How Market Orientation Enhances Performance in Manufacturing and
Services Industry?
Ruturaj Baber & Prerana Baber
Research Scholar, Jiwaji University, Gwalior
Yogesh Upadhyay
Vice-Chancellor, ITM University, Gwalior
The concept of market orientation was introduced as a key construct by Payne (1989), Kohli
and Jaworski (1990) and Narver and Slater (1990) to improve business performance. In this
article the authors try to identify the variable and constructs which constitute the concept of
market orientation (MO). How the concept of MO has been implemented and has benefited
Manufacturing and Services Industry is explored through this article. Secondary data has
been used as a source for revelation in this research. This article also recommends
preposition for top level executives who desire enhancing performance in manufacturing and
services industry. Few limitations and directions for the future researches are discussed at
the end of the article.
Keywords: Market orientation; Business performance; Manufacturing industry; Service
industry.
Market Orientation: An Introduction
Nearly five decades ago the concept of market orientation (MO) was introduced by the researchers. The concept of MO was derived from the marketing concept and which was first proposed by Mckitterick (1957). The concept of MO was first broadly pinned down by Payne (1988), he stated that “Market orientation is extremely important for transitional organizations and market orientation is necessary to face the competition also. He stated the need which forces an organization to be market oriented. Kohli and Jaworski (1990) defined market orientation as “the organization-wide generation of market intelligence, dissemination of the intelligence across departments and organization-wide responsiveness to it". Kohli and Jaworski (1990) considered MO as a marketing concept. Whereas Narver and Slater (1990)
defined MO as “the organization culture that most effectively and efficient creates the necessary behaviors for the creation of superior value for buyers and, thus, continuous superior performance for the business”. Narver and Slater (1990) considered MO as an organizational culture. Shapiro (1988) considered market orientation as a decision making and he referred market orientation as getting firm take those decisions which are according to the time and demand of the market. Reukert (1992), examined and stated about a relationship between market orientation and organizational strategies being implied. He imaged market orientation as strategic perspective. Finally there were Deshpande and Farley and Webster (1993), viewed market orientation as making changes according to the information given back by the customers in form of feedback. The authors particularly viewed market orientation as customer orientation perspective.
Table 1: Literature Review of MO in different manufacturing and services backgrounds
Authors (year) Aim Back Ground
Variables
Main Findings–
Discussion Topics Payne (1988) Development of Market
orientation in firms.
Customer Philosophy, Integrated Marketing Organization,
Adequate Marketing Information, Strategic Orientation,
Operational Efficiency.
Closeness to customer considered as key for profits and long term sustainability in market
Noburn,
Birley& Payne (1990)
To identify potential barriers to implementation of marketing strategies in four countries and thought process of executives in these countries.
Customer Closeness, MO and Corporate Values.
Dissimilarity among the thoughts and beliefs of executives of four nations was found.
Kohli&Jaworsk i (1990)
Development of
framework to understand MO. Intelligence Generation, Intelligence Dissemination and Responsiveness
MO Leads to Business
Performance.
Narver& Slater (1990)
Development of Measure for MO.
Customer Orientation, Competitor orientation and inter-functional Coordination, Long Term Horizon and profit emphasis.
MO is important factor effecting business profitability in services and manufacturing businesses. Narver& Slater
(1993)
To examine the
relationship between MO,
Profitability, sales growth, customer
customer service, customer satisfaction and business performance.
retention, new product success, customer satisfaction and employee satisfaction
performance. Study also revealed a positive relationship between MO and customer service, customer service and customer satisfaction,
customer
satisfaction and customer retention and sales growth in manufacturing units. Kohli&Jaworsk
i (1993)
To find out reasons of firms being market oriented, effect of market orientation on business
performance and
employees and
Relationship between MO and business performance
and effects of
environment.
