Online Course Design Model:Literature Review
Chien-Jen LiuAssistant Professor, Department of Information Management, Kao Yuan University Candidate for PhD, Graduate Institute of Education, National Sun Yat-sen University
cjliu@cc.kyu.edu.tw
Abstract
Most university teachers who set up distance courses online just digitalize the traditional teaching materials, without integrating the design of instructional activity and interactive discussion. From the past research results, we found the drop of theory and practice. In general, theoretical researches all point out the importance of course design model and the elements included in the model. On the actual situation, however, there is difficulty for the teachers to design online courses with adopting the instructional design model. While reviewing from the literature, we find that the scholars have already begun to develop a simplifying conceptual model. This model will help the novice designers to take on the heavy responsibility of course design. This article examines the literature about online course design, inducing it as 2 types, pedagogy-based model and course-based model. Pedagogy-based model is to develop model from instructional design, but greatly parts of university teachers are not familiar with pedagogy relatively. So if the model can be developed from course, which is concrete and feasible, matching technology tool, there would be larger help for practitioner teachers. The course-based model is mainly focused on the design of online activities. This model can be cooperated with teachers’ experiences in the real classroom. It can provide help while using technology tools to design the learning activities of real classroom in the instructional platform or the related environment. Key Words:online course, online activity, e-learning, novice designer, course design
1.
Introduction
With the impact of education of information technology, international communities regard "information integration teaching" as the important indicator of competition ability, so each university in Taiwan also expands e-learning actively, and completes every kind of establishment of instructional platform under the government decided policy. The Ministry of Education regards the executive result of e-learning as one of important assessment work. Therefore, all kinds of reward measure come forth one after another for encouraging teachers design e-learning content. Under such trend, University teachers also join the group of digital teaching constantly. .
But there is one myth, that is school authorities and greatly parts of teachers think: As long as can digitalize the teaching material, then put to the platform that it is a e-learning. Therefore, they usually use streaming software to record teaching material of having the voice or image. It becomes the basic condition that opens an online course. Further for understanding whether the digital teaching materials have already reached certain quality or not, so the school authorities carry on the assessment of digital teaching material. They establish digital standard and principle of e-learning content, according to content quality good and bad to give different reward.
Li and Akins (2005) point out the higher education carries on the myth that the online teaching has four types totally, including content, context, strategy and assessment. Among them, the myth of content has two: The first, we can duplicate a traditional course become an online course directly; the second, online course is only equal to a teaching material content. These two myths respond currently the general idea of online teaching in university. The first, the course for conducting in traditional real classroom, as long as the completion satisfies the hours of audio and video of teaching material, it can place the teaching material into learning platform to set up an online course; The second, teachers and students think online learning is that reading a teaching material content . So the school regards the content as a focus of quality assessment of digital teaching. But most of teachers are limited to the time and technology ability, they can only make slides of text teaching material, combining voice or image to explain the teaching material content as far as possible for reaching assessment standard of school authorities.
When we remember the scenario of real classroom has a class, will find although the teaching material is a point of course, in addition to teaching material, also include instructional guide, instructional strategy, exercises homework and the interaction activity etc.. So when we set up a e-course, in addition to teaching material content,
should have to also present abundant media, instructional design, instructional guide etc.. Certainly more of interactive design is the point that the e-teaching material designs. Nevertheless, but it is a difficult work apparently for trying to integrate the instructional strategy at the real classroom into the teaching material. Because teachers in the universities are often busy at the research and teaching(Weaver, Robbie & Borland, 2008), the assessment standard of teaching material apparently can't run in the universities.
The content of lacking instructional design can only say to be a digitized teaching material, so it can't be called online course. Therefore, there are scholars put forward a related research continuously-- how to integrate the instructional activities and discussion at traditional real classroom with online teaching by using suitable for university's teachers' way. And teachers having technology knowledge that the online course designs is also valued increasingly (Angeli & Valanides,2009; Weaver, Robbie & Borland, 2008). The main purpose of these researches is hopes and can provide a simplifying, practical model to provide a practitioner’s basis of designing e-course. Consequently, this article examines the evolution of online teaching model first, compiling immediately after what scholar put forward online course to design model with discussion, inducing a fitter university teacher finally of digital course design model.
