AN EMPIRICAL STUDY ON THE CUSTOMER SATISFACTION OF
SELECTED INDIAN PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS IN
INDIA
Dr. Rameesha Kalra Associate Professor Dr. G.D. Pol Foundation
YMT College of Management, Navi Mumbai. &
Ms. Monika Bhatia
Assistant Professor, Ansal University Gurgaon.
ABSTRACT
With increasing competition and advent of globalization, banking is now-a-days regarded
more of a customer-centric service industry and banks have alsorealized that their
growth/success depends upon the quality of customer service provided and the overall
satisfaction of customers with their bank. Customer satisfaction ultimately leads to high
retention levels and also helps in expandingbanks’customer base.
This empirical research study focuses upon comparing customer satisfaction in retail
banking with reference to public and private banks in India.This research is based on
primary data. A questionnaire based on SERVPERF model was formulated and distributed to approximately 600 customers at various branches of banks in Delhi/NCR.The findings
revealed that customers are happier and satisfied with the services of private banks as
compared to public ones. The results of regression proved that customer satisfaction had a
strong impact upon financial performance of banks. Banks need to focus upon each of the
dimension of SERVPERF. It is expected that this research paper would help the bank International Research Journal of Management and Commerce
ISSN: (2348-9766) Impact Factor- 5.564, Volume 4, Issue 10, October 2017 Website- www.aarf.asia, Email : editor@aarf.asia , editoraarf@gmail.com
management in strengthening their customer relationship program and thereby help them
highlight the areas where banks are lacking in terms of customer satisfaction.
Keywords: Customer satisfaction, banks, SERVPERF, service quality. INTRODUCTION
Undoubtedly service quality is an important component in any business/service related activity.Service quality is defined as the difference between customer’s expectations and perceptions of the service received. Customers feel delighted if the organization delivers more than they expected. Customer is regarded as the king of any business. Customer satisfaction and service quality are positively related to each other. Higher the service quality, higher is the customer satisfaction. Good quality services have become the need of the hour. Excellence in service quality is a must to achieve customer satisfaction and ultimately customer retention. So it has become imperative to retain customers and resolve customer complaints timely. Banks play a significant role in the economic growth and prosperity of any country. Customer satisfaction plays an integral role in boosting up a bank’s performance.
Today the customers aresmart, knowledgeable, well aware of their options/choices and want nothing but best of everything. Because of intense competition and development of technologythere is a constantrequirement forreview of banks’ services from customer’s previewin order to know the changing requirements of the customers and to stay ahead in the competition. Thus, considering the competitive environment, it was felt that there is a constant requirement to deliver high quality servicesso as to have an edge above the competitors and differentiate them from others. With organizations resorting to cost cutting measures due to financial constraints, it becomes even more important to closely monitor customer perceptions.
Till date, SERVPERF model is the most widely used and tested measure of service quality, especially in banks. This technique has been largely adopted by managers (Parasuraman, Zeithaml and Berry’1991) and by academicians (Cronin and Taylor’1992; Crompton and MacKay’1989) to evaluate customer perceptions of service quality for banking services. The SERVPERF model proposes five dimensions upon which service quality must be evaluated:
2) Reliability: Capability of the service provider to perform the committed service perfectly and consistently.
3) Responsiveness: Being responsive to give timely and qualitative services.
4) Assurance: Politeness of the employees and their ability to instill confidence and faith towards their clients.
5) Empathy: Providing personal attention to the clients.
RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
1) To examine the service quality of private and public sector banks in terms of five major dimensions.
2) To compare and evaluate the perceptions of customers regarding service quality in private and public sector banks.
3) To suggest the important measures that should be adopted by banks’ to ensure qualitative services.
