APPLICATION OF
COAGULATION-FLOCCULATION FOR VEGETABLE
TANNERY WASTEWATER
SMITA S. BORCHATE, DR. G. S. KULKARNI, S. V. KORE, V. S. KORE
Department of Environmental Science and Technology, Shivaji University, Kolhapur
Maharashtra, India Abstract
A coagulation-flocculation process is chemical treatment for water and industrial wastewater. This technology is used as primary treatments for removal of particulate matter and organic matter effectively. The process is very efficient in removal of total solids (TS), Total suspended solids (TSS), total dissolved solids (TDS) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) , Color .This technology is applicable in water treatment and also tannery, coffee, detergent, tar and dairy wastewater efficiently. This study shows applicability of coagulation-flocculation for raw vegetable tannery wastewater with PACl (Poly aluminum chloride) alone, also with coagulant aid removal TSS, COD and color. Coagulation- flocculation studies were performed in a conventional jar-test apparatus. The coagulant dosage of PACl ranged between 0 mg/L to 1000 mg/L, whereas the concentrations of polyelectrolyte varied between 5-100 mg/L. The optimal condition was obtained at the dosage 600 mg/L PACl at pH 4 with the TSS, COD and color removal efficiency of 45, 20 and 80%. Addition of coagulant aids provided higher removal efficiencies. Using coagulant aid at the dose of 65 mg/L with PACl provided 80, 42 and 89 % of TSS, COD and color removal. The maximum removal efficiency was obtained with the addition of polyelectrolyte and it was found that the PACl combination with coagulant aids, at certain pH and agitation speed, provided higher removal efficiencies compared to Coagulation with PACl alone. Key Words: coagulation-flocculation, raw vegetable tannery wastewater, PACl, polyelectrolyte.
1. Introduction
Industrial wastewaters are clarified to remove turbidity and color from different industries like the textile, paper, tannery and other polluting industries. In a water treatment chemical treatment that will remove color and turbidity present in raw water in the form of flocs. Coagulants neutralize the repulsive electrical charges (typically negative) surrounding particles allowing them to "stick together" creating flocks. Flocculants facilitate the agglomeration of the coagulated particles to form larger floccules and thereby hasten gravitational settling.
In wastewater treatment, coagulation and flocculation are employed to separate suspended solids from water. Although the terms coagulation and flocculation are often used interchangeably, or the single term "flocculation" is used to describe both; they are, in fact, two distinct processes. Finely dispersed solids (colloids) suspended in wastewaters are stabilized by negative electric charges on their surfaces, causing them to repel each other. Since this prevents these charged particles from colliding to form larger masses, called flocks, they do not settle. For removal of colloidal particles from suspension, chemical coagulation and flocculation are required. These processes, usually done in sequence, are a combination of physical and chemical procedures. Chemicals are mixed with wastewater to promote the aggregation of the suspended solids in to particles large enough to settle or be removed. Coagulation is the destabilization of colloids by neutralizing the forces that keep them apart. Cationic coagulants provide positive electric charges to reduce the negative charge (zeta potential) of the colloids. As a result, the particles collide to form larger particles (flocks).Rapid mixing is required to disperse the coagulant throughout the liquid.
As the chemical method helps to remove turbidity, color and chemical oxygen demand reduction. The present study is on the performance of coagulation and flocculation..An approach of this technology is made for Vegetable Tannery Wastewater.
can be relatively toxic to aquatic life, so Aygun A.et (2010) they carries Improvement of Coagulation-Flocculation Process for Treatment of Detergent Wastewaters Using Coagulant aids. coagulation flocculation also very effective in color removal in textile industry as wastewater treatments carried by Fsa et al., PeiWenWong et al (2007). Also varies study is carried for coagulation flocculation as a physical and chemical treatment for various industrial wastewater treatment [Amuda O.S. et al (2007),Roussy] for beverage and ink wastewater treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
The sample used for the experiment was raw vegetable tannery wastewater, collected from Malgaon, Miraj and Maharashtra. Wastewater sample collected from plant was placed in plastic container to be transported to the laboratory and stored at 40c in refrigerator. The raw wastewater characteristics are presented in table1.
Table 1. Characteristics of raw vegetable tannery wastewater
Parameters Range Mean
pH 4-5 4.5
Conductivity(ms/cm) 9.5-41.2 35.6
Color (PtCo) 22,000-36-000 30,000
TS (mg/l) 57,400-65,000 65,660
TSS (mg/l) 20,320-25,000 18,500
COD (mg/l) 25,000 27,000
Sulphate (mg/l) 1,060 3,930
In this study, the PACL coagulant and 3130 flocculent (coagulant aid) is used. The PACL and CA-3130 flocculent were collected from pune.
