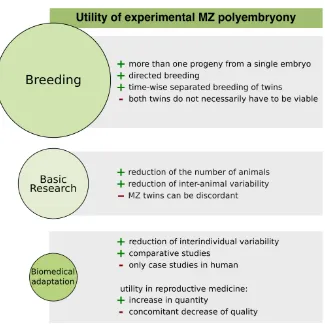
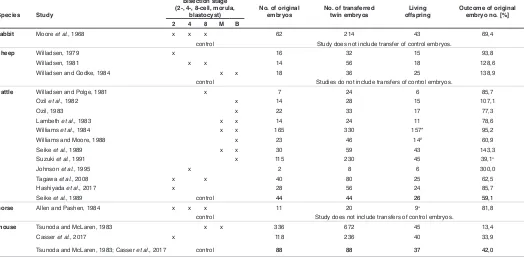
Multiplying embryos: experimental monozygotic polyembryony in mammals and its uses
Full text
Figure



Related documents
This paper presents the results of a pilot project which demonstrated that near real-time Extract, Transform and Load (ETL), using conventional ETL process with Change Data
The results show that total wheat output in the region increased at an annual rate of about 2.97 percent—84 percent (i.e., 2.49) of this growth is shared by the growth in barani
The RMS area, sway path length, ML mean vel- ocity and AP mean velocity at baseline and during stimulation were compared by two-way mixed-design analysis of variance (ANOVA),
944 Pair of late Victorian carved oak hall or dining chairs on cross stretcher bases with green upholstered seats and back pads. Estimate £40
If you would like to make sure that the representative is working on ScottishPower’s behalf, take a note of the staff reference number and telephone number on the caller’s ID
The AFRP aims to restore 15 million hectares of degraded lands in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest biome by 2050 and increase the current forest cover of the biome from 17% to at
cholamidopropyl) dimethylammonio)-1-propanesulfonate; CIPI: Cellulose- binding protein; CMC: Carboxymethyl cellulose; CMCase: Activity on carboxymethyl cellulose; CMM: Cane