Efficiency of vertebrate locomotory muscles
Full text
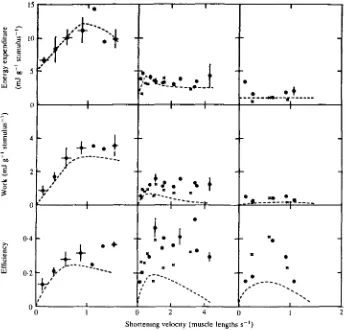
Figure

Related documents
Note: Technical efficiency level is calculated based on the stochastic frontier function under the truncated normal distribution and excluding the inefficiency
The contractile economy for each genotype was calculated from the total work performed by each muscle and the HEPC calculated between paired muscles frozen before and after the
To quantify the energy efficiency, different indicators, such as energy output/input ratio, energy productivity, energy intensity and net energy yield, have been defined
In the first stage of the analysis in Paper I, individual technical efficiency indices were calculated using multidirectional efficiency analysis (MEA) for each input
Note: Technical efficiency level is calculated based on the stochastic frontier function under the truncated normal distribution and excluding the inefficiency
Required for protection against reverse biasing between input and output (Recommended diode: SANKEN EU2Z).... Efficiency is calculated by the
(Perroni 2016; also defines energy efficiency as the energy input per output irrespective of the type of energy source related to energy supply source is a
Chemical Energy In Power (Mechanical) Fuel Utilization Efficiency of a combustion engine →. Rate of Chemical