LITERATURE REVIEW
banks in India.The findings of the research were that the customers of private sector banks perceived receiving a high level of quality than of the public banks.Culiberg Barbara and Rojsek Ica (2010) explored service quality in retail banking in Slovenia and its influence on customer satisfaction.Assurance & empathy was found to be the most significant factor influencing customer satisfaction. Human/personal contact was found to have a great impact on customer satisfaction.Amin Muslim, Isa Zaidi and Fontaine Rodrigue (2011) studied the role of customer satisfaction in enhancing the loyalty of Muslim and non-Muslim Islamic industry in Malaysia.The study revealed that customer satisfaction had a positive relationship with customer loyalty. The common factors that emerged as the indicators of customer loyalty were willingness to recommend Islamic banks to friends/relatives and continuity of association with the bank.Swar Narayan Biranchi (2011) critically examined the gap in service quality with respect to customers’ perceptions and expectations using SERVQUAL model. The conclusion of the study was that the service quality of foreign bank i.e. Citibank was high and that of public sector banks i.e. SBI and PNB was quite low due to lack of responsiveness, empathy and tangibility. Foreign banks were able to meet customers’ expectations much better than private and public banks.Shah A. (2012) explored the major factors that led to customer satisfaction in Indian retail banking by taking a sample size of 300 bank customers in Vadodara, Gujarat. The important factors that positively drive customer satisfaction were traditional banking services, internet banking services, bank image positioning, customer convenience, risk privacy in internet banking, bank charges, bank price policy, bank CRM and bank parking facility.Franklin M. and Balaji S.G. (2013) empirically tested the impact of service quality on customers’ satisfaction of selected customers of private banks in Trichy, Tamilnadu using SERVQUAL model. Out of the total 5 dimensions of service quality in SERVQUAL model, only 3 dimensions i.e. Tangibility, Reliability and Responsiveness were significantly correlated with customer satisfaction.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
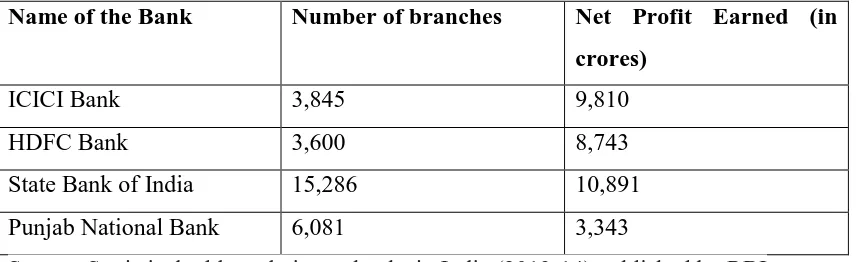
The public banks include State Bank of India (SBI) and Punjab National Bank (PNB) whereas ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank represents private sector. Table 1 shows the sample of the four banks was taken on the basis of their net profits earned and numbers of branches as on 31st March’2014 as below:
Table 1
Name of the Bank Number of branches Net Profit Earned (in crores)
ICICI Bank 3,845 9,810
HDFC Bank 3,600 8,743
State Bank of India 15,286 10,891
Punjab National Bank 6,081 3,343
Source: Statistical tables relating to banks in India (2013-14) published by RBI
Customers, specifically,of metro citiesare quite demanding, knowledgeable and expect
qualitative services from banks. Butdue to paucity of time, it was not possible to cover the
customers from all metro cities of India. Thus, primary data for evaluating customer
satisfaction is collected from customers of one of the metro city,Delhi/NCR.
DATA COLLECTION
To achieve the objectives of the study, primary data is gathered from customers who are
using the services of the selected banks through a structured questionnaire so as to examine
the level of customer satisfaction with the banks. The questionnaire was circulated on the
basis of convenience sampling. 600 questionnaires were distributed personally to the
customers of the selected branches. Though this number exceeded the sample size, but this
was done because it was felt that some respondents might not respond or may fill incomplete
information. The information of the questionnaires was coded and entered manually by using
Microsoft excel in Google drive. Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS Version 19)
was used to do the required statistical analysis.