The various parameters like pH,TSS ,COD, Color were analyzed in laboratory according to methods given in standard Methods. pH was measured by pH meter, close reflux colorimetric method was used for COD analysis.
3. Experimental procedure
Coagulation–flocculation studies were performed in six-place conventional Jar-test apparatus. Six beakers with 1000 ml volume of wastewater is use at time of experiment. The experimental process consisted of initial rapid mixing for 5 minutes with 150 rpm, followed by slow mixing stage for 30 minutes at 30 rpm and final settling step for one hour settling time. After completing the settling time the sample were withdrawn from supernatant for analyses of TSS, COD and color.
The experimental studies carried out in three steps. In the first step optimum pH was determined. The experiment was carried out for pH range of 4 - 9. The pH values of wastewater were adjusted by using 1.0 M of NAOH and 1:1 HCl. In the second step the coagulation and flocculation study was carries to determine the coagulant dose, ranging from 0-1000 mg/L and optimum coagulant dose were determine for maximum removal efficiency of TSS, COD, color of vegetable tannery wastewater. In the last step polyelectrolyte were added as flocculent and analyzed for its removal efficiency for the same. The range of flocculent used at the time of experiment is 5-100 mg/L.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1 Effect of pH on Coagulation
In the coagulation–flocculation process, pH is very important as the coagulation occurs within a specific pH range. In this study, a wide range of pH between 4 to11 was selected.
The results of the study showing the effect of pH on TSS, COD and Color removal efficiencies when PACl was used as a coagulant are presented in Figure 1. To determine optimum pH value, PACl dosage was constant at 100 mg/L. At pH 4 TSS ,COD and color removal efficiency increased but removal efficiency is reduces as the pH increases to 9,i.e At higher pH value, TSS , COD removal efficiency decreased. It is clear that optimum pH was 4 for the coagulation-flocculation process at 100 mg/L PACl with initial concentration of TSS,COD and color were 18,200 mg/L,31,467 mg/L and 35,700 .In this study, after PACL addition as a coagulant, mechanism of coagulation showed properties of sweep-floc coagulation.
Fig. 1. TSS, COD and color removal efficiency at different pH values
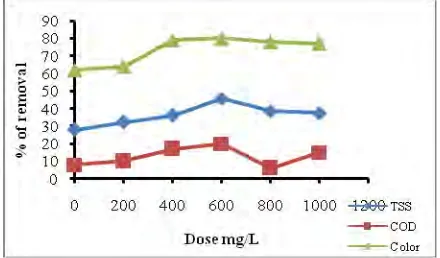
4.2 Determination of the optimal coagulant dosage
There are two general types of colloidal solids particle dispersion in liquid. When water is solvent, these are called the hydrophobic and hydrophilic collides. These two types are based on attraction of particles surface for water. Hydrophilic particles have relatively little attraction for water and hydrophilic particles have a great attraction for water. An important factor in the stability of collide particle is the presence of surface charge. It develops in a number of different ways, depending on chemical composition of wastewater and collides.
When the collide or particle surface became charge, some ions of opposite charge become attached to the surface they are held there through electrostatics and van der waals forces strongly enough to overcome thermal agitation. Surrounding this fixed layer of ions is a diffuse layer of ions, which prevent the formation of compact double layer consist of stern. To bring about the particle agitation, step must be taken to reduce particle charge. This can be accomplished by addition of potential –determining ions, addition of polymers and addition of chemicals.
Effect of PACL dosages on the TSS, COD and color removal efficiency is shown in Figure 2. Coagulation-flocculation was performed between PACl concentrations of 0-1000 m g/L. At a concentration of 600 mg/L, removal efficiency of TSS, COD and color was 45 %, 20 % and 80 % that was accepted as the optimum dosage. After 600 mg/l increasing concentration of PACl TSS, COD and color removal efficiency decreased.
4.3 Effect of Polyelectrolyte .
Generally, a little amount of polyelectrolyte dosage is enough to reach high efficiency. Because of they have some advantages including the possibility of structuration in response to specific requirements, greater purity, higher quality, stability and greater efficiency with polyelectrolytes as coagulant aids, the metal coagulant dosage can be reduced without cutting down the performance. The charge density and molecular weight of polyelectrolyte also play important role in the coagulation-flocculation process. A. Aygun et al (2010).
