cell proliferation82,83.
Notch and diversify. The size of the group of Wnt-activated cells is limited, however, as a result of the short- and long-range spatial signals we discussed in the first half of this review. Some cells therefore have to move out, losing Wnt activation. These cells differentiate as absorptive cells if Notch was still activated in them at the time of their exit, and as secretory cells if not.
This logical scheme provides a simple explanation of why Wnt pathway mutations frequently give rise to intes-tinal cancers, whereas Notch pathway mutations have not been reported to do so. A Wnt pathway mutation is sufficient to switch on both of the two activities required to make a gut cell proliferate indefinitely as a stem cell; a Notch pathway mutation is not sufficient to do this. Skin, bone marrow and brain: same principles? The Wnt and Notch pathways are essential for regulat-ing other stem-cell systems, includregulat-ing the CNS, the epi-dermis and the bone marrow. Is the logic of control the same in all these tissues? For the vertebrate epidermis, the rules are almost certainly different, and the same is true, rather surprisingly, for the midgut of Drosophila. In both these cases, Notch signalling has a function that is diametrically opposite to its role in the vertebrate gut: the stem cells deliver the Notch-activating signal, and this drives their neighbours to differentiate and cease division (BOXES 2,3).
For the CNS (discussed below) and the haemopoi-etic system (BOX 4; FIG. 4c), however, the parallels with the gut seem remarkably close: their stem cells seem to depend on Wnt and Notch in almost the same way as the stem cells of the intestine.
In the CNS, dividing neuroepithelial progenitors and stem cells give rise to neurons and glial cells, and this process can be compared with the way in which intesti-nal stem cells give rise to secretory cells and absorptive cells in the gut (FIG. 4b). The geometry is different, but the control machinery is surprisingly similar. In the embryonic chick retina, for example, blocking Notch signalling causes all the dividing neuroepithelial cells to halt division and differentiate prematurely into neu-rons; conversely, forced activation of the Notch pathway inhibits adoption of a neuronal character and main-tains the cells as dividing progenitors57 or drives them
towards a glial fate58. This exactly parallels the effects of
manipulating Notch pathway activity in the intestine. Many other studies point to similar conclusions, both in the intact neuroepithelium59–62 and for neural stem
cells in culture63–65.
Moreover, in the CNS, as in the gut, Wnt signalling also is crucial for maintenance of the progenitor or stem-cell population. Therefore, when canonical Wnt signalling is artificially blocked in the neural tube of the developing chick or mouse, the neuroepithelial cells fail to proliferate. Conversely, when this signalling path-way is artificially overactivated (by forced expression of stabilized β-catenin), the cells proliferate excessively, giving rise to a giant brain or spinal cord66–68. In the
hippocampus, where neurogenesis normally continues in adult life, the neural stem cells generate neurons at an increased rate when Wnt signalling is overactivated, and at a decreased rate or not at all when Wnt signal-ling is blocked69. These findings also parallel the effects
of corresponding treatments on stem-cell proliferation
Box 3 | Insect gut stem cells obey different rules
A recent surprise has been the finding that the intestine (or at least the midgut) of Drosophila melanogaster also contains stem cells, providing for continual renewal of the gut lining in the adult fly84,85. These stem cells give rise to absorptive cells
(with a brush border) and to enteroendocrine cells. Both these differentiated cell types are non-dividing and have a lifetime of about a week before they are replaced. Given these parallels with the vertebrate system, are the regulatory mechanisms also similar?
The role of Wnt signalling in the adult D. melanogaster gut is not yet defined, but Notch signalling is crucial. However, upsetting all expectations, it seems that Notch has a role opposite to the one we have described for the vertebrate gut: activation of Notch, instead of favouring proliferation, is required to drive cells into a post-mitotic state; and when Notch activation is artificially blocked, cells that would normally stop dividing as part of the programme of terminal differentiation instead continue to proliferate. Indirect arguments suggest that the Notch-activating signal is delivered by the stem cell to its neighbours — the exact opposite to the situation in the vertebrate gut.
Box 4 | Notch, Wnt and haemopoietic stem cells
The spatial organization of the haemopoietic stem-cell system is completely different from that of either gut or CNS. However, in this case, as Duncan et al.86 have pointed out, the stem cells again seem to be regulated by Wnt and Notch
signalling according to combinatorial rules that are similar to those that operate in the intestine (FIG. 4c).