Construction of questionnaire and its pre-testing
To develop the questionnaire, the existing literature on customer satisfaction using
reliability, responsiveness, assurance and empathy) was reviewed. This model is considered
as quite important and useful in measuring aspects of service quality. Many experts in the
marketing field were also contacted. The observations and suggestions made during the
discussions with the various marketing experts also helped in the preparation of
questionnaire. The preliminary draft of questionnaire was pre-tested and that helped in
improving the final draft of the questionnaire. The questionnaire comprises of two sections;
first section concerns with the demographic profile of the customers and the second section
concerns with the questions relating to the satisfaction of customers with the banking services
based on SERVPERF model and compared the perception of customers regarding various
services provided by private and public sector banks. Using convenience sampling, the
structured questionnaire was circulated amongst the customers of private and public sector banks. The collection of primary data has been restricted to Delhi/NCR region. Customers included those who have current account, savings account, Demat a/c, loan, credit card and term deposit account with the bank. The researcher collected the data personally or sent the questionnaire through email. A 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 to 5 was used to examine how strongly respondents agree (5) Very satisfied or (1) very dissatisfied with the statements.
The research design is exploratory in nature. A pilot study was conducted by collecting data from 33 customers. Based on the data collected from the pilot study, the reliability of the questions was tested using SPSS software. Certain items, which were found irrelevant, based on the value of Cronbach’s Alpha were deleted and then the final questionnaire was prepared. The final Cronbach’s Alpha value was 0.96, which is higher than 0.70, the standard.
HYPOTHESES OF THE STUDY
H01: There is no significant difference in the perception of consumers towards public and
private sector banks based on Tangibility.
H02: There is no significant difference in the perception of consumers towards public and
private sector banks based on Reliability.
H03: There is no significant difference in the perception of consumers towards public and
H04: There is no significant difference in the perception of consumers towards public and
private sector banks based on Assurance.
H05: There is no significant difference in the perception of consumers towards public and
private sector banks based on Empathy.
ANALYSIS - CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
The word of mouth of a satisfied customer is worth more than any advertising campaign. Continuous innovation in products/services must be done according to the needs and requirements of the customers.
Demographic Profile of the Respondents
The collected data indicates the description of the collected data regarding the demographic characteristics of the respondents of the research. The total number of responses collected was 600, out of which 569 were found complete and usable. Out of 569 responses, 25 were related to customers who preferred bank other than the 4 sample banks under study. For the purpose of analysis, those 25 responses have not been taken into consideration.
Items Frequency Percentage Gender
Male 365 64
Female 204 36
TOTAL 569 100
Age
Under 25 62 11
25-35 181 32
35-45 123 22
45-55 127 22
Over 55 76 13
TOTAL 569 100
Occupation
Government Job 84 14.76
Private Job 218 38.31
Self Employed/Business 113 19.86
Student 48 8.44
Housewife 71 12.48
Other 35 6.15
TOTAL 569 100
Most preferred bank for doing transactions
ICICI Bank 132 23.20
HDFC Bank 141 24.78
SBI 169 29.70
PNB 102 17.93
Other 25 4.39
TOTAL 569 100 Tenure of relationship with the bank
Less than 1 year 13 2.28
1-3 years 123 21.62
4-6 years 228 40.07
More than 6 years 205 36.03
Account owned by respondents in public and private banks
Private Bank 187 32.8
Public Bank 147 25.8
Private & Public Bank 235 41.4
TOTAL 569 100
The below mentioned table 3 depicts the Comparative overall satisfaction with banking services
Parameter Private Sector Banks (%) Public Sector Banks (%)
Tangibility
Strongly
Disagree 1.5 2.5 Disagree 9.6 22.4 Neutral 4.9 6.9
Agree 46.1 50.9 Strongly
Agree
37.7 17.2
Number of respondents 273 271
Reliability
Strongly
Disagree 6.6 1.03 Disagree 8.1 9.7 Neutral 5.6 3.5 Agree 48.2 65.3 Strongly
Agree
37.2 20.4
Number of respondents 273 271
Responsiveness
Strongly
Disagree 0.9 1.32 Disagree 12.6 17.5 Neutral 7.2 5.7
Agree 44.5 57.4
Strongly Agree
Number of respondents 273 271
Assurance
Strongly
Disagree 1.4 1.8 Disagree 13.1 19.6 Neutral 6.8 4.3 Agree 46.1 56.8 Strongly
Agree
32.7 17.3
Number of respondents 273 271
Empathy
Strongly
Disagree 2.4 1.8 Disagree 19.4 16.9 Neutral 18.6 11.1 Agree 68.8 51.1 Strongly
Agree
50.7 19
Number of respondents 273 271
The above table shows the comparative responses obtained from a sample of 273 respondent of private banks and 271 sample respondents of public sector banks.
