Imaging Characteristics of Schwannoma of the Cervical Sympathetic Chain: A Review of 12 Cases
Full text
Figure

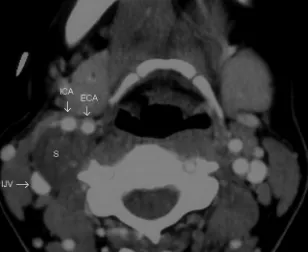
Related documents
Therefore, we compared the signal intensity of the solid part of the schwannoma with that of the brain stem, and most of the sinonasal schwannomas (8 of 9, 88.9%) were isointense
ABBREVIATIONS: CTA ⫽ CT angiography; DSA ⫽ digital subtraction angiography; DWI ⫽ diffusion- weighted MR imaging; ICA ⫽ internal carotid artery; MCA ⫽ middle cerebral artery;
Posterior view of sharp kinking* "extracranial siphon" of the highest portion of the cervical part of the left internal carotid artery (ICA) on coronal cross
MDCTA ( d ) confirming the presence of a small ulceration ( arrowhead ) in an otherwise smooth plaque causing stenosis of the internal carotid artery.. Axial contrast-
2 a Axial sonogram (5 – 12-MHz) showing a hypoechoic mass (M, dash line) centered on the right carotid sheath, between the internal jugular vein (IJA) and the common carotid
However, when masseter muscle is invaded, the common carotid artery or internal jugular vein will often be exposed after extended resection in patients with recurrence