Activation of Wnt signalling by WNT3A or by constitutively activated β-catenin maintains haemopoietic stem cells in a stem-cell state, stimulates their expression of Notch1, and promotes their proliferation, whereas blocking Wnt signalling has the opposite effect87. Studies in transgenic mice that contain a reporter for activation of the Notch pathway show that
Notch is activated in these stem cells86, and that this activation helps to keep them in a stem-cell state both in vitro88,89 and
in vivo86. Conversely, when the Notch pathway is artificially blocked by a dominant negative form of RBPSUH (recombining
binding protein suppressor of hairless), the cells differentiate precociously, even though they are exposed to a constant source of Wnt signal (WNT3A) (REF. 86).
So, as in the intestine and the CNS, it seems that Wnt activity and Notch activity are required in combination to maintain the stem-cell state in the haemopoietic system.
in the gut (although some parts of the CNS might fol-low different rules66,70). And in the neural tube as in the
intestine, it seems that Wnt signalling brings the Notch pathway and the machinery of lateral inhibition into action, regulating the extent of the domain within which one finds cells expressing the Notch target genes Hes1
and Hes5(REF. 67). Wnt pathway activation and Notch pathway activation seem to be required in combination to keep a cell in the neural progenitor/stem-cell state. Concluding remarks
In this review, we have tried to highlight some basic principles through which molecular signals organize the intestinal stem cell system. Together, the hedgehog, Wnt, BMP and Eph/ephrin pathways create and maintain the crypt–villus architecture. The Wnt and Notch signal-ling pathways combine to control the detailed pattern of cell fate choices as stem cells divide and give rise to differentiated progeny. The stem cells of the vertebrate intestine, CNS and bone marrow all seem to be governed by Wnt and Notch according to similar combinatorial logic. But equally it is clear that some other stem-cell
systems, such as in the Drosophila midgut and the mammalian epidermis, are regulated in different ways.
Progress in understanding the gut stem-cell system in the past few years has been spectacular. However, many fundamental questions remain unanswered. We do not know which signals (if any) control the choice between the different types of secretory fate (goblet, enteroendocrine or Paneth). We do not properly understand the lineage relationships between these cell types or how cell fate decisions are timed in relation to the pattern of cell divisions. Many mysteries still sur-round the intestinal stem cells, as discussed in BOX 1. Do they, as some papers have argued71,72, possess some
extraordinary asymmetrical cell-division mechanism for retaining the original strands of DNA at each cell division? How many of them are there? How often do they divide? What defines them in molecular terms? Do tumours of the gastrointestinal tract contain some minority population of cancer stem cells that corre-spond to the stem cells of the normal tissue? To answer such questions we need, above all, better intestinal stem-cell markers. There is still a lot to learn.
1. Goodlad, R. A. & Wright, N. A. The effects of starvation
and refeeding on intestinal cell proliferation in the
mouse. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. 45, 63–73
(1984).
2. Wright, N. & Alison, M. The Biology of Epithelial Cell
Populations (Clarendon, Oxford, 1984).
3. Cheng, H. & Leblond, C. P. Origin, differentiation
and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine. V. Unitarian Theory of the
origin of the four epithelial cell types. Am. J. Anat.
141, 537–561 (1974).
4. Leedham, S. J., Brittan, M., McDonald, S. A. &
Wright, N. A. Intestinal stem cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med.
9, 11–24 (2005).
5. Park, H. S., Goodlad, R. A. & Wright, N. A. Crypt
fission in the small intestine and colon. A mechanism for the emergence of G6PD locus-mutated crypts after
treatment with mutagens. Am. J. Pathol. 147,
1416–1427 (1995).
6. Bjerknes, M. & Cheng, H. Clonal analysis of mouse
intestinal epithelial progenitors. Gastroenterology
116, 7–14 (1999).
Using chemical mutagenesis to create marked clones, this paper shows that the intestinal epithelium contains not only pluripotent progenitors and stem cells, but also dividing progenitors that are destined to produce large clones of a single cell type.
7. Wong, M. H., Saam, J. R., Stappenbeck, T. S.,
Rexer, C. H. & Gordon, J. I. Genetic mosaic analysis based on Cre recombinase and navigated laser
capture microdissection. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA97,
12601–12606 (2000).
8. Potten, C. S. Stem cells in gastrointestinal
epithelium: numbers, characteristics and death. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B353, 821–830 (1998).
9. Kedinger, M. et al. Fetal gut mesenchyme induces
differentiation of cultured intestinal endodermal
and crypt cells. Dev. Biol. 113, 474–483
(1986).