Tangibility
Parasuraman et. al (1985) defined tangibility as the appearance of physical facilities, equipment, personnel and written materials. Ananth et. al (2011) referred to tangibility in their study of private sector banks as physical facility, modern looking equipment, well dressed employees and visually appealing premises and materials.
Reliability
Reliability is considered as the most important factor in banking services. It is concerned with providing the services at the promised time, maintaining error free records and providing qualitative services.
From the analysis, we can see that approx 37% respondents strongly agree and 48% agree that private banks are providing reliable services and 17% strongly agree and 65% agree with the public sector banks.
Responsiveness
Responsiveness may be defined as the willingness of the employees to provide services by understanding their specific needs and wants and taking timely actions on customer complaints.
From the analysis, we can see that approx 35% respondents strongly agree and 45% agree that private banks show responsiveness in assisting its customers and 18% strongly agree and 57% agree with the public sector banks.
Assurance
Parasuraman et. al (1985) defined assurance as knowledge and courtesy of employees and their ability to inspire trust and confidence. This dimension takes care of safety and security concern to the customers.
Approximately 32% respondents of private sector banks strongly agree that private sector banks take care of the assurance dimension whereas 2% strongly disagree with this. Similarly, 17% respondents of public sector banks strongly agree that public banks are providing assured services while 2% strongly disagree.
Empathy
Ananth et. al (2011) referred to empathy in their study on private sector banks as giving individual attention to their customers, understanding their specific needs and convenient operating hours.
services while 51% strongly agree. From the analysis, it is observed that private banks are providing services more empathetically as compared to public sector banks.
In Table 4, the mean scores of Service Quality Parameters (SERVPERF) are shown Service Quality Parameters Private bank Public bank
Tangibility 4.08 3.58
Reliability 4.13 3.94
Responsiveness 3.99 3.73
Assurance 3.95 3.68
Empathy 3.91 3.68
Source: Primary data Dimension-wise Analysis
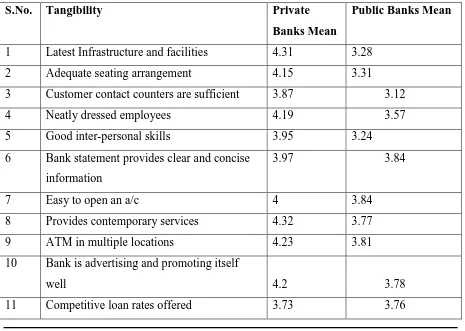
Table 5 summarizes the mean values of private and public banks with respect to Tangibility dimension
S.No. Tangibility Private
Banks Mean
Public Banks Mean
1 Latest Infrastructure and facilities 4.31 3.28
2 Adequate seating arrangement 4.15 3.31
3 Customer contact counters are sufficient 3.87 3.12
4 Neatly dressed employees 4.19 3.57
5 Good inter-personal skills 3.95 3.24
6 Bank statement provides clear and concise information
3.97 3.84
7 Easy to open an a/c 4 3.84
8 Provides contemporary services 4.32 3.77
9 ATM in multiple locations 4.23 3.81
10 Bank is advertising and promoting itself
well 4.2 3.78
[image:12.595.123.452.119.307.2] [image:12.595.67.532.416.747.2] The management of public banks must focus upon improving their physical facilities/ambience to gain better confidence and satisfaction of their customers. These visual factors form first impression in the minds of customers.
Public banks need to upgrade themselves better in terms of technology and providing e-banking facilities.
Private banks must offer loans at comparatively lower rates to its customers without much documentation. They must also increase the number of ATMs,which in turn would save their cost per transaction.
