Serial Attached SCSI RAID
Controllers Installation
and User's Guide
CDP-00283-01-A Rev. A
Issue: July 15, 2013
Copyright © PMC-Sierra, Inc. All rights reserved.
The information in this document is proprietary and confidential to PMC-Sierra, Inc. In any event, no part of this document may be reproduced or redistributed in any form without the express written consent of PMC-Sierra, Inc.
CDP-00283-01-A Rev. A, IssueNumber
None of the information contained in this document constitutes an express or implied warranty by PMC-Sierra, Inc. as to the sufficiency, fitness or suitability for a particular purpose of any such information or the fitness, or suitability for a particular purpose, merchantability, performance, compatibility with other parts or systems, of any of the products of PMC-Sierra, Inc., or any portion thereof, referred to in this document. PMC-Sierra, Inc. expressly disclaims all representations and warranties of any kind regarding the contents or use of the information, including, but not limited to, express and implied warranties of accuracy, completeness, merchantability, fitness for a particular use, or non-infringement.
In no event will PMC-Sierra, Inc. be liable for any direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages, including, but not limited to, lost profits, lost business or lost data resulting from any use of or reliance upon the information, whether or not PMC-Sierra, Inc. has been advised of the possibility of such damage.
For a complete list of PMC-Sierra’s trademarks and registered trademarks, visit: http://www.pmc-sierra.com/legal/.
Other product and company names mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
Revision History
Details of Change Issue Date
Issue
Adaptec Firmware/BIOS/Drivers/Utilities Version 1.03 July 15, 2013
Contents
Adaptec by PMC Product Support...8
Limited 3-Year Hardware Warranty...10
Regulatory Compliance Statements...11
1 About This Guide...14
What You Need to Know Before You Begin...14
Terminology Used in this Guide...14
How to Find More Information...14
2 Kit Contents and System Requirements...16
Kit Contents...16
System Requirements ...16
3 About Your RAID Controller...17
Standard RAID Controller Features...17
Array-level Features...17
Advanced Data Protection Suite...17
Adding a Flash Backup Module...18
Upgrading the Controller Firmware...18
About the Adaptec RAID 7805/7805Q...19
About the Adaptec RAID 71605/71605Q...20
About the Adaptec RAID 71605E...21
About the Adaptec RAID 71685...22
About the Adaptec RAID 72405...23
About the Adaptec RAID 78165...24
4 Getting Started...25
Choosing a RAID Level...25
Selecting Disk Drives and Cables ...25
Disk Drives...25
Cables...25
Replacing the Full-Height Bracket with a Low-Profile Bracket...26
Installation Options...27
Basic Installation Steps...27
Installing with an Operating System...28
Installing on an Existing Operating System...28
5 Installing the Controller and Disk Drives...29
Before You Begin...29
Installing the Controller...29
Installing a RAID Controller without Zero Maintenance Cache Protection...29
Installing a RAID Controller with Zero Maintenance Cache Protection ...30
Connecting Disk Drives to Your Controllers...33
Connecting Drives Directly to the Controller...33
Connecting Drives to a System Backplane...33
Connecting Solid State Drives (SSDs) ...33
Connecting External Devices ...34
7 Installing the Driver and an Operating System ...40
Before You Begin...40
Creating a Driver Disk...40
Creating a Driver Disk for Debian Linux or Ubuntu Linux ...41
Creating a Driver Disk for VMware ESX 4.1 ...41
Installing with Windows ...42
Installing with Red Hat Linux 5 or Cent OS 5 ...42
Installing with Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6, or Fedora Linux ...42
Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6 with Dynamic Kernel Module Support ...42
Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6, Fedora Linux without Dynamic Kernel Module Support ...43
Installing with SuSE Linux Enterprise Server ...44
Installing with Debian Linux...44
Installing with Ubuntu Linux...45
Installing with Solaris...46
Installing with FreeBSD ...47
Installing with VMware ESX 4.1 ...47
Installing with VMware ESXi 5.x ...48
Installing with Citrix XenServer ...51
8 Installing the Driver on an Existing Operating System ...52
Before You Begin...52
Creating a Driver Disk...52
Installing on Windows ...52
Installing on Red Hat, Cent OS, SuSE, or Fedora Linux...53
Installing on Debian Linux...53
Installing on Ubuntu Linux...53
Installing on Solaris ...54
Installing on FreeBSD ...54
Installing on VMware...55
Installing on Citrix XenServer...56
9 Managing Your Storage Space...57
About maxView Storage Manager...57
Installing maxView Storage Manager...57
About the Adaptec RAID Controller Configuration Utility...57
About the Adaptec RAID Configuration Utility...57
About the Adaptec Flash Utility...58
Which Utility Should I Use?...58
10 Solving Problems ...59
Troubleshooting Checklist...59
Monitoring Disk Drives Status...59
Silencing the Alarm ...59
Recovering from a Disk Drive Failure ...59
Failed Disk Drive Protected by a Hot Spare ...60
Failed Disk Drive Not Protected by a Hot Spare ...60
Failure in Multiple Arrays Simultaneously ...60
Disk Drive Failure in a RAID 0 Array ...60
Multiple Failures in the Same Array ...60
Failed SSD in maxCache Container...61
Resetting the Controller ...61
Appendix A Introduction to SAS...62
Terminology Used in This Appendix ...62
What is SAS?...62
How Do SAS Devices Communicate?...62
What’s a Phy?...63
What’s a SAS Port?...63
What do SAS Cables Look Like?...64
How are Disk Drives Identified in SAS? ...64
What are the SAS Connection Options?...64
Direct-attach Connections...64
Backplane Connections...65
SAS Expander Connections...65
How is SAS Different from Parallel SCSI? ...66
Appendix B Understanding RAID...67
Understanding Drive Segments...67
Non-redundant Arrays (RAID 0)...67
RAID 1 Arrays ...68
RAID 1 Enhanced Arrays...68
RAID 10 Arrays...69
RAID 5 Arrays...70
RAID 50 Arrays...71
RAID 6 Arrays...72
RAID 60 Arrays...72
Comparing RAID Levels...73
Appendix C Using the Adaptec RAID Configuration Utility...74
Introduction to the ARC Utility...74
Ctrl-A or uEFI/HII? ...74
Running the ARC Utility...74
Using the ARC Utility to Create and Manage Arrays...75
Creating a New Array...75
Managing Existing Arrays...75
Creating Bootable Arrays...75
Modifying Power Management Settings...76
Modifying Cache Settings...76
Initializing Disk Drives...77
Rescanning Disk Drives...77
Secure Erasing Disk Drives...77
Stopping a Secure Erase...77
Uninitializing Disk Drives...77
Using the ARC Utility to Modify Controller Settings...78
Opening the Controller Settings Tool ...78
Applying Changes and Exiting...78
Modifying Your Controller’s Configuration...78
General Controller Settings ...78
Power Management Settings...80
Checking Backup Unit Status...80
Formatting and Verifying Disk Drives...80
Locating Disk Drives...81
Identifying Disk Drives ...81
Viewing the Event Log ...81
Appendix D Using the Adaptec Flash Utility...83
System Requirements...83
Compatibility Notes...83
Before You Begin...83
Obtaining the Firmware...83
Creating the Firmware Update Disk ...83
Running the Menu-based AFU...84
Help...86
Updating the Flash Using the AFU Command Line...87
Appendix E Controller Alarm Connector Quick Reference...88
Adaptec RAID 7805/7805Q/71605/71605Q/71605E Alarm Connector Specification...88
Adaptec RAID 71685/72405/78165 Alarm Connector Specification...88
Appendix F Safety Information...89
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)...89
Appendix G Technical Specifications...90
Environmental Specifications...90
DC Power Requirements...90
Adaptec by PMC Product Support
If you have questions about installing or using your Adaptec by PMC product, check this document first—you will find answers to most of your questions. If you need further assistance, use the support options listed below. To expedite your service, have your computer in front of you.