10. Madison, B. B. et al. Epithelial hedgehog signals
pattern the intestinal crypt–villus axis. Development
132, 279–289 (2005).
Shows that the intestinal epithelium sends a hedgehog signal to the mesenchyme, and that this signal is required, through a secondary effect of the mesenchyme on the epithelium, to restrict the sites of activation of the canonical Wnt pathway and limit the development of the proliferative (crypt-like) epithelium.
11. Apelqvist, A., Ahlgren, U. & Edlund, H. Sonic hedgehog directs specialised mesoderm differentiation
in the intestine and pancreas. Curr. Biol. 7, 801–804
(1997).
12. Sukegawa, A. et al. The concentric structure of the developing gut is regulated by Sonic hedgehog derived
from endodermal epithelium. Development127,
1971–1980 (2000).
13. Wang, L. C. et al. Disruption of hedgehog signaling reveals a novel role in intestinal morphogenesis and intestinal-specific lipid metabolism in mice. Gastroenterology122, 469–482 (2002).
14. Ramalho-Santos, M., Melton, D. A. & McMahon, A. P. Hedgehog signals regulate multiple aspects of
gastrointestinal development. Development127,
2763–2772 (2000).
15. Roberts, D. J. et al. Sonic hedgehog is an endodermal signal inducing Bmp-4 and Hox genes during induction
and regionalization of the chick hindgut. Development
121, 3163–3174 (1995).
16. Roberts, D. J., Smith, D. M., Goff, D. J. & Tabin, C. J. Epithelial-mesenchymal signaling during the
regionalization of the chick gut. Development125,
2791–2801 (1998).
17. van den Brink, G. R. et al. Indian Hedgehog is an antagonist of Wnt signaling in colonic epithelial
cell differentiation. Nature Genet. 36, 277–282
(2004).
18. Karlsson, L., Lindahl, P., Heath, J. K. & Betsholtz, C. Abnormal gastrointestinal development in PDGF-A and PDGFR-α deficient mice implicates a novel mesenchymal structure with putative instructive
properties in villus morphogenesis. Development127,
3457–3466 (2000).
19. Haramis, A. P. et al. De novo crypt formation and juvenile polyposis on BMP inhibition in mouse
intestine. Science303, 1684–1686 (2004).
Shows that BMP signalling from the villus mesenchyme is necessary to prevent the villus epithelium from adopting a crypt-like proliferative character.
20. He, X. C. et al. BMP signaling inhibits intestinal stem
cell self-renewal through suppression of Wnt–β-catenin
signaling. Nature Genet. 36, 1117–1121 (2004).
21. Howe, J. R. et al. Mutations in the SMAD4/DPC4 gene
in juvenile polyposis. Science280, 1086–1088
(1998).
22. Howe, J. R. et al. Germline mutations of the gene encoding bone morphogenetic protein receptor 1A in
juvenile polyposis. Nature Genet. 28, 184–187 (2001).
23. Meinhardt, H. & Gierer, A. Pattern formation by local
self-activation and lateral inhibition. BioEssays22,
753–760 (2000).
24. Gregorieff, A. et al. Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine. Gastroenterology129, 626–638 (2005).
25. Logan, C. Y. & Nusse, R. The Wnt signaling pathway in
development and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol.
20, 781–810 (2004).
26. Korinek, V. et al. Depletion of epithelial stem-cell compartments in the small intestine of mice
lacking Tcf-4. Nature Genet. 19, 379–383
(1998).
The first direct evidence that when the Wnt signalling pathway is defective, the intestinal stem-cell population is not maintained. 27. Pinto, D., Gregorieff, A., Begthel, H. & Clevers, H.
Canonical Wnt signals are essential for homeostasis of
the intestinal epithelium. Genes Dev. 17, 1709–1713
(2003).
By forced expression of DKK1, a secreted Wnt inhibitor, this paper shows that Wnt signalling is needed not only to maintain proliferation of the intestinal epithelium, but also to drive the differentiation of secretory cells.
28. Kuhnert, F. et al. Essential requirement for Wnt signaling in proliferation of adult small intestine and colon revealed by adenoviral expression of
Dickkopf-1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA101, 266–271
(2004).
29. Korinek, V. et al. Constitutive transcriptional activation
by a β-catenin–Tcf complex in APC–/– colon carcinoma.
Science275, 1784–1787 (1997).
30. Andreu, P. et al. Crypt-restricted proliferation and
commitment to the Paneth cell lineage following Apc
loss in the mouse intestine. Development132,
1443–1451 (2005).