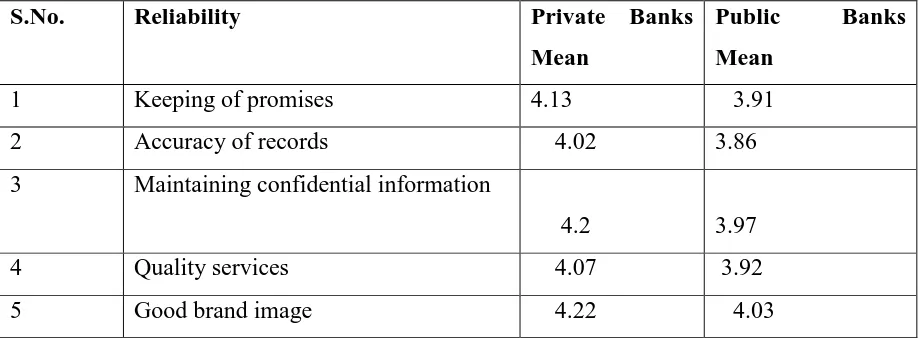
Table 6 summarizes the mean values of private and public banks with respect to Reliability dimension
S.No. Reliability Private Banks
Mean
Public Banks Mean
1 Keeping of promises 4.13 3.91
2 Accuracy of records 4.02 3.86
3 Maintaining confidential information
4.2 3.97
4 Quality services 4.07 3.92
5 Good brand image 4.22 4.03
The above analysis shows that customers believe private banks as more reliable than public banks; however the difference is not very significant.
Public banks must try to keep their promises as per the timelines committed and provide error-free and qualitative services to its customers.
Employees of the public banks should be eager to instil confidence in their customers and make them feel safe and secure in transacting with them.
Private sector banks must also increase their branch network by penetrating even in rural areas for easy accessibility.
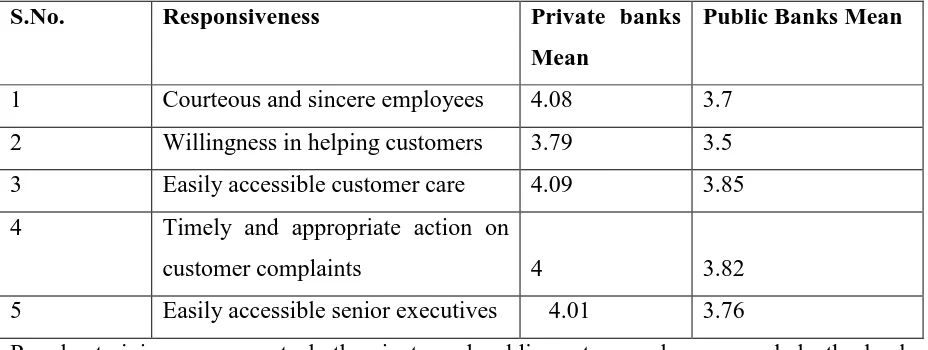
[image:13.595.67.527.276.445.2]Table 7 summarizes the mean values of private and public banks with respect to Responsiveness dimension
S.No. Responsiveness Private banks
Mean
Public Banks Mean
1 Courteous and sincere employees 4.08 3.7
2 Willingness in helping customers 3.79 3.5
3 Easily accessible customer care 4.09 3.85
4 Timely and appropriate action on
customer complaints 4 3.82
5 Easily accessible senior executives 4.01 3.76
Regular training programs to both private and public sector employees can help the bank employees to exhibit better performance and in turn, help their banks to gain competiveness and higher efficiency. These trainings would play an important role in developing their overall personality and skills.
The customers of public sector banks were not happy with the employee behaviour and attitude. Thus, specifically, the public sector employees should be imparted training for enhancing their communication skill, behavioural aspect, interpersonal skills and public dealing.
Public sector employees need to improve upon this dimension by providing individualized services by providing/training courteous and helpful employees who understand customer’s needs specifically.
Table 8 summarizes the mean values of private and public banks with respect to Assurance dimension
S.No. Assurance Private sector
Mean
Public sector Mean
1 Employees eager to gain confidence 3.95 3.58
2 Employees aware of all bank services
3.96 3.72
3 Employees tell approximate time
required to perform a service 3.94 3.70
4 Employees keep updated on new services
[image:14.595.67.531.87.262.2] [image:14.595.68.531.546.744.2]From the analysis, it is proved that customers are happy with the services of private banks better than public ones; although not much difference has been observed.
Employees of both the banks should keep their promises and provide error-free and reliable services to their customers. Also they should be able to gain trust of their customers.