2. The evolution of e-learning model
From the findings of the past research, e-learning has already had some typical model, including Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) in common, which is from the user to accept the degree of technology to analyze the influence of technology on teaching. Besides, the Information Communication Technology (ICT) is also a familiar model. The above two models are often quoted while studying e-learning(Kim, Jung & Lee, 2008;Senteni, 2006;Sue, 2008;Wang, 2008).
Meredith and Newton(2003) once explore the related literature that the e-learning designs, from two views to see the design of e-learning. They are “technology promise” and “learner needs”, and induce two types of models which contribute to understanding this subject, include: heuristic development model and convergence model. The former is through practice; carry on learning in the continuous exploration, experiment and the trial mistake. The latter thinks the e-learning design needing to be the integration of technology, learner ability and pedagogy. And the Technology-Mediated Learning (TML) is a model to see the technological impact on learning, think related factor about the result of e-learning in addition to technology, also need to consider learner to
would have different mental learning process under the influence of pedagogy (Alavi & Leidner, 2001).
Some scholars designed e-learning from learning, having some to take pedagogy as foundation to design, but producing to take course as to design basally from the practitioner’s model. Bradley and Oliver (2002) outline four pedagogic models that were adopted and how they evolved as the development:
I. Model one, flexibile learning:
Include open learning (OL), computer based learning (CBL) and work based learning (WBL).
II. Model two, socio-constructivist learning:
According to similar have a conversation interaction learning structure in the Laurillard (1993), the learners can dialogue and discuss each other actively, through learning activity design, self assessment and peers assessment.
III.Model three, Experiential learning:
Design online material according to the Kolb(1984) learning circle, the teaching material musts be to take concrete experience of the job field as starting point, knowing to do link to become concept, and encourage to participate through the activity through experience and the new information, problem discussion, evaluate by one's own and homework to make to introspect observation, then promote its working experience and actual situation applied.
IV.Model four, pragmatic synthesis:
We can integrate any kind of above-mentioned model, the teacher places teaching material on the instructional platform in general, and guides learning. The teaching material will be separated smaller component, the basis actual delivery system does to design, the online activity matches with a teaching material content to design, learner oneself can arrange learning path to construct personal learning portfolio.
Besides the Mason (1998) is in the eyes of the online course design model, and induce to 4 types:
I. Model one, Content+ Support Model:
Pack teaching material good apposition in the web page, guide to carry on a learning through the teacher, the tool canning support includes E-mail or computer conference etc..
II. Model two, Wrap Around Model
Usually pack some teaching materials which have already existed, become contents such as the learning guide, activity and discussion etc., in advance schedule to of the teaching materials have half of learning time, another half is interaction and discussion, the roles of teacher or instructor than the first model more extensive, because greatly part of course contents are in advance the interaction and the discussion which came from and don't schedule to. III.Model three, Integrated Model:
Include cooperative activity, learning resource and related homework, discuss, access and processing the information also complete task. The ones that are totally different from model one are that the course content comes from personal and the activity of team, so usually is fluctuant. This model breaks the differentiation of content and support, mainly is the construction that the basis learning community.
The above e-learning models are induced according to the pedagogy or the course. We can find that learner-centered design is a trend. This model let learner oneself can control learning progress and establishment to learning portfolio. Its importance to reduce increasingly in advance fixed teaching material and the resource, changing to become the reference which supports task or discussion, in the middle of learning mission and activity let learning clubs to carry on team learning etc. This article's connecting down to explore is an online course design relevant of model development, including: according to the design model of pedagogy, and according to the design model of course, the so-called ‘course’ means valid teaching content, and the ‘pedagogy’ means effective strategy of delivering the teaching content.
3. The pedagogy-based design model
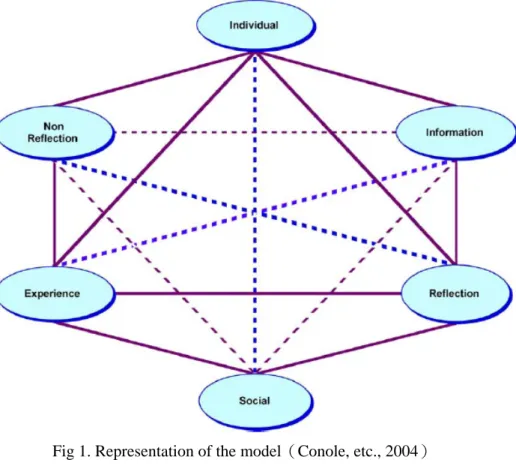
Conole etc.(2004) propose a model for learning which articulates the key components of existing learning theories, displays their inter-relationships and offers a means of mapping them against each other. This methodological approach consisted of the following five stages:
1. Reviewing learning theories
2. Identifying common characteristics across different learning theories. 3. Building a model using these characteristics.