31. Sansom, O. J. et al. Loss of Apcin vivo immediately perturbs Wnt signaling, differentiation, and migration. Genes Dev. 18, 1385–1390 (2004).
32. Morin, P. J. et al. Activation of β-catenin–Tcf signaling
in colon cancer by mutations in β-catenin or APC.
Science275, 1787–1790 (1997).
33. Su, L. K. et al. Multiple intestinal neoplasia caused by
a mutation in the murine homolog of the APC gene.
Science256, 668–670 (1992).
34. Haramis, A. P. et al. Adenomatous polyposis coli-deficient zebrafish are susceptible to digestive
tract neoplasia. EMBO Rep. 27 Jan 2006
(doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400638).
35. Bjerknes, M. & Cheng, H. Colossal crypts bordering
colon adenomas in ApcMin mice express full-length Apc.
Am. J. Pathol. 154, 1831–1834 (1999). 36. Merritt, A. J., Gould, K. A. & Dove, W. F. Polyclonal
structure of intestinal adenomas in ApcMin/+ mice with
concomitant loss of Apc+ from all tumor lineages.
Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA94, 13927–13931 (1997). 37. Novelli, M. R. et al. Polyclonal origin of colonic
adenomas in an XO/XY patient with FAP. Science272,
1187–1190 (1996).
38. Xu, Q., Mellitzer, G., Robinson, V. & Wilkinson, D. G. In vivo cell sorting in complementary segmental domains mediated by Eph receptors and ephrins. Nature399, 267–271 (1999).
39. Winslow, J. W. et al. Cloning of AL-1, a ligand for an Eph-related tyrosine kinase receptor involved in axon
bundle formation. Neuron14, 973–981 (1995).
40. van de Wetering, M. et al. The β-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt progenitor phenotype on
colorectal cancer cells. Cell111, 241–250 (2002).
41. Batlle, E. et al. β-Catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the
expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell111, 251–263 (2002).
A screen for genes that are misregulated in Wnt pathway mutants identifies genes of the EphB and ephrin B families as targets of Wnt signalling in the intestinal epithelium. Knockouts of these genes show that EphB/ephrin B signalling controls the positioning of cell types along the crypt–villus axis. 42. Batlle, E. et al. EphB receptor activity suppresses
colorectal cancer progression. Nature435,
1126–1130 (2005).
43. van Es, J. H. et al. Wnt signalling induces maturation
of Paneth cells in intestinal crypts. Nature Cell Biol. 7,
381–386 (2005).
44. Schroder, N. & Gossler, A. Expression of Notch pathway components in fetal and adult mouse small
intestine. Gene Expr. Patterns2, 247–250 (2002).
45. Jensen, J. et al. Control of endodermal endocrine
development by Hes-1. Nature Genet. 24, 36–44
(2000).
One of the first papers to show that Notch signalling affects cell fate choices in the intestinal epithelium.
46. Crosnier, C. et al. Delta–Notch signalling controls commitment to a secretory fate in the zebrafish
intestine. Development132, 1093–1104 (2005).
47. van Es, J. H. et al. Notch/γ-secretase inhibition turns proliferative cells in intestinal crypts and adenomas
into goblet cells. Nature435, 959–963 (2005).
By conditional knockout of the Notch pathway effector RBPSUH, and also by blocking Notch signalling with a γ-secretase inhibitor, this paper shows that Notch signalling is needed to maintain the proliferative intestinal stem or progenitor population and to prevent all these cells from differentiating as secretory cells.
48. Milano, J. et al. Modulation of notch processing by
γ-secretase inhibitors causes intestinal goblet cell
metaplasia and induction of genes known to specify
gut secretory lineage differentiation. Toxicol. Sci. 82,
341–358 (2004).
49. Itoh, M. et al. Mind bomb is a ubiquitin ligase that is essential for efficient activation of Notch signaling by
Delta. Dev. Cell4, 67–82 (2003).
50. Fre, S. et al. Notch signals control the fate of immature
progenitor cells in the intestine. Nature435,
964–968 (2005).
Conditional overexpression of NICD in the intestinal
epithelium is used to show that activation of Notch prevents cell differentiation towards the secretory fate and helps to maintain the proliferative state. 51. Chitnis, A., Henrique, D., Lewis, J., Ish-Horowicz, D. &
Kintner, C. Primary neurogenesis in Xenopus embryos
regulated by a homologue of the Drosophila
neurogenic gene Delta. Nature375, 761–766 (1995).
52. Ben-Arie, N. et al. Functional conservation of atonal and Math1 in the CNS and PNS. Development127, 1039–1048 (2000).