Employees, specifically of public banks, need to improve their treatment towards their customers by willingly helping them and keeping them aware of the latest products/services offered by the bank from time-to-time.
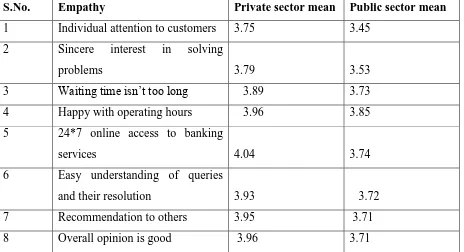
Table 9 summarizes the mean values of private and public banks with respect to Empathy dimension
S.No. Empathy Private sector mean Public sector mean
1 Individual attention to customers 3.75 3.45
2 Sincere interest in solving
problems 3.79 3.53
3 Waiting time isn’t too long 3.89 3.73
4 Happy with operating hours 3.96 3.85
5 24*7 online access to banking
services 4.04 3.74
6 Easy understanding of queries
and their resolution 3.93 3.72
7 Recommendation to others 3.95 3.71
8 Overall opinion is good 3.96 3.71
From Table 9 it is inferred that customers of private banks were comparatively more satisfied with the empathetic attitude of their banks employees. Our research has proved that taking care of customers’ comfort and paying attention to their specific requirements is a must. Customer satisfaction with respect to service quality is an invaluable asset for banks.
Both private as well as public banks should ensure that there is no communication gap between customers and their bank and have a proper feedback mechanism and complaint resolution process.
[image:15.595.69.533.296.548.2] Public banks must also work upon increasing their customer contact counters so that waiting time to receive customer service is not too long.
In Table 10, the results of hypotheses testing (Using Mann Whitney U Test in SPSS version 19) are summarized
Question no. Null Hypotheses Mann-Whitney U Wilcoxon W
Z Asymp.
Sig. (2-tailed) Mean Rank Private Bank Mean Rank Public Bank Decision (Accept/Reject Null) Q 8
I think that the Bank has latest infrastructure and
facilities.
18763.5 55619.5 -10.62
0.000
339.27 205.24
Reject
Q 9
There is an adequate seating arrangement in the
bank
22472.5 59328.5 -8.42 0.000
325.68 218.92
Reject
Q 10
I believe that the number of customer contact
counters in my branch are
sufficient
24522 61378 -7.13 0.000
318.18 226.49
Reject
Q 11
The employees of the bank are neatly
dressed
25143 61999 -6.96 0.000
315.90 228.78
Reject
Q 12
The employees of the bank have good
inter-personal skills
25025 61881 -6.86 0.000
316.33 228.34
Q 13
I feel that the bank statements provide clear and concise
information
32787 69643 -2.51 0.012
287.90 256.99
Reject
Q 14
I am of the opinion that it is easy to open an a/c
with the bank
32213 69069 -2.87 0.004
290.00 254.87
Reject
Q 15
The bank provides contemporary
services like internet banking
and mobile banking
25187.5 62043.5 -7.23 0.000
315.74 228.94
Reject
Q 16
The Bank provides ATM service in
multiple convenient
locations
26828.5 63684.5 -6.11 0.000
309.73 235.00
Reject
Q 17
I am of the opinion that Bank is advertising and promoting itself
well
27071 63927 -5.95 0.000
308.84 235.89
Reject
Q 18
I think the loan rates offered by the
bank are competitive
35991 72847 -0.60 0.552
276.16 268.81
Accept
Q 19
The Bank keeps promises on the
timelines
30875 67731 -3.72 0.000
294.90 249.93
committed.
Q 20
The Bank maintains accuracy
of the records. (Like error free pass book, contact
details etc.)