Note: The phone numbers below are subject to change. Please visit the Support section ofwww.adaptec.comfor the most up to date contact information. Technical Support Identification (TSID) Number
• Before contacting Technical Support, you need your product unique TSID number. The TSID number identifies your product and support status.
• The TSID number is included on a white, bar-coded label, like this example:
• It's recommended that you register your product so that you have easy access to your TSID when contacting product support.
Self Help and Support in English
• Visit our Web site atwww.adaptec.com.
• Search the Adaptec Support Knowledgebase (ASK) atask.adaptec.comfor articles, troubleshooting tips, and frequently asked questions for your product.
• For support via e-mail, submit your question atask.adaptec.com.
• To speak with a Technical Support Specialist, call +1 408 934 7274 or +49 89 4366 5544 or +44 845 266 8773.
Technische Informationen und Support in Deutsch
• Besuchen Sie unsere Webseitewww.adaptec.com/de-de
• Suchen Sie in der Adaptec Support Knowledgebase (ASK) unterask-de.adaptec.comnach Artikeln, Tipps zur Fehlerbehebung und häufig gestellten Fragen zu Ihrem Produkt.
• Support per Email erhalten Sie unterask-de.adaptec.com. • Für telefonischen Support wählen Sie +49 89 4366 5522. Техническая поддержка и информация на русском языке • Посещаете наш сайтwww.adaptec.com/ru-ru/.
• База знаний Adaptec (ASK) на сайтеask-ru.adaptec.comask-ru.adaptec.com – статьи, советы по устранению неисправностей и часто задаваемые вопросы о Вашем продукте. • Для поддержки по электронной почте отправьте Ваш запрос на сайтеask-ru.adaptec.com • Чтобы обратиться к специалисту технической поддержки по телефону, звоните на +7 499 918 7200 или +49 89 4366 5555. 日本語での技術情報とサポート • 弊社のウェブサイト、www.adaptec.com/ja-jpをご覧ください。
Information Technique et d'assistance en Français
• Visitez notre site Web à l'adressewww.adaptec.com/fr-fr.
• Rechercher dans le base de connaissances Adaptec (ASK)ask-fr.adaptec.compour des articles, conseils de dépannage et les questions fréquemment posées pour votre produit.
Limited 3-Year Hardware Warranty
1. PMC-Sierra, Inc. (“PMC-Sierra”) warrants to the purchaser of this product that it will be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of three (3) years from the date of purchase. If the product should become defective within the warranty period, PMC-Sierra, at its option, will repair or replace the product, or refund the purchaser's purchase price for the product, provided it is delivered at the purchaser's expense to an authorized PMC-Sierra service facility or to PMC-Sierra. 2. Repair or replacement parts or products will be furnished on an exchange basis and will either be
new or reconditioned and will be subject to original warranty term. All replaced parts or products shall become the property of PMC-Sierra. This warranty shall not apply if the product has been damaged by accident, misuse, abuse or as a result of unauthorized service or parts.
3. Warranty service is available to the purchaser by delivering the product during the warranty period to an authorized PMC-Sierra service facility or to PMC-Sierra and providing proof of purchase price and date. The purchaser shall bear all shipping, packing, and insurance costs and all other costs, excluding labor and parts, necessary to effectuate repair, replacement or refund under this warranty. 4. For more information on how to obtain warranty service, write or telephone:
• Americas PMC-Sierra, Inc. at 1380 Bordeaux Drive Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA, +1 408 934-7274 • EMEA PMC-Sierra, at Lise-Meitner-Strasse 7, 85737 Ismaning, Germany, +49 89 43665544 • Asia Pacific PMC-Sierra, at PO Box 110, Peakhurst NSW 2210, Australia, +61 2 8212-5531 • Japan PMC-Sierra, at Tokumasu-Building 4F, 5-5-5, Higashinakano, Nakano-ku, Tokyo 164-0003,
Japan, 03-3367-3970 (fax).
5. THIS LIMITED WARRANTY DOES NOT EXTEND TO ANY PRODUCT WHICH HAS BEEN DAMAGED AS A RESULT OF ACCIDENT, MISUSE, ABUSE, OR AS A RESULT OF UNAUTHORIZED SERVICE OR PARTS. 6. THIS WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER EXPRESS WARRANTIES WHICH NOW OR HEREAFTER MIGHT
OTHERWISE ARISE RESPECT TO THIS PRODUCT. IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT SHALL (A) HAVE NO GREATER DURATION THAN 3 YEARS FROM THE DATE OF PURCHASE, (B) TERMINATE AUTOMATICALLY AT THE EXPIRATION OF SUCH PERIOD AND (C) TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW BE EXCLUDED. IN THE EVENT THIS PRODUCT BECOMES DEFECTIVE DURING THE WARRANTY PERIOD, THE PURCHASER'S EXCLUSIVE REMEDY SHALL BE REPAIR, REPLACEMENT OR REFUND AS PROVIDED ABOVE. INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION LOSS OF DATA, ARISING FROM BREACH OF ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY ARE NOT THE RESPONSIBILITY OF PMC-SIERRA AND, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, ARE HEREBY EXCLUDED BOTH FOR PROPERTY DAMAGE, AND TO THE EXTENT NOT UNCONSCIONABLE, FOR PERSONAL INJURY DAMAGE. 7. WITHIN THE US, SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES FOR CONSUMER PRODUCTS, AND SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW LONG AN IMPLIED WARRANTY LASTS, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
8. THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS, AND YOU MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER RIGHTS WHICH VARY DEPENDING ON WHERE YOU RESIDE.
9. FOR AUSTRALIA RESIDENTS, IF THE PRODUCT SHOULD BECOME DEFECTIVE WITHIN THE WARRANTY PERIOD, PMC-SIERRA, AT ITS OPTION, WILL REPAIR OR REPLACE THE PRODUCT, OR REFUND THE PURCHASER'S PURCHASE FOR THE PRODUCT, PROVIDED IT IS DELIVERED AT THE PURCHASER'S EXPENSE BACK TO THE PLACE OF PURCHASE AFTER PMC-SIERRA TECHNICAL SUPPORT HAS ISSUED AN INCIDENT NUMBER. IN ADDITION TO THE WARRANTIES SET FORTH HEREIN, OUR GOODS COME WITH GUARANTEES THAT CANNOT BE EXCLUDED UNDER THE AUSTRALIAN CONSUMER LAW. YOU ARE ENTITLED TO A REPLACEMENT OR REFUND FOR A MAJOR FAILURE AND FOR COMPENSATION
Regulatory Compliance Statements
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference Statement
Attention: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. However, if this equipment does cause interference to radio or television equipment reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures: • Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected. • Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
• Use a shielded and properly grounded I/O cable and power cable to ensure compliance of this unit to the specified limits of the rules.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
UL Compliance Statement
Adaptec by PMC products are tested and listed by Underwriters Laboratories, Inc. to UL 60950 -1 Second Edition and IEC-60950-1 Second Edition standards, file numbers E175975. Adaptec by PMC products are for use only with UL listed ITE.
Use only with the listed ITE:
PMC-Sierra, Inc.
