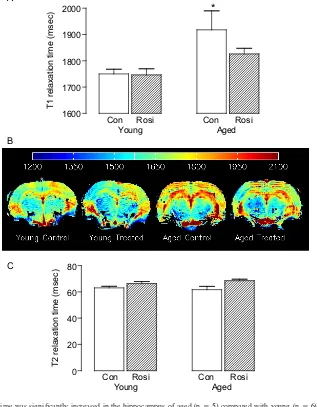
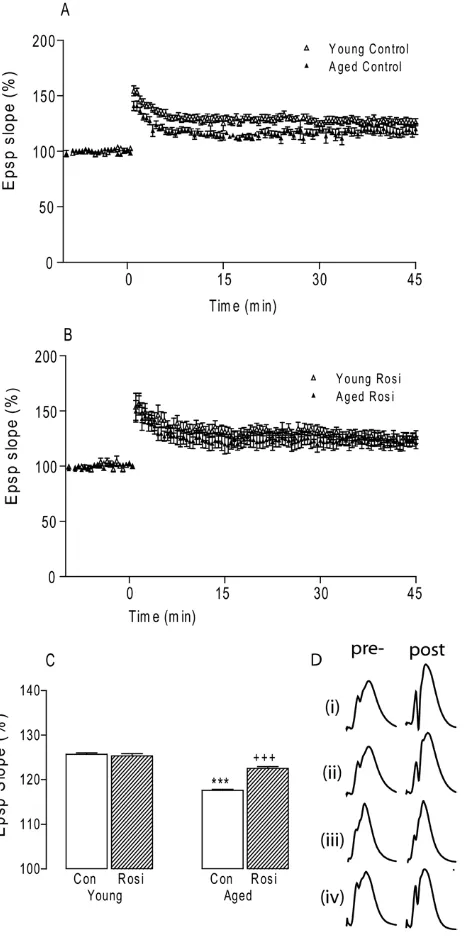
Rosiglitazone attenuates the age related changes in astrocytosis and the deficit in LTP
14
0
0
Full text
Figure


+4
Related documents
Relative to HRT continuers, discontinuers aged 85 and older experienced apparent HRQOL improvements following cessation, with fewer days in which physical health was not good (p
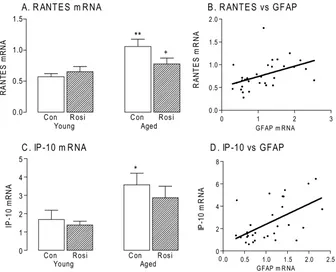
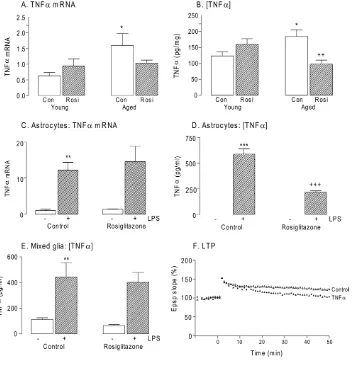
Similarly the significant age-related increases in CD11b and MHCII, and the chemokines, MCP-1 and IP-10 (p < 0.01 or p < 0.001; ANOVA; Figure 3D-G), which are chemotactic for
MnSOD activity in the liver and brain mitochondria of aged animals was significantly higher compared to the values obtained from young rats (p<0.05 and 0.001,