Original Article Risk factors for incisional hernia in gynecological cancer patients
Full text
Figure


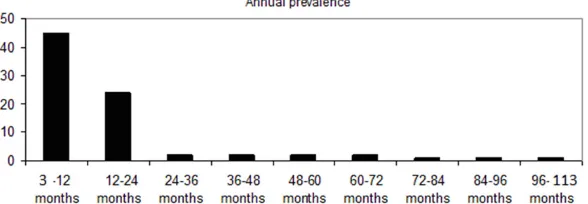
Related documents
Conclusion: Evidence-based nursing in postoperative chemotherapy patients with breast cancer can reduce the incidence of adverse reactions and the length of in-hospital stays,
In the study by Viale et al., multivariate analysis also showed that tumor size, the number of tumors and SLN positive rates were independent risk factors for axillary
In conclusion, compared with that of a conven- tional nursing protocol, the application of a comprehensive nursing internal protocol during chemotherapy for patients with lung cancer
In conclusion, our study reported that the GSTM1 null genotype was correlated with good response to chemotherapy and improved the overall survival of breast cancer, but the GSTT1
In conclusion, we identified the presence of VI detected by H&E staining as a risk factor for recurrence and an independent predictor of poor survival in
Better clinical outcomes were found in patients with low preoperative serum albumin levels in the FOLFOX and XELOX adjuvant chemotherapy groups, compared to those with similar
Conclusion: FOLFOX4 chemotherapy regimen can improve the disease-free survival rate and reduce the recurrence and metastasis rate and mortality of patients with stage II/III
The presence of Lp-PLA 2 triggers the reactive metabolin to pro- duce inflammatory mediators such as platelet- derived growth factor (PDGF), interleukins (ILs), and leukotriene.