ASR-7805/ASR-7805Q/ASR-71605/ ASR-71605E/ASR-71605Q/ASR-71685/ ASR-72405/ASR-78165/ AFM-700
European Union Compliance Statement
This Information Technology Equipment has been tested and found to comply with EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, as amended by 92/31/EEC and 93/68/EEC, in accordance with: • EN55022 (1998+A1:2000+A2:2007) Emissions
∘ Class B ITE radiated and conducted emissions • EN55024 (1998+A1:2001+A2:2010) Immunity:
∘ EN61000-4-2 (2009) Electrostatic discharge: ±4 kV contact, ±8 kV air ∘ EN61000-4-3 (2010) Radiated immunity: 3V/m
∘ EN61000-4-4 (2004) Electrical fast transients/burst: ±1 kV AC, ±0.5 kV I/O ∘ EN61000-4-5 (2006) Surges: ±1 kV differential mode, ±2 kV common mode ∘ EN61000-4-6 (2009) Conducted immunity: 3 V
∘ EN61000-4-11 (2004) Supply dips and variations: 30% and 100% • EN50581 (2012) Technical Documentation:
∘ For the assessment of electrical and electronic products with respect to the restriction of hazardous substances
In addition, all equipment requiring U.L. listing has been found to comply with EMC Directive 73/23/EEC as amended by 93/68/EEC in accordance with EN60950 with amendments A1, A2, A3, A4, A11.
Australian/New Zealand Compliance Statement
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to the Australian/New Zealand standard AS/NZS 3548 set out by the Spectrum Management Agency.
Canadian Compliance Statement
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du Canada.
Japanese Compliance (Voluntary Control Council Initiative)
This equipment complies to class B Information Technology equipment based on VCCI (Voluntary Control Council for Interface). This equipment is designed for home use but it may causes radio frequency interference problem if used too near to a television or radio. Please handle it correctly per this documentation.
Korean Compliance (KCC) Statement
Adaptec by PMC products are tested and certified by KCC: KCC-REM-KHK-ASR-7xxx5
The above certification covers the following series:
ASR-7805, ASR-7805Q, ASR-71605 ASR-71605E, ASR-71605Q
ASR-71685, ASR-72405, ASR-78165 AFM-700
This equipment is home use (Class B) electromagnetic wave suitability equipment and to be used mainly at home and it can be used in all areas.
1
About This Guide
This Installation and User's Guide explains how to install your Adaptec® by PMC™ RAID controller. It also describes the utilities included in your controller kit, and provides a basic overview of Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) and Redundant Array of Independent Disk (RAID) technology.
These Adaptec Serial Attached SCSI RAID (ASR) controller models are described in this guide: • ASR-7805, ASR-7805Q
• ASR-71605, ASR-71605E, ASR-71605Q • ASR-71685
• ASR-72405 • ASR-78165
What You Need to Know Before You Begin
You should be familiar with computer hardware, data storage, RAID technology, and SAS and Serial ATA (SATA) technology. (For more information about SAS technology, seeIntroduction to SASon page 62.) You should also be familiar with direct-attached storage (DAS) concepts and technology.
Note: Because this guide covers multiple Adaptec RAID products, some of the features and functions described may not be available for your controller. For more information, seeAbout Your RAID Controlleron page 17.
Terminology Used in this Guide
Because you can use your Adaptec RAID controller to manage data storage in a variety of configurations, the generic term “storage space” is used to refer to controller(s) and disk drives being managed with Adaptec maxView Storage Manager™ (called simply maxView Storage Manager in the remainder of this guide) or the other utilities described in this guide.
Many of the terms and concepts referred to in this guide are known to computer users by multiple names. This guide uses these terms:
• Controller (also known as adapter, board, or card)
• Disk drive (also known as hard disk, hard drive, or hard disk drive) • Solid State Drive (also known as SSD or non-rotating storage media)
• Enclosure (also known as a RAID enclosure, storage enclosure, or disk drive enclosure) • Array (also known as a container, logical device, or logical drive)
Note: maxView Storage Manager refers to arrays as logical drives. Your RAID controller creates arrays, which your operating system (and maxView Storage Manager) recognizes as logical drives. For more information, refer to the maxView Storage Manager User’s Guide on the Adaptec Installation DVD.
How to Find More Information
You can find more information about your Adaptec RAID controller and the software and utilities included with it by referring to these documents:
• Readme.txt—Includes updated product information and known issues; located on the Adaptec Installation DVD.
• Adaptec RAID Controller Command Line Utility User’s Guide—Describes how to use the included Adaptec RAID Controller Configuration (ARCCONF) command line utility (seeAbout the Adaptec RAID Controller Configuration Utilityon page 57) to perform basic array and configuration management functions; located on the Adaptec Installation DVD.
2
Kit Contents and System Requirements
This chapter lists the contents of your Adaptec RAID controller kit and the system requirements that must be met for you to successfully install and use your controller.
Kit Contents
• Adaptec RAID controller
• Adaptec Installation DVD (bootable), including controller drivers, Adaptec maxView Storage Manager, ARCCONF command line utility, and documentation
• Cables (Not included in Adaptec 'Single' product. If your kit includes cables, the type and quantity vary—for more information, seeCableson page 25.)
• (Select models only) Low-profile bracket
• Adaptec Serial Attached SCSI RAID Controllers Quick Start Guide (on the installation DVD)
System Requirements
• PC-compatible computer with Intel Pentium, or equivalent, processor • Motherboard with these features:
∘ Support for multi-function devices where one of the devices is a PCI bridge ∘ Large memory-mapped address ranges
Refer to the Readme file on the Adaptec Installation DVD for additional motherboard compatibility information.
• One of these operating systems:
Note: For up-to-date operating system version support check the readme on the Adaptec Installation DVD or visit the Adaptec Web Site atwww.adaptec.com. To download Linux driver sources, visit the Support area of the Adaptec Web site at www.adaptec.com/en-us/support.
∘ Microsoft® Windows® Server 2012 (64-bit), Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit), Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit), Windows SBS 2011, Windows Storage Server 2008 R2, Windows Storage Server 2011, Windows 7 and Windows 8 (32-bit and 64-bit)
∘ Red Hat® Enterprise Linux 6.3, 5.9 (32-bit and 64-bit) ∘ SuSE Linux Enterprise Server 11, 10 (32-bit and 64-bit) ∘ FreeBSD 9.1, 9.0 (32-bit and 64-bit)
∘ Debian Linux 6 (32-bit and 64-bit)
∘ Ubuntu Linux 12, 11, 10 (32-bit and 64-bit) ∘ Fedora Linux 18, 17 (32-bit and 64-bit) ∘ CentOS 6.3, 5.9 (32-bit and 64-bit) ∘ Solaris 10, Solaris 11 Express
∘ VMware ESXi 5.1, VMware ESX 4.1 Classic ∘ Citrix XenServer 6.1
• 2 GB of RAM minimum
• Available compatible PCIe slot (depending on your controller model—see the descriptions inAbout Your RAID Controlleron page 17)
• 350 MB of free disk drive space
• 16-bit SVGA color monitor with a resolution of at least 800 x 600 • DVD-ROM drive
3
About Your RAID Controller
This chapter provides an overview of the features of your Adaptec RAID controller.
Standard RAID Controller Features
• Support for SAS disk drives, SATA/SATA II disk drives, and SATA and SAS Solid State Drives (SSDs) • Flash ROM for updates to controller firmware, BIOS, and the Adaptec RAID Configuration utility • Disk drive hot-swapping
• Event logging and broadcasting, including email notification messages
• Multiple options for creating and managing RAID arrays—A browser-based software application (maxView Storage Manager), a BIOS-based utility (ARC), a command line utility (ARCCONF) (see Managing Your Storage Spaceon page 57)
• Native command queuing (NCQ), which lets disk drives arrange commands into the most efficient order for optimum performance
• Support for disk drive enclosures with SES2 enclosure management hardware • Support for a flash backup module (seeAdding a Flash Backup Moduleon page 18)
• Support for Adaptec maxCache™ SSD read and write caching (seeModifying Cache Settingson page 76)
Note: Adaptec maxCache is supported on Adaptec Series Q controllers only.