31863.5 68719.5 -3.10 0.002
291.28 253.58
Reject
Q 21
I think the bank keeps information
of customers confidential
30529.5 67385.5 -3.98 0.000
296.17 248.65
Reject
Q 22
My bank provides quality services
32785.5 69641.5 -2.56 0.010
287.91 256.98
Reject
Q 23
My bank carries a good brand image
32001 68857 -3.14 0.002
290.78 254.08
Reject
Q 24
The employees of the bank are courteous and
sincere
28979.5 65835.5 -4.76 0.000
301.85 242.94
Reject
Q 25
The employees of the bank show willingness in
helping its customers
31258 68114 -3.33 0.001
293.50 251.34
Reject
Q 26
I believe that the customer care of the bank is easily
accessible
30359.5 67215.5 -3.98 0.000
296.79 248.03
Reject
Q 27 Bank takes appropriate and
32297 69153 -2.81 0.005 289.70 255.18
timely action on customer complaints
Q 28
I believe that senior executives
of the bank are easily accessible
31684.5 68540.5 -3.18 0.001
291.94 252.92
Reject
Q 29
The employees of the bank are eager to gain confidence in their customers
29713.5 66569.5 -4.28 0.000
299.16 245.64
Reject
Q 30
The employees are aware of all services offered by
my bank
31210 68066 -3.44 0.001
293.68 251.17
Reject
Q 31
Employees tell the approximate time
required to perform a service
31814 68670 -3.10 0.002
291.47 253.39
Reject
Q 32
Bank keeps me updated on new services offered
31616 68472 -3.20 0.001
292.19 252.66
Reject
Q 33
The employees of my bank provide individual attention
to customers
31304 68160 -3.28 0.001
293.33 251.51
Reject
Q 34
Employees show sincere interest in solving problems
31792 68648 -3.00 0.003
291.55 253.31
Q 35
I am of the opinion that waiting time to receive service is
not too long
33190.5 70046.5 -2.25 0.024
286.42 258.47
Reject
Q 36
I am happy with the operating hours
of the bank
34308 71164 -1.61 0.108
282.33 262.60
Accept
Q 37
My bank caters to my specific needs by providing 24*7 online access to various banking
services
30465 67321 -3.82 0.000
296.41 248.42
Reject
Q 38
I feel that my queries are easily
understood and responded to.
32177 69033 -2.82 0.005
290.14 254.73
Reject
Q 39
Would you recommend this
bank to your friends, relatives or
others?
31506 68362 -3.19 0.001
292.59 252.26
Reject
Q 40
My overall opinion about my bank is
good
31950.5 68806.5 -2.92 0.003
290.97 253.90
Table 11 depicts the summary of results of hypotheses testing
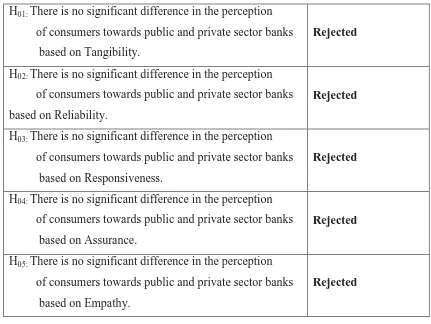
H01: There is no significant difference in the perception
of consumers towards public and private sector banks
based on Tangibility.
Rejected
H02: There is no significant difference in the perception
of consumers towards public and private sector banks
based on Reliability.
Rejected
H03: There is no significant difference in the perception
of consumers towards public and private sector banks
based on Responsiveness.
Rejected
H04: There is no significant difference in the perception
of consumers towards public and private sector banks
based on Assurance.
Rejected
H05: There is no significant difference in the perception
of consumers towards public and private sector banks
based on Empathy.
Rejected
Influence of Customer Satisfaction on Financial Performance
[image:21.595.99.530.63.387.2]To determine the influence of internal business process efficiency on performance of the bank bi-variate regression model was used. The results of the model (Table 5.21) table show that customer satisfaction has a very strong positive correlation/impact upon financial performance at (r = 0.978, t=9.586, p>0.05) with a model fit (R2 = 0.957) which implies that focusing on customer satisfaction contributes up to 95.7% of financial performance of banks. It is undoubtedly true that customer satisfaction is the most important aspect of banking industry
Table 5.21 – Regression (Customer Satisfaction)
Model R R Square Adjusted R Square
Std. Error of the Estimate
Managerial Implications
Bank, whether private or public, should give more focus upon enhancing tangibility, reliability, responsiveness, assurance and empathy. Bank statements should be sent to the customer timely and enquiry letters should be answered as soon as possible. The management of the bank should regularly undertake research activities or have a feedback system in place in order to keep a track of customer satisfaction level. Banking, being a customer-oriented organization, hiring of self-motivated and motivated human resource is a must who will try their best to resolve customer complaints in an effective manner.
