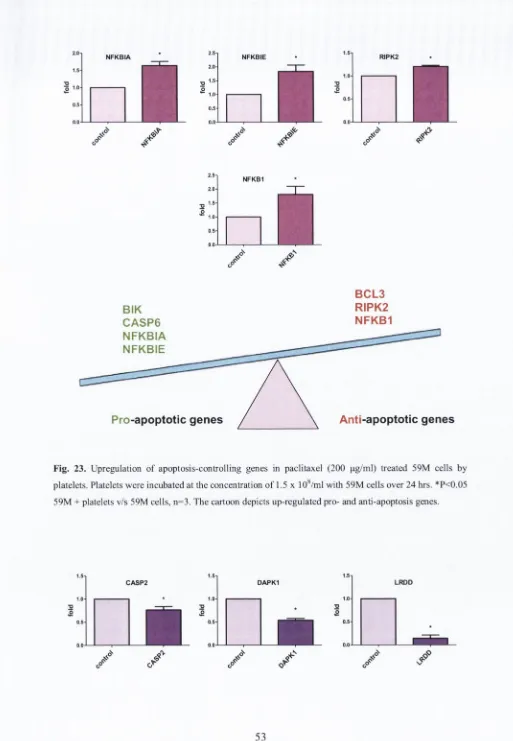
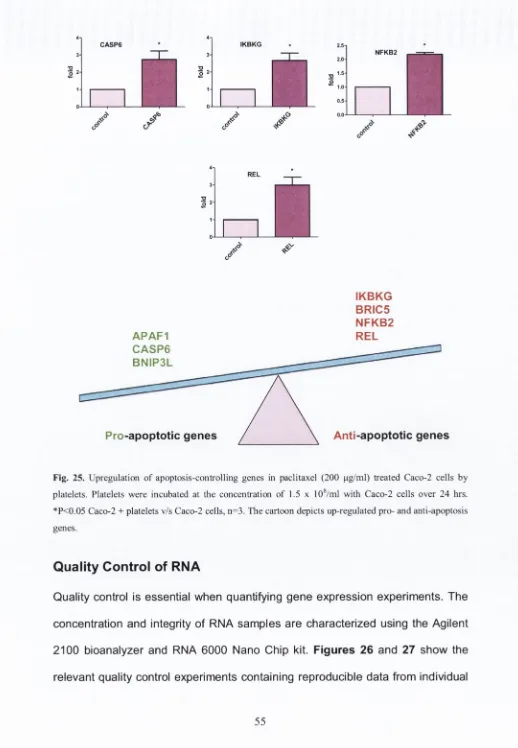
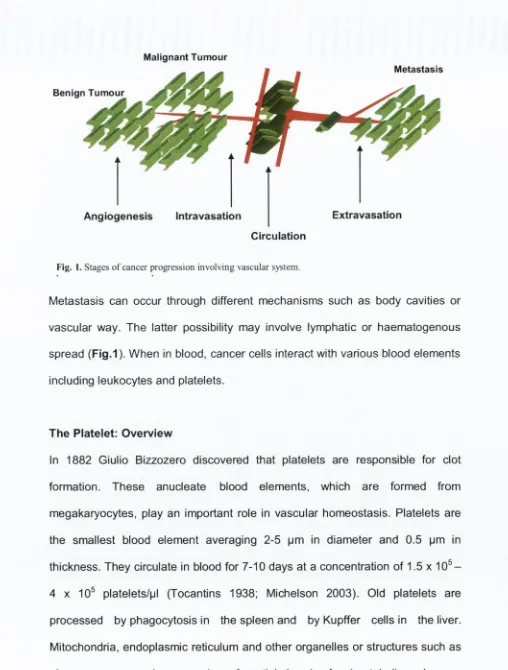
Platelets decrease chemotherapy induced cancer cell damage by increasing cell survival : mechanisms and significance
Full text
Figure



Outline
Related documents
The result of study also showed that entrepreneurship initiative has translated positively towards poverty reduction in rural communities through jobs creation,
The entire controversy concerning what conditions justify the with- drawal of life-sustaining treatment from a person in a persistent vege- tative state would
The seed of M.oleifera contained a number of phytochemical compounds such as alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, carbohydrates, tannins, steroids, glycoside, fixed oils
And also this study presents an intelligence approach for the oil reservoir characterization by using seismic elastic properties and rock physics model together
(2001) Influence of Static Magnetic Fields on Cell Viability, Ne- crosis and Apoptosis. (2001) Cell Proliferation/Cell Death Balance in Renal Cell Cultures after Exposure to a Static
Tumor cell PD-L1 predicts poor local control for rectal cancer patients following neoadjuvant radiotherapy.. Lingdong Shao* Qingqin Peng* Kaixin Du* Junyan He Yaping Dong
To implement PID control as a process of active inference, we will first describe an agent’s generative model as a generalised linear state-space model of second order