• Power-management of disk drives in your storage space to reduce cooling and electricity costs (see Modifying Power Management Settingson page 76)
• Audible alarm • I/O statistics logging
Array-level Features
Note: Not all features are supported by all controllers. For more information, see the maxView Storage Manager User's Guide.
• Support for RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10, RAID 50, and simple volumes
• Support for hybrid RAID 1 and RAID 10 arrays comprised of hard drives and Solid State Drives (SSDs) • Support for hot spares (global and dedicated)
• Support for automatic failover, so arrays are automatically rebuilt when a failed drive is replaced (applies to redundant arrays in SES2- or SAF-TE-enabled disk drive enclosures only)
• Optimized disk utilization, which ensures that the full capacity of all disk drives can be used, even if the disk drives vary in size
• Online capacity expansion, so you can increase the capacity of an array without recreating it • Support for array migration from one RAID level to another
Advanced Data Protection Suite
• Copyback Hot Spare—You can use this feature to move data from a hot spare back to its original location after a failed disk drive is replaced.
• Striped Mirror (RAID 1E)—A RAID 1 Enhanced array is similar to a RAID 1 array except that data is both mirrored and striped, and more disk drives can be included.
• Dual Drive Failure Protection (RAID 6)—A RAID 6 array is similar to a RAID 5 array except that it includes two independent sets of parity data instead of one.
• Dual Drive Failure Protection (RAID 60)—A RAID 60 array is similar to a RAID 50 array except that it includes four independent sets of parity data instead of two.
Adding a Flash Backup Module
This table shows the flash backup module (or “zero maintenance cache protection”) supported by your Adaptec RAID controller. To purchase a flash backup module, refer to the Adaptec Web site at
www.adaptec.com.
Flash Module RAID Controller
Adaptec Flash Backup Module AFM-700 with Supercapacitor Card (optional)
Adaptec RAID 7805/Adaptec RAID 71605/Adaptec RAID 71685/ Adaptec RAID 72405/Adaptec RAID 78165
Adaptec Flash Backup Module AFM-700 with Supercapacitor Card (pre-installed)
Adaptec RAID 7805Q/Adaptec RAID 71605Q
Upgrading the Controller Firmware
To upgrade the firmware on your Adaptec RAID controller, follow the instructions inUsing the Adaptec Flash Utilityon page 83. You can also upgrade the controller firmware with maxView Storage Manager or the ARCCONF command-line utility. Refer to the maxView Storage Manager User's Guide and the Adaptec Command Line Interface User's Guide for more information. If the firmware upgrade is unsuccessful, follow the instructions inResetting the Controller on page 61.
About the Adaptec RAID 7805/7805Q
The Adaptec RAID 7805/7805Q is a SAS RAID controller with these features:
Ext. Alarm connector HDA mode connector
Daughterboard connector PCIe x8 connector
Mounting bracket
2 internal mini-SAS HD connectors
CN0 CN1 Low-profile MD2 Form Factor PCIe Gen3 Bus compatibility x8 PCIe bus width
6 Gb/s per port Data transfer rate
8 Phys (Unified Serial Ports)
1024 MB DDR3 Standard cache
2 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8643) Connectors, internal
8 direct-attached (or up to 256 with expanders) Maximum number of disk drives
7805Q: Up to 8 solid state drives, 2TB capacity, max. See the maxCache
compatibility list at www.adaptec.com/compatibility. maxCache SSD support
IBPI and SGPIO (Serial General Purpose Input/Output) Enclosure Support
Yes Onboard speaker
Adaptec Flash Backup Module AFM-700 (7805: optional, sold separately; 7805Q: standard, pre-installed)
Zero Maintenance Cache Protection Module
About the Adaptec RAID 71605/71605Q
The Adaptec RAID 71605/71605Q is a SAS RAID controller with these features:
4 internal mini-SAS HD connectors
Ext. Alarm connector HDA mode connector
CN0 CN1 CN2 CN3 Daughterboard connector PCIe x8 connector Mounting bracket Low-profile MD2 Form Factor PCIe Gen3 Bus compatibility x8 PCIe bus width
6 Gb/s per port Data transfer rate
16 Phys (Unified Serial Ports)
1024 MB DDR3 Standard cache
4 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8643) Connectors, internal
16 direct-attached (or up to 256 with expanders) Maximum number of disk drives
71605Q: Up to 8 solid state drives, 2TB capacity, max. See the maxCache
compatibility list at www.adaptec.com/compatibility. maxCache SSD support
IBPI and SGPIO (Serial General Purpose Input/Output) Enclosure Support
Yes Onboard speaker
Adaptec Flash Backup Module AFM-700 (71605: optional, sold separately; 71605Q: standard, pre-installed)
Zero Maintenance Cache Protection Module
About the Adaptec RAID 71605E
The Adaptec RAID 71605E is a SAS RAID controller with these features:
4 internal mini-SAS HD connectors
Ext. Alarm connector HDA mode connector
CN0 CN1 CN2 CN3 PCIe x8 connector Mounting bracket Low-profile MD2 Form Factor PCIe Gen3 Bus compatibility x8 PCIe bus width
6 Gb/s per port Data transfer rate
16 Phys (Unified Serial Ports)
256 MB DDR3 Standard cache
4 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8643) Connectors, internal
16 direct-attached (or up to 256 with expanders) Maximum number of disk drives
IBPI and SGPIO (Serial General Purpose Input/Output) Enclosure Support
Yes Onboard speaker
No Zero Maintenance Cache Protection
About the Adaptec RAID 71685
The Adaptec RAID 71685 is a SAS RAID controller with these features:
Ext. Alarm connector Daughterboard connector PCIe x8 connector Mounting bracket HDA mode connector 2 external mini-SAS HD connectors
4 internal mini-SAS HD connectors
Full Height, Half Length Form Factor
PCIe Gen3 Bus compatibility
x8 PCIe bus width
6 Gb/s per port Data transfer rate
24 Phys (Unified Serial Ports)
1024 MB DDR3 Standard cache 4 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8643) Connectors, internal 2 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8644) Connectors, external
24 direct-attached (or up to 256 with expanders) Maximum number of disk drives
IBPI and SGPIO (Serial General Purpose Input/Output) Enclosure Support
Yes Onboard speaker
Adaptec Flash Backup Module AFM-700 (optional, sold separately) Zero Maintenance Cache Protection
About the Adaptec RAID 72405
The Adaptec RAID 72405 is a SAS RAID controller with these features:
Ext. Alarm connector Daughterboard connector PCIe x8 connector Mounting bracket HDA mode connector HD connectors 4 internal mini-SAS HD connectors 2 internal mini-SAS
Full Height, Half Length Form Factor
PCIe Gen3 Bus compatibility
x8 PCIe bus width
6 Gb/s per port Data transfer rate
24 Phys (Unified Serial Ports)
1024 MB DDR3 Standard cache
6 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8643) Connectors, internal
24 direct-attached (or up to 256 with expanders) Maximum number of disk drives
IBPI and SGPIO (Serial General Purpose Input/Output) Enclosure Support
Yes Onboard speaker
Adaptec Flash Backup Module AFM-700 (optional, sold separately) Zero Maintenance Cache Protection
About the Adaptec RAID 78165
The Adaptec RAID 78165 is a SAS RAID controller with these features:
Ext. Alarm connector Daughterboard connector PCIe x8 connector Mounting bracket HDA mode connector 4 external mini-SAS HD connectors
2 internal mini-SAS HD connectors
2 3
Note: To provide optimal cooling for the Adaptec 78165 controller, it is recommended to provide air intake through the ventilated full-height bracket. For more information about cooling requirements, seeEnvironmental Specificationson page 90.
