Peer assessment in an EFL context: attitudes and friendship bias
Full text
Figure

Related documents
This study also aimed at revealing which of the editing tasks, peer or self, resulted in the improvement of language learners’ writing performance better, and
The purpose of this research was to compare the students’ writing achievement scores and attitudes toward the use of self- correction, paper-pencil peer feedback, and electronic
To bridge the gap, we investigated the writing proficiency, writing assessment ability, and written corrective feedback beliefs and practices of Iranian English teachers who
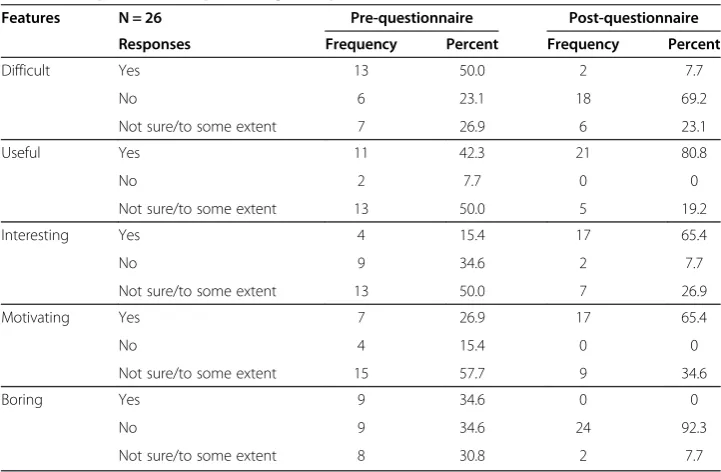
Although the amount of research on peer assessment has increased over the last three decades, peer assessment of oral language skills, and teachers’ conceptions of using it
Written corrective feedback at a Saudi University: English language teachers’ beliefs, students’ preferences, and teachers’ practices.. Focus on the language classroom:
To answer the second research question regarding which of the two procedures, peer feedback or teacher feedback, is more effective in L2 learners‟ writing development, a
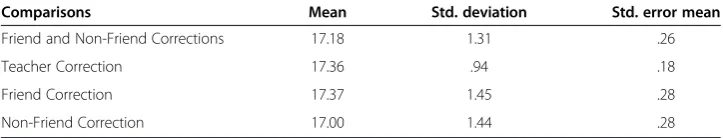
Peer-evaluation of writing was also found to have a significant impact on the improvement of the student writers (Brown, 2001; Patri, 2002).The difference in the performance
Furthermore, studies by Storch (2002, 2005, 2007) add some insights into the peer scaffolding mechanisms with the findings that during collaborative writing L2, learners are able