5. Applying and testing that model, and developing a learning design toolkit for mapping learning theories to learning activities, related tools and resources. This model consists of the following six components (Fig. 1):
Individual – Where the individual is the focus of learning.
Social – learning is explained through interaction with others, through discourse and collaboration and wider social context within which the learning takes place.
Reflection – Where conscious reflection on experience is the basis by which experience is transformed inti learning.
Non-reflection – Where learning is explained with reference to processes such as conditioning, preconscious learning, skills learning and memorization. Information – Where an external body of information such text, artefacts and
bodies of knowledge from the basis of experience and the raw material for learning.
Experience – Where learning arises through direct experience , activity and practical application.
The Conole etc. think it is useful to help practitioner’s teachers to understand the technology original ability. They propose a model to lead how use and integrate different learning technology to enhance learning performance. So, the toolkit thus focus on eliciting actual practice, rather than on prescribing correct solutions. Therefore, Conole and Oliver (2002) suggest the following five steps:
I. Review of a current course structure.
II. Analysis of the course to identify areas of learning that could be supported more effectively.
III. Comparison of different teaching techniques, in order to select those that seem to address areas of weakness in the course.
IV. Comparison of different course formats. V. Specification of the final course format.
The above is the represents a linear process. The learning design toolkit that Conole propose consists of the following stages:
I. Outlining the overall learning activity and associated learning outcomes. II. Listing potential mini-activities.
III.Outlining the contextual details in terms of resources and constraints. IV.Mapping mini-activities to potential tools and resources.
V. Selecting mini-activities and tools and resources based on their contribution to the overall pedagogic theory.
VI.Planning of the actually learning activity.
Conole etc. aim at the model that it puts forward, suggesting the future research can investigate this model latent ability and limit, and can inquire into personal standpoint, culture and academics difference etc. related factor impact particularly. Future investigation have to focus on different standpoint and comprehend to the different type for carrying on model expression, and understand this model whether have flexibility and apply in the different advantage.
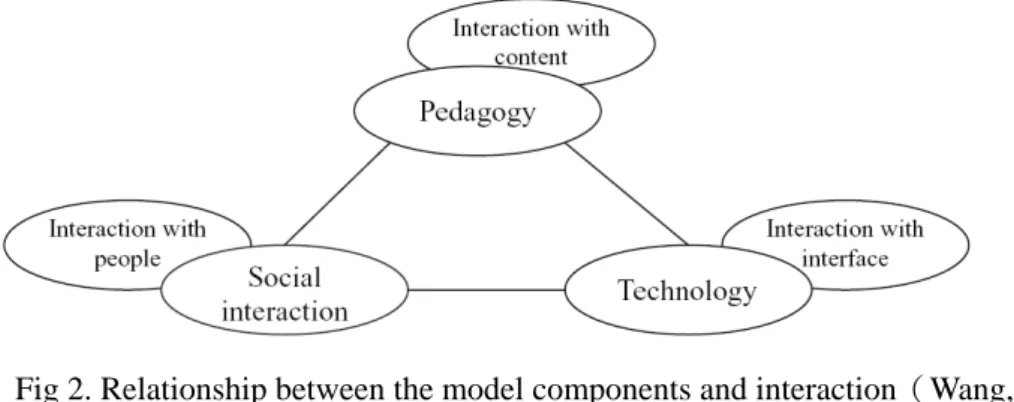
Besides Wang's (2008) thinking to integrate the ICT to the teaching is a teacher important ability. The teacher does not adopt linear process to design course, so he proposes a generic model, which consists of three elements: pedagogy, social interaction and technology.
constructivism suggests the learning should be constructed meaningful knowledge by collaborative learning. As a practical guideline, the model consists of three types of interaction: learner-content, learner-interface and learner-people (including learner- instructor, learner- learner). The Relationship between the model components and interaction is showed at Fig 2.