Low-profile MD2 Form Factor
PCIe Gen3 Bus compatibility
x8 PCIe bus width
6 Gb/s per port Data transfer rate
24 Phys (Unified Serial Ports)
1024 MB DDR3 Standard cache 2 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8643) Connectors, internal 4 mini-SAS HD x4 (SFF-8644) Connectors, external
24 direct-attached (or up to 256 with expanders) Maximum number of disk drives
IBPI and SGPIO (Serial General Purpose Input/Output) Enclosure Support
Yes Onboard speaker
Adaptec Flash Backup Module AFM-700 (optional, sold separately) Zero Maintenance Cache Protection
4
Getting Started
This chapter provides the basic information you need to set up your disk drives and arrays the way you want them. It describes the options you have for installing your Adaptec RAID controller and disk drives and creating arrays for storage. It also describes how to prepare your controller for installation into a low-profile computer cabinet.
Choosing a RAID Level
This section provides a brief overview of the RAID levels supported by your Adaptec RAID controller, including the minimum and maximum number of disk drives required by each.
Note: Before you begin, familiarize yourself with your controller's physical features and the RAID levels that it supports (seeStandard RAID Controller Featureson page 17).
• RAID 0 (Non-redundant Array)—Stripes data across multiple disk drives. Improved performance but no redundancy (seeNon-redundant Arrays (RAID 0)on page 67).
• RAID 1 Array—Created from two disk drives where one disk drive is a mirror of the other (the same data is stored on each disk drive). Redundancy, but reduced capacity (seeRAID 1 Arrays on page 68).
• RAID 1E Array—Similar to a RAID 1 array except that data is mirrored and striped, and more disk drives can be included (seeRAID 1 Enhanced Arrayson page 68).
• RAID 5 Array—Stripes data for improved performance and uses parity data to provide redundancy (seeRAID 5 Arrayson page 70).
• RAID 10 Array—Built from two or more equal-sized RAID 1 arrays, stripes and mirrors data across multiple disk drives. Redundancy and improved performance (seeRAID 10 Arrayson page 69). • RAID 50 Array—Built from multiple disk drives configured as two or more RAID 5 arrays, stripes
stored data and parity data across all disk drives (seeRAID 50 Arrayson page 71).
• RAID 6 Array—Similar to a RAID 5 array except that it includes two independent sets of parity data instead of one (seeRAID 6 Arrayson page 72).
• RAID 60 Array—Similar to a RAID 50 array except that it includes four independent sets of parity data instead of two (seeRAID 60 Arrayson page 72).
SeeComparing RAID Levelson page 73 to see how many disk drives you must connect to your RAID controller to support the RAID level you want.
Selecting Disk Drives and Cables
Disk Drives
Your SAS controller supports SAS disk drives, SATA disk drives, and SATA and SAS Solid State Drives (SSDs). When selecting disk drives for your RAID array, ensure that all the disk drives have the same performance level. You can use different-sized disk drives in the array, but the array will be limited to the capacity of the smallest and slowest disk drive. For more information about arrays, refer to the maxView Storage Manager User’s Guide or online Help. For more information about compatible disk drives, refer to the Adaptec Web site atwww.adaptec.com/compatibility.
Cables
Depending on your requirements, you can use any of the cables listed below. Cable connectors are keyed so that you can't insert them incorrectly. For more information about cabling options for your RAID controller, visit the Adaptec Web site atwww.adaptec.com.
Adaptec SAS Adapter 7xxx5 Cables
Internal mini-SAS HD to mini-SAS HD (SFF-8643 to SFF- 8643)—Connects to a backplane or enclosure.
External mini-SAS HD to mini-SAS HD (SFF-8644 to SFF- 8644)—Connects to a backplane or enclosure.
Replacing the Full-Height Bracket with a Low-Profile Bracket
If you are installing your Adaptec RAID controller into a low-profile computer cabinet, replace the original full-height bracket with the low-profile bracket included in your distribution kit. The full-height bracket is mounted on the front of the controller, the low-profile bracket is mounted on the back of the controller, as shown in the figure below.
Front of board Full-height bracket
Back of board
Low-profle bracket
To replace the full-height bracket with the low-profile bracket:
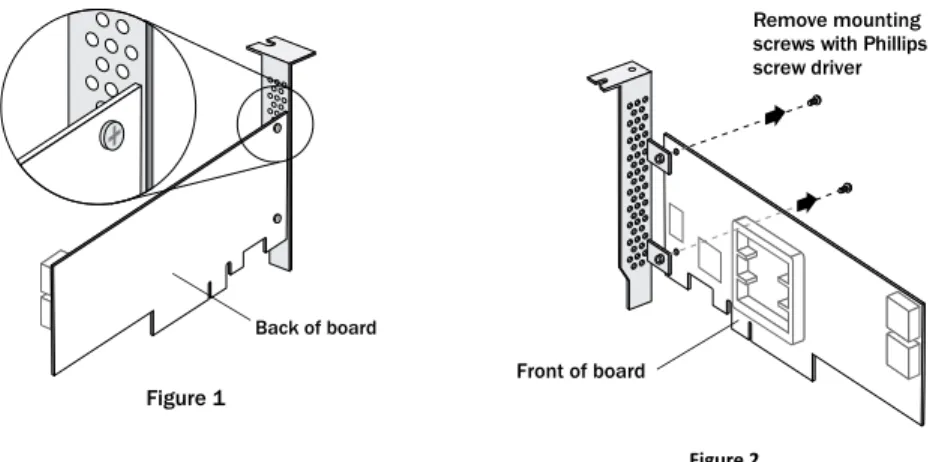
1. Remove the full-height bracket from the controller board. The full-height bracket is installed on the front side of the controller, with the mounting screws inserted from the back of the controller, as shown in the Figure 1.
Using a Phillips head screw driver, remove the mounting screws, as shown in Figure 2, then set the screws aside for use in the next step.
Remove mounting screws with Phillips screw driver
Front of board
Figure 2 Back of board
Figure 1
2. Attach the low-profile bracket to the controller board. The low-profile bracket is installed on the back side of the controller, with the mounting screws inserted from the front of the controller, as shown the Figure 3.
Insert the screws through the holes on the front of the controller, then fasten the screws to the bracket with a Phillips screw driver.
Caution: The mount points on the low-profile bracket have a smooth or flat side and a raised side that looks like a spacer (see Figure 3). Be sure to install the bracket with the flat side against the controller PCB and the raised side facing away from the PCB.
Figure 3
Raised side of bracket
Front of board Flat side of bracket
Back of board
Caution: The torque on the mounting screws should be a maximum of 3.0-4.0 lbf-in to avoid deformation. Be sure that the controller is not bent after attaching the low-profile bracket to the controller board.
Installation Options
When you install your Adaptec RAID controller, you can choose to create a bootable array and then install your operating system and the controller driver on that array.
Alternatively, you can complete a standard installation, where the controller driver is installed on an existing operating system.
Basic Installation Steps
Installing with an Operating System
1. Install and connect your controller and internal disk drives (seeInstalling the Controller and Disk Driveson page 29).
If your controller has an external connector, you can connect external disk drives as well (or instead). 2. Set the boot controller (seeSetting the Boot Controlleron page 36).
3. Create a bootable array (seeCreating an Arrayon page 36).
4. Install your operating system and the controller driver (seeInstalling the Driver and an Operating System on page 40.)
5. Install maxView Storage Manager and begin to manage your data storage (seeManaging Your Storage Spaceon page 57).
Installing on an Existing Operating System
1. Install and connect your controller and internal disk drives (seeInstalling the Controller and Disk Driveson page 29).
