Detecting Disagreement in Conversations using Pseudo Monologic Rhetorical Structure
Full text
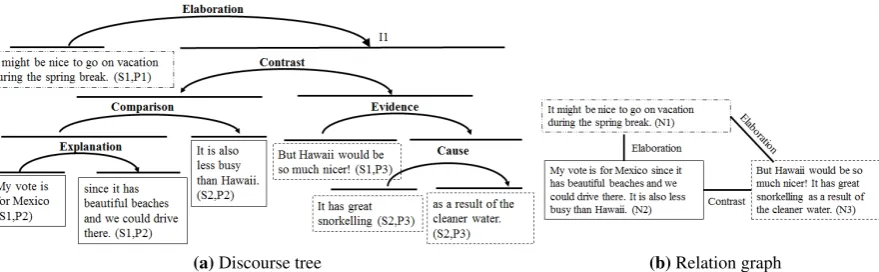
Figure



Related documents
In general, the model was found to be highly sensitive to diffusion rate (A^), transit time (t), and carbonic anhydrase catalysis (F, k 6 and k^), It was less sensitive to changes
indicating that the buffer does not exist Otherwise it uses the contents of b(x) and continues. In this case it could be some time before you find that it did not do as
Based on the stimulus-organism-reaction model, we study the direct effects of the three interpersonal attraction factors (perceived similarity, perceived familiarity, and
ABSTRACT: Nowadays urban environment has a great potential to increase the applications of renewable energy, solar-scape is one critical step in the acceleration
In this paper, we present impossible differential attacks against reduced-round versions of all the 6 members of the SKINNY family in the single-tweakey model.. To the best of
But frequency (1.15 days a week) and amount (1.60 drinks per day) were relatively lower in this sample compared to rates reported for the general Mexican adult population [9]..
The base spare battery charger does NOT charge a battery pack as quickly as the handset battery charger4. A full charge requires 24 hour when using the spare
Among students who reported using the eText that was provided, users of Courseload were more likely to rate themselves as an Active or Moderately Active reader for the course