53. Bermingham, N. A. et al. Math1: an essential gene for
the generation of inner ear hair cells. Science284,
1837–1841 (1999).
54. Yang, Q., Bermingham, N. A., Finegold, M. J. &
Zoghbi, H. Y. Requirement of Math1 for secretory cell
lineage commitment in the mouse intestine. Science
294, 2155–2158 (2001).
Shows that Math1 is expressed in secretory cells and their precursors in the intestinal epithelium, and that when it is knocked out these cell types are lost. 55. Kayahara, T. et al. Candidate markers for stem and
early progenitor cells, Musashi-1 and Hes1, are expressed in crypt base columnar cells of mouse small
intestine. FEBS Lett. 535, 131–135 (2003).
56. Zecchini, V., Domaschenz, R., Winton, D. & Jones, P. Notch signaling regulates the differentiation of
post-mitotic intestinal epithelial cells. Genes Dev. 19,
1686–1691 (2005).
57. Henrique, D. et al. Maintenance of neuroepithelial progenitor cells by Delta–Notch signalling in the
embryonic chick retina. Curr. Biol. 7, 661–670 (1997).
58. Scheer, N., Groth, A., Hans, S. & Campos-Ortega, J. A. An instructive function for Notch in promoting
gliogenesis in the zebrafish retina. Development128,
1099–1107 (2001).
59. Yang, X. et al. Notch activation induces apoptosis in neural progenitor cells through a p53-dependent
pathway. Dev. Biol. 269, 81–94 (2004).
60. Handler, M., Yang, X. & Shen, J. Presenilin-1 regulates neuronal differentiation during neurogenesis. Development127, 2593–2606 (2000). 61. Dorsky, R. I., Chang, W. S., Rapaport, D. H. &
Harris, W. A. Regulation of neuronal diversity in the Xenopus retina by Delta signalling. Nature385, 67–70 (1997).
62. Hatakeyama, J. et al. Hes genes regulate size, shape and histogenesis of the nervous system by control of the timing of neural stem cell differentiation. Development131, 5539–5550 (2004). 63. Hitoshi, S. et al. Notch pathway molecules are
essential for the maintenance, but not the generation,
of mammalian neural stem cells. Genes Dev. 16,
846–858 (2002).
64. Nyfeler, Y. et al. Jagged1 signals in the postnatal subventricular zone are required for neural stem
cell self-renewal. EMBO J. 24, 3504–3515 (2005).
65. Kohyama, J. et al. Visualization of spatiotemporal activation of Notch signaling: live monitoring and
significance in neural development. Dev. Biol. 286,
311–325 (2005).
66. Megason, S. G. & McMahon, A. P. A mitogen gradient of dorsal midline Wnts organizes growth in the CNS. Development129, 2087–2098 (2002). 67. Zechner, D. et al. β-Catenin signals regulate cell
growth and the balance between progenitor cell expansion and differentiation in the nervous system. Dev. Biol. 258, 406–418 (2003).
68. Chenn, A. & Walsh, C. A. Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural
precursors. Science297, 365–369 (2002).
69. Lie, D. C. et al. Wnt signalling regulates adult
hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature437, 1370–1375
(2005).
70. Kubo, F., Takeichi, M. & Nakagawa, S. Wnt2b inhibits differentiation of retinal progenitor cells in the absence of Notch activity by downregulating the
expression of proneural genes. Development132,
2759–2770 (2005).
71. Cairns, J. Mutation selection and the natural history of
cancer. Nature255, 197–200 (1975).
72. Potten, C. S., Owen, G. & Booth, D. Intestinal stem cells protect their genome by selective segregation of
template DNA strands. J. Cell Sci. 115, 2381–2388
(2002).
73. Stappenbeck, T. S., Mills, J. C. & Gordon, J. I. Molecular features of adult mouse small intestinal
epithelial progenitors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA100,
1004–1009 (2003).
74. Subramanian, V., Meyer, B. & Evans, G. S. The murine
Cdx1 gene product localises to the proliferative
compartment in the developing and regenerating
intestinal epithelium. Differentiation64, 11–18 (1998).
75. Potten, C. S. et al. Identification of a putative intestinal stem cell and early lineage marker; musashi-1. Differentiation71, 28–41 (2003).
76. Bettess, M. D. et al. c-Myc is required for the formation of intestinal crypts but dispensable for
homeostasis of the adult intestinal epithelium. Mol.
