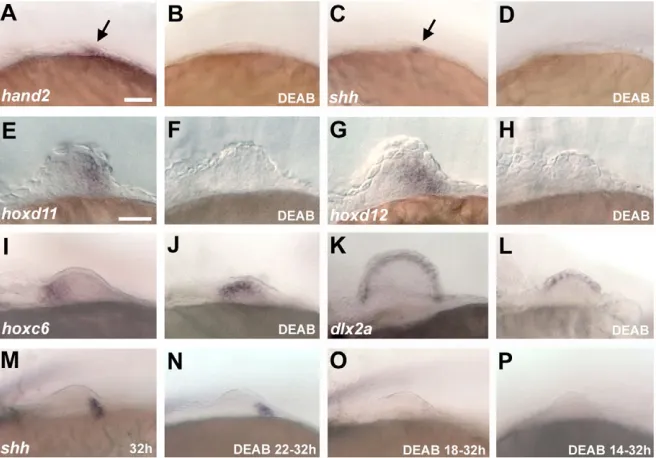
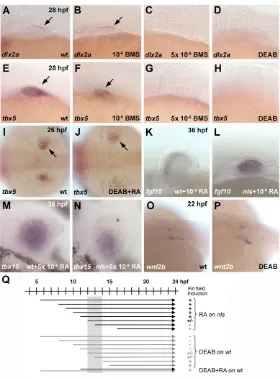
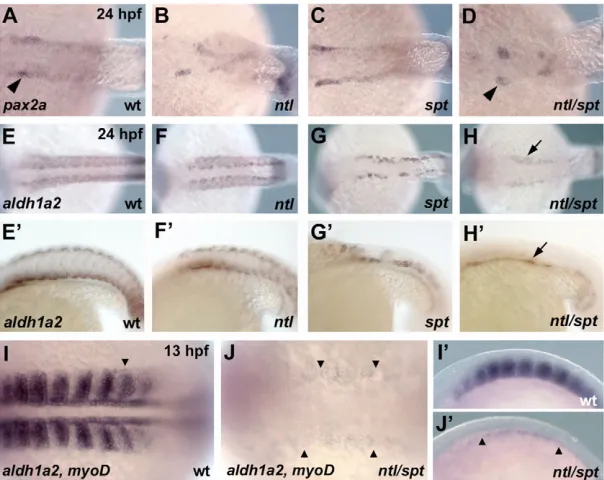
Induction and prepatterning of the zebrafish pectoral fin bud requires axial retinoic acid signaling
Full text
Figure


Related documents
RpoS contributes to resistance to phagocyte oxidase-mediated stress during urinary tract infection by Escherichia coli CFT073.. This is an open-access article distributed under
These include: (i) levels of total cholesterol, random blood glucose and blood pressures increase with advancing age, (ii) prevalence of hypercholesterolaemia,
In this study, we identified several strains with mutations in the ribosomal proteins putatively associated with linezolid resistance; two linezolid- resistant isolates harbored only
A table of the top 20 most common DUFs (ranked by the number of sequenced bacterial genomes) for which a structure has been deposited in Protein Data Bank (PDB) (13) is provided
In this regard, Farnsworth deviated from the customary restitution principle that "fault may be relevant to the measure of unjust enrichment and other features
(A) Type I IFN production by SV40T MEFs from matched wild-type and Sting -deficient mice stimulated with 0.1 M CPT for 48 h, measured by bioassay on LL171 cells (data shown as
This protection, and the consensual sequence (ELDKWA) of the corresponding epitope (26), led us to select this peptide to investigate the induction of a mucosal immune response by