In Figure 3, percentage removal of TSS, COD and color removal efficiencies versus different polyelectrolyte dosages are given .At the lowest concentration of 65 mg/L polyelectrolyte, TSS, COD and color removal efficiency was 80% , 42% and 89% and treated effluent TSS, COD and color concentration was 3,700mg/l, 1800mg/L and 3,900 Pt.Co. From this experiment the optimum dose of polyelectrolyte is 65 mg/L. Optimum concentration of polyelectrolyte forms a bridge between particles and cause good flocculation. However high concentration of polyelectrolyte forms an envelope on the suspending particles and causes them to remain in suspension thus removal efficiency decreases. Same result was obtained with Aygun A. et.al. Performed Improvement of Coagulation-Flocculation Process for Treatment of Detergent Wastewaters Using Coagulant Aids and result for the same showed that the matter expressed as chemical oxygen demand (COD) was as high as 24.3 g/L while the biochemical oxygen demand was low. The coagulant dosage of ferric chloride ranged between 0.5g/L and 3 g/L, whereas the concentrations of polyelectrolyte and clay minerals varied between 5-75 mg/L and 25-750 mg/L, respectively. The optimal condition was obtained at the dosage 2 g/L ferric chloride at pH 11 with the COD removal efficiency of 71%. Addition of coagulant aids provided higher removal efficiencies. Using clay minerals at the dose of 500 mg/L with ferric chloride provided 84% of COD removal and the removal efficiency of COD increased with using polyelectrolyte resulting in an efficiency of 87%. The maximum removal efficiency was obtained with the addition of polyelectrolyte. The ferric chloride combination with coagulant aids provided higher removal efficiencies compared to coagulation with ferric chloride alone.
Fig. 3. TSS, COD and color removal efficiency at different dose of polyelectrolyte
5. Conclusion
The vegetable tannery wastewater contained high percentage of suspended and dissolved solids, high organic load and hence required the treatment before disposal in to the natural recourse. The chemical coagulation-flocculation is one of the simplest methods for the treatment of tannery wastewater.
References
[1] Baisali Sarkar, P.P. Chakrabarti, A. Vijaykumar,Vijay Kale,(2005) ,”Wastewater treatment in dairy industries — possibility of
reuse’’,Lipid Science and Technology Division, Indian Institute of Chemical Technology, Hyderabad 500007, India
[2] Mohd Ariffin Abu Hassan1, Tan Pei Li, Zainura zainon noor,”
[3] Coagulation and Flocculation treatment of wastewater in textile industry using chitosan”, Journal of Chemical and Natural Resources
Engineering, Vol.4 (1):43-53
[4] Afshin Maleki , Mohammad Ali Zazouli, Hassan Izanloo and Reza Rezaee,(2010), “Composting Plant Leachate Treatment by
Coagulation-Flocculation Process.” ,American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 5 (5): 638-643, 2009
[5] PeiWenWong ,Tjoon Tow Teng and Nik Abdul Rahman Nik Norulaini,(2007).” studied Efficiency of the Coagulation-Flocculation
Method for the Treatment of Dye Mixtures Containing Disperse and Reactive Dye “,Water Qual. Res. J. Canada, 2007 _ Volume 42, No. 1.
[6] Vrajesh Mehta, and Anal Chavan,(2009),” Physico-chemical Treatment of Tar-Containing Wastewater Generated from Biomass
Gasification Plants”, World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 57 2009.
[7] G. Lofrano, G. Lofrano1 V. Lgiorno, M. Gallo, A. Raimo ,S. Meri (2006),”Toxicity Reduction in Leather Tanning Wastewater by
Improved Coagulation Flocculation process” Department of Civil Engineering, 2Campania Regional Agency for Environmental Protection Naples, Italy, Consorzio Disinquinamento Solofra, Italy
[8] O.S. Amudaa, I.A. Amoo,(2006),” Coagulation/flocculation process and sludge conditioning in beverage industrial wastewater
treatment”, Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, Nigeria
[9] M. A. Aboulhassan, 1S. Souabi, Yaacoubi,(2008),” Pollution reduction and biodegradability index improvement of tannery effluents,
Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5 (1), 11-16, Winter 2008 ISSN: 1735-1472
[10] J Roussy, Philippe Chastellan , Maurice van Vooren and Eric Guibal , “ Treatment of ink-containing wastewater by coagulation/
flocculation using biopolymers”, Ecole des Mines d’Alès, Laboratoire Génie de l’Environnement Industriel, 6 avenue de Clavières, F-30319 ALES cedex, France, Société Diagonal, 490 Rue André Boulle, F-30100 ALES, France.
[11] K. M. Nazmul Islam1, Khaled Misbahuzzaman1, Ahemd Kamruzzaman Majumder and Milan Chakrabarty,(2011),”Efficiency of
different coagulants combination for the treatment of tannery effluents: A case study of Bangladesh”, African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology Vol. 5(6), pp. 409-419, June 2011