Cell. Biol. 25, 7868–7878 (2005). 77. Merok, J. R., Lansita, J. A., Tunstead, J. R. &
Sherley, J. L. Cosegregation of chromosomes containing immortal DNA strands in cells that cycle
with asymmetric stem cell kinetics. Cancer Res. 62,
6791–6795 (2002).
78. Karpowicz, P. et al. Support for the immortal strand hypothesis: neural stem cells partition DNA
asymmetrically in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 170, 721–732
(2005).
79. Smith, G. H. Label-retaining epithelial cells in mouse mammary gland divide asymmetrically and retain their
template DNA strands. Development132, 681–687
(2005).
80. Lowell, S., Jones, P., Le Roux, I., Dunne, J. & Watt, F. M. Stimulation of human epidermal differentiation by delta-notch signalling at the
boundaries of stem-cell clusters. Curr. Biol. 10,
491–500 (2000).
81. Nicolas, M. et al. Notch1 functions as a tumor
suppressor in mouse skin. Nature Genet. 33,
416–421 (2003).
82. Alonso, L. & Fuchs, E. Stem cells in the skin: waste
not, Wnt not. Genes Dev. 17, 1189–1200
(2003).
83. Watt, F. M. Unexpected Hedgehog–Wnt interactions
in epithelial differentiation. Trends Mol. Med. 10,
577–580 (2004).
84. Micchelli, C. A. & Perrimon, N. Evidence that stem
cells reside in the adult Drosophila midgut epithelium.
Nature439, 475–479 (2006).
85. Ohlstein, B. & Spradling, A. The adult Drosophila posterior midgut is maintained by pluripotent stem
cells. Nature439, 470–474 (2006).
86. Duncan, A. W. et al. Integration of Notch and Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Nature Immunol. 6, 314–322 (2005). This paper uses transgenic mice that contain reporter genes to show that in haemopoietic stem cells the Notch and Wnt pathways are both active and serve jointly to maintain the proliferative pluripotent stem-cell state. 87. Reya, T. et al. A role for Wnt signalling in self-renewal
of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature423, 409–414
(2003).
88. Varnum-Finney, B. et al. Pluripotent, cytokine-dependent, hematopoietic stem cells are immortalized by constitutive Notch1 signaling. Nature Med. 6, 1278–1281 (2000).
89. Karanu, F. N. et al. The notch ligand jagged-1 represents a novel growth factor of human
hematopoietic stem cells. J. Exp. Med. 192,
1365–1372 (2000).
90. Pack, M. et al. Mutations affecting development of
zebrafish digestive organs. Development123,
321–328 (1996).
91. Grapin-Botton, A. & Melton, D. A. Endoderm development: from patterning to organogenesis. Trends Genet. 16, 124–130 (2000).
92. Wallace, K. N., Akhter, S., Smith, E. M., Lorent, K. & Pack, M. Intestinal growth and differentiation
in zebrafish. Mech. Dev. 122, 157–173
(2005).
93. Pinto, D., Robine, S., Jaisser, F., El Marjou, F. E. & Louvard, D. Regulatory sequences of the mouse
villin (Vill) gene that efficiently drive transgenic
expression in immature and differentiated epithelial cells of small and large intestines. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–6482 (1999).
94. Robine, S., Jaisser, F. & Louvard, D. Epithelial cell growth and differentiation. IV. Controlled
spatiotemporal expression of transgenes: new tools to
study normal and pathological states. Am. J. Physiol.
273, G759–762 (1997).
95. el Marjou, F. et al. Tissue-specific and inducible Cre-mediated recombination in the gut epithelium. Genesis39, 186–193 (2004).
96. Ireland, H. et al. Inducible Cre-mediated control of gene expression in the murine gastrointestinal tract:
effect of loss of β-catenin. Gastroenterology126,
1236–1246 (2004). Acknowledgements
We thank N. Wright and the anonymous referees for helpful comments, and Cancer Research UK for financial support. Competing interests statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
DATABASES
The following terms in this article are linked online to: Entrez Gene:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query. fcgi?db=gene
Apc | BMP2 | BMP4 | BMPR1A | ephrin B1 | EPHB2 | EPHB3 |
Gli1 | Gli2 | Gli3 | Hes1 | HHIP | Ihh | Math1 | noggin | PDGFA | PDGFRA | Ptch1 | Ptch2 | Rbpsuh | Shh | Tcf4 | WNT3 | WNT6 | WNT9B
OMIM: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query. fcgi?db=OMIM
juvenile polyposis syndrome
Access to this links box is available online.