On the link between real exchange rate misalignment and growth: theory and empirical evidence
Full text
Figure


Related documents
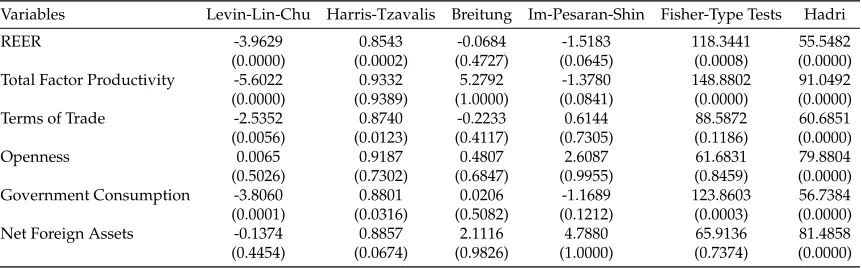
(2001) also known as the Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) approach has been applied in this study to detect the presence of any long run equilibrium relationships among
To compute our theory-based measure of a RER misalignment, we first obtain a long-run RER equation from a theoretical model that considers the equilibrium real exchange
The effects of a permanent increase in inflows of workers’ remittances on a country’s long-run equilibrium real exchange rate would appear to be rather straightforward: thinking of
The dynamic general equilibrium model with endogenous productivity dynamics is presented in section 3, and section 4 investigates the impact of the 1970s resource boom on the
and Nishat, M (2006), found in their study that the volatility of exchange rate had a negative and significant effect both in the long run and short run with UK, US,
NEER is the Nominal Effective Exchange Rate, P dt is the price level in Kenya proxied by Consumer Price Index (CPI) at time t, and P wt is the weighted average
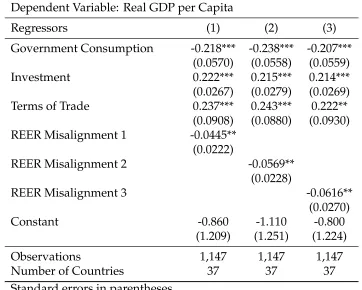
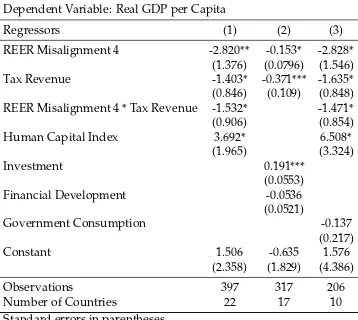
Our empirical estimation of the System GMM panel growth model has shown that estimated coeffi cient for RER misalignment is negative and statistically signifi cant, which means that
The results revealed that in both short-run and long-run, exports and imports were chiefly influenced by real exchange rate, real exchange rate volatility, foreign income,