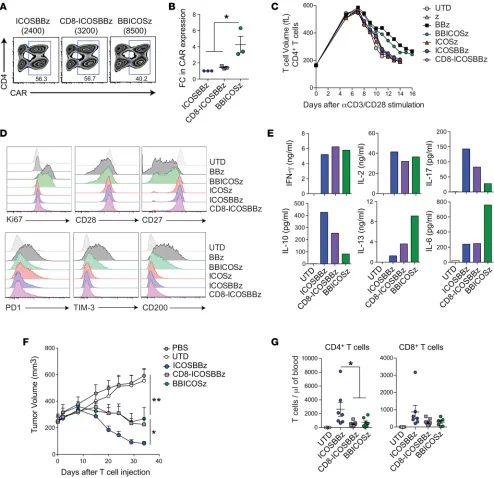
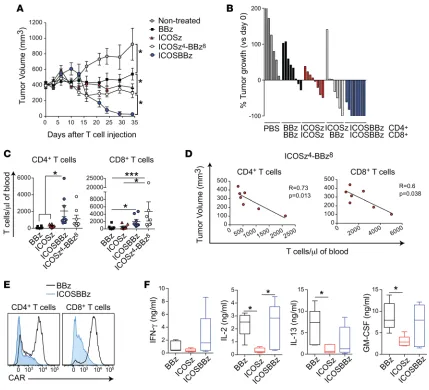
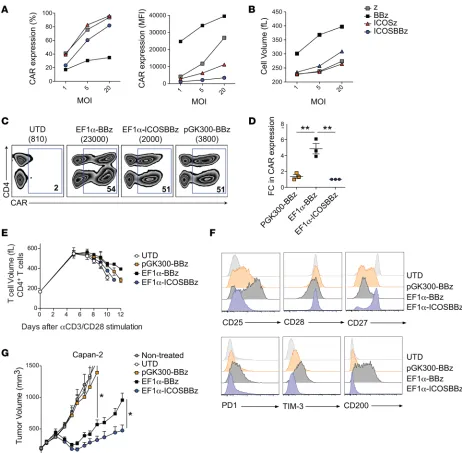
Enhancing CAR T cell persistence through ICOS and 4-1BB costimulation
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Guru Nanak, thus, gave the people and insight into the nature of the ultimate reality. He made them realize, not just intellectually but in personal experience of
It is noteworthy that the momentum of Indian growth was able to uphold, whereas countries like China which opened up their economy even before India and
Manna and Chaudhuri (2006) have developed a production inventory model with ramp-type two time periods classified demand pattern where the finite production rate
In this paper, we derive the perturbation and post Markovian perturbation to non-Markovian equation of motion(NMEM) that correspond to coherent and quad- rature non-Markovian
Portunid crabs, especially Portonus segnis, are the most commercially important of all true crabs in coastal waters of Hormozgan province (Safaie et al., 2013 ). The
One non-Hodgkin lymphoma cell line Raji cells co-cultured with peripheral blood-derived T cells were stably transfected with anti-CD20scFvFc/CD28/ CD3zeta gene or anti-CD20scFvFc
The aim of this study was to compare the immediate effect of different supportive conditions (VR versus non-VR conditions) on motor output in patients and healthy control