If your controller has an external connector, you can connect external disk drives as well (or instead). 2. Install the controller driver (seeInstalling the Driver on an Existing Operating System on page 52). 3. Install maxView Storage Manager and begin to manage your data storage (seeManaging Your
5
Installing the Controller and Disk Drives
This chapter explains how to install your Adaptec RAID controller, and how to install and connect internal and external disk drives.
Before You Begin
• ReadSafety Informationon page 89.
• Familiarize yourself with your RAID controller's physical features and the RAID levels that it supports (seeStandard RAID Controller Featureson page 17).
• Ensure you have the right quantity of disk drives for the RAID level you want to use for your arrays (seeSelecting Disk Drives and Cables on page 25).
• If you are installing the RAID controller into a low-profile computer cabinet, replace the original full-height bracket with the low-profile bracket included in the kit (seeReplacing the Full-Height Bracket with a Low-Profile Bracketon page 26).
Installing the Controller
This section describes how to install the Adaptec RAID controller into your computer cabinet. Adaptec RAID controllers come in two basic configurations: standard and zero maintenance cache protection with batteryless backup (ZMCP). ZMCP uses flash memory and a supercapacitor module to protect the cache without a battery.
Follow one of these sets of instructions:
• To install an Adaptec RAID controller without zero maintenance cache protection, see the next section.
• To install an Adaptec RAID controller with zero maintenance cache protection, seeInstalling a RAID Controller with Zero Maintenance Cache Protection on page 30.
Caution: Be sure to handle the controller by its bracket or edges only.
Installing a RAID Controller without Zero Maintenance Cache Protection
To install an Adaptec RAID controller without zero maintenance cache protection:1. Turn off your computer and disconnect the power cord. Open the cabinet, following the manufacturer's instructions.
2. Select an available PCIe expansion slot that's compatible with your RAID controller and remove the slot cover, as shown below. (PCIe bus compatibility is marked to the controller figures inAbout Your RAID Controlleron page 17.)
3. Insert the RAID controller into the expansion slot and press down gently but firmly until it clicks into place. When installed properly, the RAID controller should appear level with the expansion slot.
Caution: Touch a grounded metal object before handling the RAID controller.
4. Secure the bracket in the expansion slot, using the retention device (for instance, a screw or lever) supplied with your computer.
5. Prepare and install your internal disk drives, following the instructions inConnecting Disk Drives to Your Controllerson page 33.
If you are not installing internal disk drives, close your computer cabinet, reattach the power cord, then continue withConnecting External Devices on page 34.
Installing a RAID Controller with Zero Maintenance Cache Protection
Adaptec RAID controllers with zero maintenance cache protection (Adaptec Series Q controllers) include a flash module daughterboard and a supercapacitor module. The daughterboard is pre-installed on these controller. On Adaptec RAID controllers with optional zero maintenance cache protection (see Adding a Flash Backup Moduleon page 18), the daughterboard is user installed. The supercapacitor module is always user installed.
The following instructions describe how to install the supercapacitor module on a Series Q controller using the mounting plate method. It assumes that the daughterboard is already installed. Refer to the flyer, in the flash module distribution kit, for details about installing the daughterboard on the controller, as needed; the flyer also describes other supercapacitor installation options.
Warning: Do NOT remove or insert a fully charged supercapacitor module. Always discharge the unit first to avoid damage to the controller or flash backup module. The factory ships with discharged units, so they are safe to install when you receive them. To ensure that an installed unit is discharged, switch your system OFF, then wait 5 minutes. After a dirty shutdown, wait 3 minutes after backup is complete, then remove the unit.
To install an Adaptec RAID controller with zero maintenance cache protection: 1. Assemble the mounting plate and attach the supercapacitor module:
a) Attach the full-height bracket and mounting clip to the mounting plate. The full-height bracket is installed on the front side of the mounting plate (the side with the bents), with the mounting
Mounting clip Recessed side Large friction
clip
b) Insert the supercapacitor module into the mounting clip. The supercapacitor module snaps securely into place between the large and small friction clips, as shown in the figure below. Be sure to orient the supercapacitor module such that the connecting cable faces the rear of the mounting plate.
c) Set the mounting plate aside; continue with the steps below.
2. Turn off your computer and disconnect the power cord. Open the cabinet, following the manufacturer's instructions.
3. Select an available PCIe expansion slot that's compatible with your RAID controller and remove the slot cover, as shown in the figure below. (PCIe bus compatibility is marked on the controller figures inAbout Your RAID Controlleron page 17.) Be sure to choose a slot in the backplane with an empty slot next to it; you will use the empty slot to install the supercapacitor mounting plate, after you install the controller. Remove the slot cover for the mounting plate, then continue with the next step.
4. Insert the RAID controller into the expansion slot and press down gently but firmly until it clicks into place. When installed properly, the RAID controller should appear level with the expansion slot. Secure the bracket in the expansion slot, using the retention device (for instance, a screw or lever) supplied with your computer.
Caution: Touch a grounded metal object before handling the RAID controller.
5. Attach the supercapacitor module to the RAID controller by inserting the connector into the socket on the flash module daughterboard, as shown in the figure below. (The connector attaches to the socket in only one direction.) Use the included extender cable if you need extra length to reach the connector on the daughterboard.
Extender cable
6. Install the mounting plate in the empty slot next to the controller, as shown in the next figure. After securing the mounting plate to the card cage, verify that the supercapacitor module and mounting plate sit above (and do not touch) the PCIe slot.
Gap Gap
7. Prepare and install your internal disk drives, following the instructions inConnecting Disk Drives to Your Controllerson page 33.
If you are not installing internal disk drives, close your computer cabinet, reattach the power cord, then continue withConnecting External Devices on page 34.
Connecting Disk Drives to Your Controllers
You can connect SAS disk drives, SATA disk drives, and SATA and SAS Solid State Drives (SSDs) to your Adaptec RAID controller. (Seewww.adaptec.com/compatibilityfor a list of compatible drives.) There are no jumpers or switches to set before installation.
If you plan to build a bootable array, ensure that you install at least the minimum number disk drives required to support the RAID level you want. SeeChoosing a RAID Levelon page 25 for more information.
Note: Although you can connect both SAS and SATA disk drives to your SAS controller, we recommend that you do not combine SAS and SATA disk drives within the same array. SeeWhat is SAS?on page 62 for more information.
You have two connection options:
• To connect directly to the controller, see the following section.
• To connect to a backplane, seeConnecting Drives to a System Backplaneon page 33.
To connect Solid State Drives to your controller, seeConnecting Solid State Drives (SSDs) on page 33.
Connecting Drives Directly to the Controller
In a direct-attach connection, SAS or SATA disk drives are connected directly to a SAS card with SAS cables. The number of direct-attached disk drives is limited to four per internal SAS connector. (For more information about direct-attach connections, seeHow are Disk Drives Identified in SAS? on page 64.)
1. Install your internal SAS or SATA disk drives, following the instructions in your system's documentation. 2. Use internal mini-SAS HD cables to attach the disk drives to the controller, as required.
3. When all internal disk drives have been installed and attached to the controller, close your computer cabinet, reattach the power cord, then continue withConnecting External Devices on page 34.
Connecting Drives to a System Backplane
In a backplane connection, disk drives and SAS cards are attached to and communicate with each other through a system backplane.
The number of disk drives is limited to the number of slots available on the backplane. Some backplanes have embedded SAS expanders and can support up to 128 end devices. (For more information about backplane and expander connections, seeHow are Disk Drives Identified in SAS? on page 64.) 1. Connect one or more internal SAS or SATA disk drives to the backplane. (Refer to your system's
documentation for more information.)
