Relative resistance to Rice yellow mottle virus in rice
Full text
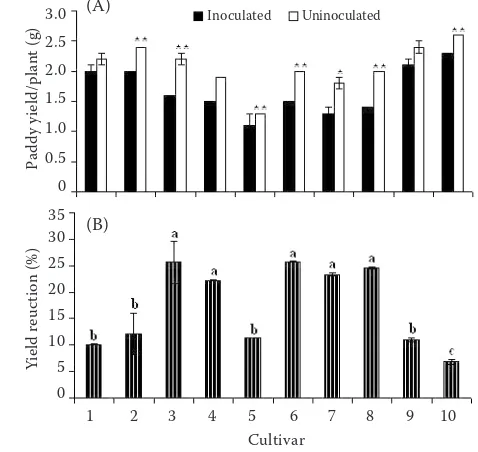
Figure
Related documents
Transgenic tomato lines expressing A22 or A64 and inoculated with To- mato yellow leaf curl virus or Tomato mottle virus exhibited delayed viral DNA accumulation and often
Rice yellow mottle virus is classified in five major serotypes; the molecular diversity of the coat protein (CP) is well established, but the amino acids involved in the recognition
Fourteen isolates of Rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV) were selected as representative of the genetic variability of the virus in Africa from a total set of 320 isolates
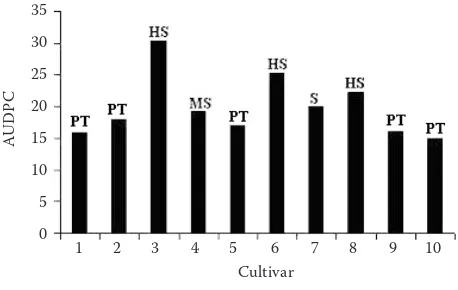
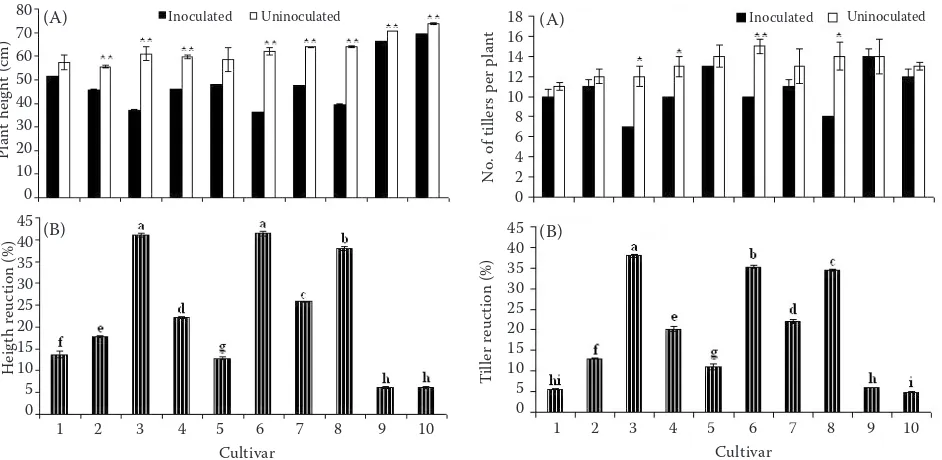
Keywords : Rice yellow mo�le virus ; Sobemovirus ; strains; rice; Africa.. The disease was later found in most countries where rice is grown, i.e. 2000) show that RYMV is
BioMed CentralVirology Journal ss Open AcceResearch Genetic diversity and silencing suppression effects of Rice yellow mottle virus and the P1 protein Christelle Sir?1, Martine
Mechanical inoculation of a mixture of four IYMV isolates to 18 plant species, including four crops (maize, rice, sorghum and pearl millet) and 14 wild grasses showed clear
Mineral nutrition N, and K affect the growth and production of the rice variety Bouake 189 infected with yellow rice variegation virus.. The direction of the interactions is
glaberrima resistant cultivars to RYMV despite the differences of their genetic determinants (deletion vs. point mutation) suggested that RYMV1 resistance breakdown was