Fig 2. Relationship between the model components and interaction(Wang, 2008)
It is very different between Wang and Conole’s model. Wang lists as an element of the e-learning model of "society interaction" directly. Generally, it is a familiar standpoint for e-learning to make the society interaction listing as the foundation directly while carrying on instructional design. It is belong to an ideal model. The model which is unlike Conole is tendency the instructional theories which consider teacher's adoption and course structure. This kind of design is relatively nearing a teaching practice, which aims at an online activity directly, and does link with related tool, resource, but the key is whether there are information tools and environments that are supported.
4. The course-based design model
Carr-Chellman and Duchastel (2000) are based their experience on distance learning and network course design, trying to distinguish the factor that must be considered for an ideal online course. They point out the whole online course has to include two elements: content and technology. The namely basic instructional design element of the content element, such as teaching target and other traditional instructional designs; Another is technology element, that is used to a course infrastructure of supporting learning, such as the audio conference, network discussion room, web page etc.. All articles which discuss online course model development observe practitioner teachers, who possess the cognition and prepare skill for opening online course. That is, the general teacher can hardly go deep into understanding information technology and can provide teaching what benefit, and technology development rapidly very much, let the practical teacher can't control. But university teachers set up online course increase
gradually, so teacher absolutely can't just content expert, also must be course design and development. Otherwise, they think teaching material narrowly to be a course, with the result that online course only present static information, and without valid method and usage of tool which delivers information (Weaver, Robbie & Borland, 2008) .
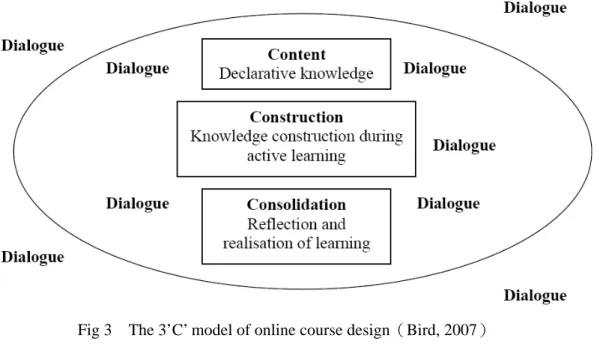
Bird (2007) aims at most university teachers systematically first rather than the technology user of earlier period to develop an online course design model. This model proposes a tool for novice designers. The key strength is that applies simply and easily. Its simplicity springs from an extensive application of pedagogy theoretical thinking on the networked collaborative e-learning. His paper builds on the work of Flower and Mayes (2000) by examining the basic theory. This conceptual model is called "3 Cs" course design model, including three design ingredients, as Fig3:
Content: consists of the declarative knowledge associated with the course. Construction: refers to the social construction of knowledge that occurs whilst
students engaged on authentic learning activities.
Consolidation: encompasses the reflective process by which learners develop new understandings and appreciations of the learning they have just realized.
Fig 3 The 3’C’ model of online course design(Bird, 2007)
The key point of the design model lies in social interaction between learners, including dialogue and discussion. The type of dialogue surrounding each ‘C’ is likely to be different, and the discussion surrounding the content is likely to be between learners as they determine what knowledge is required for the learning activities. The knowledge construction stage requires a dialogical interchange between learners or teachers as they
consider different interpretations of the issues. On the other hand, consolidation can be facilitated by private and public reflection via conversations both with oneself and with other learners or teachers(Bird, 2007).
5. Conclusion
The purpose of e-learning model development is for providing the basis of course and instructional design. The past trend of research is based on traditional instructional theories to identify whether such online teaching have rationality and usefulness or not. Although there is the development of model, overly idealize. That ideal model supposes carry on the persons of online teaching are all technological earlier period users, neglected practical context and relation between the teachers and students. And we also find to develop model from the standpoint of teaching to be a familiar way. The performance of online learning and instructional design are vitally related. It has become a trend according to instructional design to develop model, but university teachers is not familiar with pedagogy relatively.
Setting up an online course in the university, the non- information teacher has to face the problem of lacking technical ability, and non-education teacher can't even control teaching ability. Therefore, while reviewing from the literature, we find scholars have already begun to develop a simplifying conceptual model. This model will be useful for novice designers can take on the heavy responsibility with course design. So if the model can be developed from course, which is concrete and feasible, matching technology tool, there would be larger help for practitioner’s teachers. This direction is the motive that the Bird (2007) develops the 3 ’C’ course design model.