2. Use an internal mini-SAS HD cable to connect the controller to the backplane, as required. 3. When all internal disk drives have been installed and connected, close your computer cabinet,
reattach the power cord, then continue withConnecting External Devices on page 34.
Connecting Solid State Drives (SSDs)
To connect a Solid State Drive to your controller, you can use a direct-attached connection or a backplane connection, as required. If your server does not have a standard 2.5-inch drive tray, you must use a bracket/SLED which enables the SSD to fit properly.
Note: For Adaptec maxCache applications or hybrid RAID arrays (comprised of hard drives and SSDs) you can use any Solid State Drive on the compatibility list. See www.adaptec.com/compatibilityfor a list of compatible SSDs. Adaptec maxCache is supported on Adaptec Series Q controllers only.
In a direct-attach connection (described in the steps below), you connect SSDs directly to the controller with SAS cables (mini-SAS to SATA). In a backplane connection, use the appropriate cable for your backplane type (seeConnecting Drives to a System Backplaneon page 33 for more about backplane connections). For maxCache caching applications, you can connect a maximum of 8 maxCache-compatible SSDs to a controller. For RAID arrays, Adaptec controllers support a maximum of 256 drives, including SSDs (for details, seeAbout Your RAID Controlleron page 17).
1. Install the SSDs in your server. For servers with a standard 2.5-inch drive tray, install the SSD directly into the tray. If your server does not have a standard 2.5-inch drive tray, use a bracket or adapter which enables it to fit properly.
Use a 2.5” to 3.5” adapter to install your SSD if server does not have 2.5” tray.
Typical SSD installation
2. Use an internal mini-SAS HD to SATA cable, as required, to attach the SSD(s) to the controller, as shown in the example below.
To other SSDs
SSD connected to controller with internal mini-SAS HD to SATA Fanout cable
Single-port connector Internal x4 mini-SAS HD connector
Use high-quality cables to connect your controller to your external device(s), such as disk drives or disk drive enclosures.
We recommend using only Adaptec cables. For more information about cabling options for your controller, seeCableson page 25.
Next Steps
If you are installing the controller driver and an operating system onto a bootable array, continue with Creating a Bootable Array on page 36.
If you are completing a standard installation onto an existing operating system, continue withInstalling the Driver on an Existing Operating System on page 52.
6
Creating a Bootable Array
This chapter explains how to set your Adaptec controller to be the boot controller, and how to create a bootable array.
Note: If you are completing a standard installation onto an existing operating system, you don’t have to complete this task. Skip toInstalling the Driver on an Existing Operating System on page 52.
Setting the Boot Controller
Note: If your system won’t contain more than one bootable controller, skip to the next section,Creating an Arrayon page 36.
Your Adaptec RAID controller supports bootable disk drives and bootable arrays. To enable your system to boot from either a disk drive or an array connected to your controller:
1. Enter the system setup.
2. Navigate to the drive boot sequence.
3. Move the boot controller to the top of the list.
For more information, refer to your computer documentation.
Creating an Array
This section explains how to create an array.
A RAID 5 array is created in the examples shown in this section because RAID 5 provides the most security and best performance with a minimum of three disk drives. However, you can choose to create an array with a different RAID level; you can also change array level later, after the operating system is installed. You can create an array using any of these tools:
• Adaptec RAID Configuration Utility (ARC)—BIOS-based menus and keyboard navigation (see the following section).
• maxView Storage Manager—Graphical software application (running from a bootable installation DVD) that you can navigate with your mouse (seeAbout maxView Storage Manageron page 57). • ARCCONF—Command line utility. For instructions, refer to the Adaptec RAID Controller Command
Line Utility User’s Guide.
You can use any of these tools, but the ARC utility is the quickest and easiest tool for this task. Note: We recommend that you do not combine SAS and SATA disk drives within the same array. maxView Storage Manager displays a warning if you try to create a logical drive using a combination of SAS and SATA disk drives. SeeWhat is SAS?on page 62 for more information.
Creating an Array with the ARC Utility
The ARC utility is menu-based. Instructions for completing tasks appear on-screen. Menus can be navigated using the arrows, Enter, Esc, and other keys on your keyboard.
To create a RAID 5 array:
1. Power on your computer. When prompted, pressCtrl+Ato enter the ARC utility.
Note: On servers that support the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, or uEFI, ARC utility options are presented with a uEFI/HII interface rather than the Adaptec
3. Select Logical Device Configuration, then pressEnter.
4. Select Initialize Drives, then pressEnter.
5. Select at least three disk drives for the array, pressInsertfor each selected disk drive, then press Enter.
Caution: During initialization, all data is deleted from the disk. Before continuing, back up any data you want to keep.
6. PressY, then pressEnter.
The selected disk drives are initialized, then the Logical Device Configuration screen appears. 7. Select Create Array, then pressEnter.
8. Select the disk drives that were just initialized, pressInsertfor each selected disk drive, then press Enter.
9. When the Array Properties screen opens, follow the instructions in the following table. Entry or Selection
Property Line
Select RAID 5, then pressEnter.
Array Type
Type a name, then pressEnter.
Array Label
PressEnter, then pressEnteragain to use the default granularity of GB. Array Size
PressEnterto use the default (256 KB).
Stripe Size
PressEnterto use the default (Enable).
Read Caching
PressEnterto use the default (Enable always), then pressYto confirm.
Write Caching
PressEnterto use the default (Build/Verify). Create RAID via
PressEnterto use the default (Enable)
MaxCache Read
PressEnterto use the default (Disable)
MaxCache Write
PressEnter.
[Done]
10. When a cache warning message displays, typeY.
11. Once the array is created, a message displays telling you that the array can now be used. Press any key to return to the Logical Device Configuration menu.
You can start using the array immediately. However, performance is reduced until the build process is complete.
12. PressEscuntil the Exit utility window appears.
13. SelectYes, then pressEnter. The computer restarts.
14. Continue withMaking Your Array Bootableon page 39.
Creating an Array with maxView Storage Manager
This section describes how to use the maxView Storage Manager configuration wizard to build an array. Note: You will need the Adaptec Installation DVD to complete this task.
To create a RAID 5 array:
1. Insert the Adaptec Installation DVD into your DVD drive, then restart your computer. 2. When prompted, select the language you want, then pressEnter.
3. Review the license information, then pressEnter.
The DVD main menu opens. 4. Click Launch Configuration Utility .
maxView Storage Manager opens.
5. On the ribbon, in the Logical Disk group, click Create Logical Drive.
6. When the wizard opens, ensure that Express Configuration is selected, then click Next.
7. Review the logical drive configuration summary.
maxView Storage Manager uses the term logical drive when referring to an array (seeTerminology Used in this Guideon page 14).
8. Click Finish.
maxView Storage Manager builds the logical drives. 9. Partition and format your logical drive.
The logical drives you created appear as a physical disk drives on your operating system. You must partition and format these logical drives before you can use them to store data.
10. Close all windows, then click Reboot to restart your system. 11. Remove the Adaptec Installation DVD.
For information on installing and using maxView Storage Manager as a full software application, refer to the maxView Storage Manager User's Guide.
12. Continue with the following section.
Making Your Array Bootable
Use the ARC Utility to make the array bootable (seeCreating Bootable Arrayson page 75). Then continue withInstalling the Driver and an Operating System on page 40.
7
Installing the Driver and an Operating System
This chapter explains how to install your Adaptec RAID controller driver and an operating system on a bootable array (seeCreating a Bootable Array on page 36).
To install the driver on an existing operating system, seeInstalling the Driver on an Existing Operating System on page 52.
Before You Begin
• Install and connect your Adaptec RAID controller and internal disk drives (seeInstalling the Controller and Disk Driveson page 29).
• Create a bootable array (seeCreating a Bootable Array on page 36). • Create a driver disk (see the following section).