The management of the banks should put in their whole hearted efforts to ensure that the expectations of the customers with regard to service quality are completely met. Banks have to be innovative and diversify its products & services to sustain in the tough competitive environment.
Since the major key factor for the growth of banking industry is its customer, thus a bank’s success/failure largely depends upon its customer’s satisfaction/dissatisfaction. Thus, in order to attract customers, it is important to know the determinants of customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The present study undertaken has critically examined the level of customer satisfaction in private and public sector banks using SERVPERF model. The study found that service quality and satisfaction is more with private banks, though they are newer generation banks. Although the customer base of public banks is quite large as compared to the private sector banks, but the customers of public banks are not much satisfied with their service quality. There is a room for improvement to fulfil this service quality gap in order to meet the expectations of the customers.
suggestions will serve as an aid to the bank managers in understanding the factors affecting customer satisfaction and consequently on how to improve their satisfaction with respect to service quality aspects.
It has become increasingly important to determine the customer’s perception of quality of services provided by banks. Customer satisfaction research has become an essential ingredient for running a successful business/organization that aims at increasing and retaining its customer base. Studies have proved the positive relationship of customer satisfaction with the business’ profitability. Thus, regular surveys offer an opportunity to build true relationships with customers and provide important input as to how to improve and manage their business operations.
Limitations of the Study
1) The collection of primary data was restricted to the city of Delhi/NCR.
2) The research is restricted only to comparison between private and public sector banks. 3) Sample size is limited due to time constraint and that has restricted the use of many
statistical analysis techniques that require larger data sets. Scope for further research
1) The service quality of Indian banking sector has been assessed in Delhi/NCR only. Service quality could be studied for other states/cities as well.
2) The present study is confined to the Indian banking sector only, it can also be undertaken to compare the performance of Indian banks viz-a-viz foreign banks and the results should indicate the best banks in the globalized competitive environment.
References
Amin M., Isa Z. & Fontaine R. (2011). The role of customer satisfaction in enhancing customer loyalty in Malaysian Islamic banks, The Services Industries Journal, Vo. 31 (9), July 2011:1519-1532.
Anton (1996). Customer Relationship Management, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall Inc. Bedi M. (2010). An Integrated Framework for Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction
and Behavioral Responses in Indian Banking Industry – A Comparison of Public and Private Sector Banks, Institute for International Management and Technology, Vol. 10 (1), April-September’2010 :157-172.
Crompton J.L. & McKay K.J. (1989). Users’ Perceptions of the Relative Importance of Service Quality Dimensions in selected Public Recreation Programs. Leisure Sciences, 11: 367-75.
Cronin J.J. & Taylor S.A. (1992). Measuring Service Quality: A re-examination and extension, Journal of Marketing, Vol. 56(3):55-68.
Culiberg B. & Rojsek I. (2010). Identifying Service Quality Dimensions as Antecedents to Customer Satisfaction in Retail Banking, Economic and Business Review, Vol. 12 (3), 2010:151-166.
Day G.S. (1994).The Capabilities of market-driven organizations, Journal of Marketing, 58(4) :37-52.
Fornell (1992). A National Customer Satisfaction Barometer: The Swedish Experience, Journal of Marketing, 56:1-18.
Franklin M. & Balaji S. (2013). Service Quality Dimensions and its Effect on Customer Satisfaction: A Case Study Across the Private Banks in Trichy, International Journal of Management Research and Review, Vol. 3(6), June 2013 :2986-2991.
Oliver R. (1980). A cognitive model of the antecedent and consequences of satisfaction decisions, Journal of Marketing, 17(10):460-469.
Parasuraman B., Zeithmal, Berry (1991). Understanding Customer Expectations of Service, Sloan Management Review, Spring: 39-48.
Swar N.B. (2011). A Study of Customer Satisfaction & Service Quality Gaps in Selected Private, Public and Foreign Banks, SIES Journal of Management, March 2011, Vol. 7(2): 62-73.