Human Factor Based Leadership: Critical Leadership Tools to Reduce Burnout and Latent Error in a Time of Accelerating Change
Full text
Figure
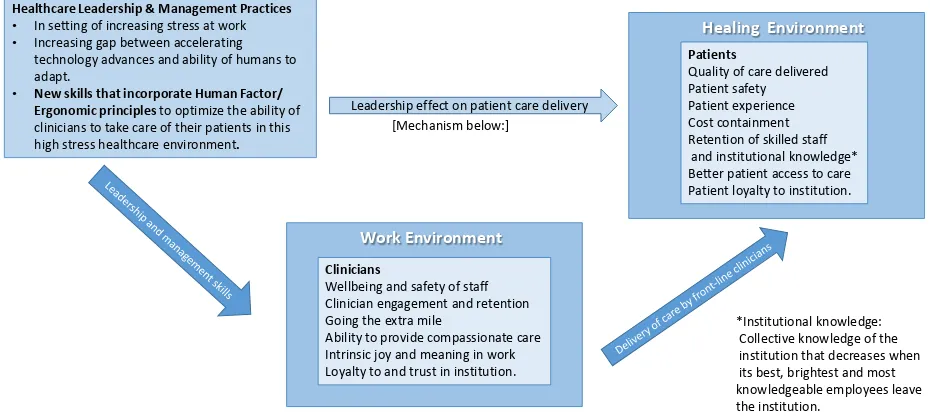


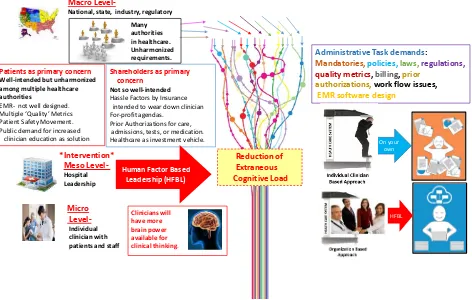
Related documents
They would not only become aware of their own inner strengths and characteristics (Seligman et al., 2009), but they would also feel the use of true partnership of the family
Components of the groundwater budget that represent annual flowrates of groundwater recharge and discharge under steady-state conditions are determined based on the model
In Georgia, net sales in local currency decreased by 1.2 percent, equivalent of SEK 203 million (215), with positive effects from recently introduced equipment sales, but contin-
a finite ring with identity, any zero divisor is a two-sided zero divisor and every element that is not a zero divisor is invertible (see Ganesan [ 2, Theorem 5, p.245 ] ).. A
The purpose of this thesis is to analyze the retention behavior of immediate graduate education program participants, specifically USNA graduates who participated in the VGEP
For this comparison, discount stores were separately compared to grocery and corner stores, as opposed to being combined with corner stores to be labeled convenience stores
The full scale score on the WISC test for the entire population group correlated with birth weight at the 10% confidence level (correlation coefficient: 0.230; p < 0.1).
Prognostic Significance of Combination of Preoperative Platelet Count and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (COP- NLR) in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Based on a Large