Note: For up-to-date operating system version support, visit the Adaptec Web Site atwww.adaptec.com. From the main menu select Support>Knowledgebase>Find Answers. Select your controller type and OS to generate a list of supported operating systems and to download the latest drivers.
Creating a Driver Disk
This section describes how to create a driver disk for the operating systems that require one. You will need a USB flash drive or writable CD to complete this task.
• Windows operating systems do not require a driver disk. For Windows, the driver is loaded directly from the Adaptec Installation DVD; seeInstalling with Windows on page 42.
• For Debian Linux, Ubuntu Linux, and VMware ESX 4.1, you must create the driver disk manually on a USB flash drive (“USB stick”) or writable CD. See the instructions for your operating system, below. • For Red Hat 6 and Cent OS 6 DKMS driver installation, seeRed Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6 with Dynamic
Kernel Module Support on page 42.
• For VMware ESXi 5.x, seeInstalling with VMware ESXi 5.x on page 48. • For Citrix XenServer, seeInstalling with Citrix XenServer on page 51.
• For all other OSs, create the driver disk using the Create Diskette menu on the Adaptec Installation DVD.
To create a driver disk using the Create Diskette menu:
1. Set your system BIOS so that your computer boots from the DVD drive. 2. Turn on your computer, then insert the Adaptec Installation DVD. 3. Click Create Diskette, then select your operating system and version. 4. When prompted, insert a USB flash drive, then click OK.
The system creates the driver disk on the USB drive. 5. Remove and label the driver disk.
6. Continue with the instructions for your operating system:
• For Red Hat Linux 5 or Cent OS 5, seeInstalling with Red Hat Linux 5 or Cent OS 5 on page 42. • For Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6, or Fedora Linux, seeRed Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6, Fedora Linux
without Dynamic Kernel Module Support on page 43.
• For SuSE Linux, seeInstalling with SuSE Linux Enterprise Server on page 44. • For Solaris, seeInstalling with Solarison page 46.
Creating a Driver Disk for Debian Linux or Ubuntu Linux
Note: You will need the Adaptec Installation DVD and a USB flash drive to complete this task.
To create a driver disk for Debian or Ubuntu Linux: 1. Insert and mount the Adaptec Installation DVD:
mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
2. Insert and mount a USB flash drive:
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/aacraid-driver
3. Change to the Linux driver directory on the Adaptec Installation DVD, locate the .tgz archive file for your Debian or Ubuntu operating system version (32-bit or 64-bit), then extract the contents of the archive to a temporary location.
4. Copy the contents of the archive to the USB drive by typing this command:
cp /<tempdir>/* /mnt/aacraid-driver
where tempdir is the temporary location of the driver files. 5. Unmount and remove the Adaptec Installation DVD and USB drive.
6. Continue withInstalling with Debian Linuxon page 44 orInstalling with Ubuntu Linuxon page 45.
Creating a Driver Disk for VMware ESX 4.1
Note: You will need the Adaptec Installation DVD and a writeable CD to complete this task.
To create a driver disk for VMware ESX 4.1: 1. Insert and mount the Adaptec Installation DVD:
mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
2. Insert and mount a writable CD:
mount /dev/cdrom1 /mnt/cdrom1
3. Change to the Linux driver directory on the Adaptec Installation DVD, locate the VMware iso image,
vmware-aacraid-400.4.2.1.xxxxx-esx4.1.iso(where xxxxx is the build number), then burn
the iso to the CD.
Note: Use whatever tool you prefer to burn the CD, such as an interactive (GUI-based) tool or the Linux command line.
4. Unmount and remove the Adaptec Installation DVD and CD drive. 5. Continue withInstalling with VMware ESX 4.1 on page 47.
Installing with Windows
Note: The following instructions apply to all supported Windows operating systems. You will need your Windows Installation CD to complete this task.
To install the Adaptec RAID controller driver while installing Windows: 1. Insert your Windows CD, then restart the computer.
2. Follow the on-screen instructions to begin the Windows installation. 3. When prompted to specify a location for Windows, select Load Driver.
4. Insert the Adaptec Installation DVD, browse to the driver location, then click OK. The 64-Bit driver is located within the AMD64 folder.
5. When the Adaptec driver is found, press Next.
You may see the message ‘No drives were found’. RepeatStep 3,Step 4(browse to driver location), andStep 5. On the second attempt, the driver will load successfully.
6. Click Next again to accept the default partition configuration, or refer to your Windows documentation to configure partitions manually.
7. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. 8. Continue withManaging Your Storage Spaceon page 57.
Installing with Red Hat Linux 5 or Cent OS 5
Note: You will need the installation CD for your operating system to complete this task.
To install the Adaptec RAID controller driver while installing Red Hat Linux 5 or Cent OS 5: 1. Insert your installation CD.
2. Restart your computer.
3. When the first installation screen appears, insert the USB driver disk. 4. Type this command at the Boot: prompt and pressEnter:
linux dd
5. Select Yes to indicate that you have a driver disk, then select the driver image from the USB drive (typically,/dev/sda1).
6. Complete the Linux installation, following the on-screen instructions. 7. Continue withManaging Your Storage Spaceon page 57.
Installing with Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6, or Fedora Linux
Follow the instructions in this section to install the controller driver with Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6, or Fedora Linux. We recommend that you install the driver with Dynamic Kernel Module Support, or DKMS. DKMS ensures that the driver remains installed across OS or online updates. The DKMS instructions are valid for Red Hat 6 and Cent OS 6 only.
Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6 with Dynamic Kernel Module Support
Note: You will need your OS installation CD and a USB flash drive to complete this task. You must have root privileges to install the driver image.
4. Make sure that "Install a new system or upgrade an existing system" is highlighted, then, at the end of the "vmlinuz initrd=initrd.img" line pressSpace, type the following command, and pressEnter: linux dd
5. Select Yes to indicate that you have a driver disk, then select the driver image from the USB drive (typically,/dev/sda1).
6. Complete the Linux installation, following the on-screen instructions, then reboot.
7. Assuming the USB driver disk is/dev/sda1, type the following commands to ensure that the driver
remains installed when you update the OS:
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
cp /mnt/aacraid.conf /etc/depmod.d/aacraid.conf
8. Continue withManaging Your Storage Spaceon page 57.
Red Hat Linux 6, Cent OS 6, Fedora Linux without Dynamic Kernel Module Support
Note: You will need the Installation CD for your operating system to complete thistask. You must have root privileges to install the driver image.
To install the Adaptec RAID controller driver while installing Red Hat 6, Cent OS 6, or Fedora Linux: 1. Insert your installation CD.
2. Restart your computer.
3. When the Welcome screen appears, pressEnterat the boot prompt, typeCTRL+ALT+F2to switch
to the shell, then continue the installation by selecting your language and keyboard. 4. Insert the USB driver disk.
5. Assuming the USB drive is assigned to/dev/sda1, type the following commands to load the controller driver: mkdir /mnt2 /AACRAID mount /dev/sda1 /mnt2 cp -r /mnt2/* /AACRAID umount /mnt2 cd /AACRAID sh ./fc-pre-install.sh
6. PressALT+F6to switch back to the installation screen, then click Next.
7. Follow the on-screen prompts to continue the installation. When prompted to reboot the system, pressCTRL+ALT+F2to switch to the console. Do not reboot before completing Step8!
8. Type the following commands to complete the driver installation:
mkdir /mnt/sysimage/tmp/AACRAID cp -r /AACRAID/* /mnt/sysimage/tmp/AACRAID chroot /mnt/sysimage/ cd /tmp/AACRAID sh ./fc-post-install.sh exit
9. PressALT+F6to switch back to the installation screen, finish the installation, then reboot.