From the above literature review, we observe there is a common point between these models, that is "know how to use existing tool to design an online course activity". To carry on dialogue and discussion in the activity with construction knowledge, it certainly can't be without pedagogy. That is we needn't overemphasize pedagogy to avoid the complication of the model. Without reinforcing pedagogy, don't mean it is not importance. Because the design of online activities oneself include instructional theories and pedagogical application, such of the actual situation process near more with the teacher's teaching. If the teacher can design a course step by step according to the 3 ‘C’ model, it is believed that online course to be just teaching material myth can be avoided; and the model can cooperate with the teacher's experience in the real classroom. While using technology tool to design the learning activities, it can merge the intension of pedagogy into e-course. In addition, if we can use online course design model to replace assessment standard of teaching material, the teachers would not always pay close attention to the content.
References
[1] Alavi, M. & Leidner, D. E. , “Research commentary: Technology-mediated learning---A call for greater depth and breadth of research.”, Information Systems Research, 12(1), 2-10. , 2001
[2] Angeli, C. & Valanides, N., “Epistemological and methodological issues for the conceptualization, development, and assessment of ICT–TPCK: Advances in technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPCK).”, Computers & Education, 52, 154-168. , 2009
[3] Bird, L. , “The 3 ‘C’ design model for networked collaborative e-learning: a tool for novice designers.”, Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 44(2), 153-167. , 2007
[4] Bradley, C. & Oliver, “M.. Developing e-learning courses for work-based
learning”, in: Proceedings of the 11th International World Wide Web Conference, Honolulu, HI, 7–11 May. Available online at:
http://www2002.org/CDROM/alternate/703/index.html (accessed 21 November 2008). ,2002
[5] Conole, G. & Oliver, “M.. Embedding theory into learning technology practice with toolkits”, Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 8. Available online at: http://www-jime.open.ac.uk/2002/8 (accessed 20 November 2008). ,2002
[6] Fowler, C. & Mayes, J. , “Learning relationships from theory to design, In D. Squires, G. Conole & G. Jacobs (Eds)”, The changing face of learning technology, 39–50. Cardiff:University of Wales Press. ,2000
[7] Carr-Chellman, A. & Duchastel, P. , “The ideal online course.”, British Journal of Educational Technology, 31(3), 229-241. , 2000
[8] Conole, G., Dyke, M., Oliver, M. & Seale, J. ,“Mapping pedagogy and tools for effective learning design.”, Computer & Education, 43, 17-33. , 2004
[9] Kim, J. H., Jung, S. Y. & Lee, W. G. , “Design of contents for ICT literacy in-service training of teachers in Korea.” ,Computers & Education, 51, 1683-1706. ,2008
[10] Kolb, “D.. Experiential learning: experience as a source of learning and development. Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Prentice Hall.” ,1984
[11] Laurillard, “D.. Rethinking university teaching. London: Routledge.” ,1993 [12] Li, Q. & Akins, M. , “Sixteen myths about online teaching and learning in higher
education: Don’t believe everything you hear.”, TechTrends, 49(4), 51-60. ,2005 [13] Mason, “R.. Models of online courses, in: L. Banks, C. Graebner & D.
McConnell (Eds)”,Networked lifelong learning: innovative approaches to education and training through the internet. Sheffield: University of Sheffield.
Available online at: http://www.aln.org/alnweb/magazine/vol2_issue2/Masonfinal.htm (accessed 20
November 2008). ,1998
[14] Meredith, S. & Newton, B., “Models of eLearning: Technology promise vs learner needs literature review.”, The International Journal of Management Education, 43-56. ,2003
[15] Weaver, D., Robbie, D. & Borland, R., “The practitioner’s model: designing a professional development program for online teaching.”, International Journal on E-learning, 7(4), 759-774. ,2008
[16] Senteni, A., “Information and Communications Technology Integration and Developmental Intervention: Enabling Knowledge Creation and Capacity
Building in Developing Countries’ Organizations.”, International Review, 300-311. ,2006
[17] Sue, K.- D., “An integrated science course designed with information communication technologies to enhance university students’ learning performance.”, Computer & Education, 51, 1365-1374. , 2008
[18] Wang, Q. “A generic model for guiding the integration of ICT into teaching and learning.”, Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 45(4), 411-419. ,2008
[19] Weaver, D., Robbie, D. & Borland, R., “The practitioner’s model: Designing a professional development program for online teaching.”, International Journal on E-Learning, 7(4), 759-774. , 2008