Top management emphasis, risk aversion, interdepartmental conflicts,
connectedness and formalization,
centralization, departmentalization, reward systems, Intelligence generation, Intelligence
dissemination, responsiveness,
economic and non-economic business performance
MO is due to efforts placed under by senior managers and result in economic and non-economic business
performance.
Kohli&Jaworsk i (1993)
Development of valid measure for MO.
Intelligence Generation, Intelligence
Dissemination and Responsiveness.
Development of 20 item valid scale for measurement of MO in services industry
Siguaw, Brown &Widing (1993)
To identify orientation of firm from sales person’s point of view. Also to find out relationship of MO with job attitude of sales person.
Customer Orientation, Market Orientation, Role Conflict, Role Ambiguity, Job Satisfaction, Organizational commitment MO significantly influences customer orientation of sales person.
(1996) and innovation are linked or not.
to firm & customer, Innovation marketing & technology fit, product advantage, teamwork, market success and project performance
impact on product newness. Whereas MO is positively associated with significantly and positively associated with innovation-marketing fit. Langerak (2001)
To study influence of manufacturers MO on behavior of sales persons and purchasers. Also to study impact of their behavior on customer and supplier
Downstream,
upstream MO.
Supplier and customer orientation. Supplier and customer trust. Supplier and customer cooperative norms. Supplier and customer satisfaction. Financial performance. Positive relationship between the described variables. Harris &Ogbonna (2001)
To describe the role of top management’s leadership style which influence the
process of MO
development in retailing scenario.
Market orientation, supportive,
participative,
instrumental leadership.
Participative and supportive
leadership styles positively linked
with MO.
Instrumental
leadership style negatively linked with MO
Sciascia, Naldi& Hunter (2006)
To study relationship
between MO and
entrepreneurship
orientation (EO) in Sweden.
Market Orientation and Entrepreneurship Orientation.
Authors stated MO as key determinant of EO from results of the study
Demirbag et. al. (2006)
To study impact of MO on TQM, and organizational performance
Market orientation,
TQM and
Organizational Performance
A strong and positive impact of MO on TQM and no significant impact on organizational performance was found in the study by the authors. Schlosser &
McNaughton
To study antecedents to individual MO (IMO) by
Psychological
contracts, learning
(2006) employees of financial organization.
orientation, MO and customer contact.
Psychological contracts, learning orientation and customer contact were considered as antecedents to IMO. Boo Ho,
Niden&Johneny (2011)
To study consequences of IMO on Remeisers in Malaysia.
IMO, work
performance and future intentions.
A significant relationship was found on work performance and future intentions of IMO in Malaysia on Remeisers.
Research Methodology
As it was stated in the abstract it, the nature of this article is conceptual. An extensive literature review was made for identification of all the constructs and variables for completion of the study. The various perspectives of market orientation are presented in tabular form for proper dissemination of the desired information in the area of research.
This article recognizes all the literature related to market orientation and its components. The study is secondary data based. The data has been collected through various international and national journals/periodicals/books.
The scope of study has been both services and manufacturing industry. As business performance is dependent on employee’s performance and how well the marketing concept has been adopted by the organizations.
Perspectives of Market Orientation
[image:5.595.65.530.69.570.2]Various perspectives have been presented by the scholars since inception of the marketing concept. Table 2 represents the major perspectives presented by the scholars.
Table 2: Perspectives of Market Orientation
Author/Year Perspective Components
Shapiro (1988) Decision making perspective Information dissemination, decision making & execution
Kohli&Jaworski (1990)
Market intelligence perspective Intelligence generation, Intelligence dissemination & responsiveness Narver& Slater
(1990)
Culturally based behavioral perspective
Customer orientation, competitor orientation & inter-functional coordination
develop strategy for customer&implement Strategy
Deshpande et. al. (1993)
Customer orientation perspective
Customer orientation, customer information & coordinated utilization of resources
The key component in all the presented perspectives of market orientation is (i) generation of information, and (ii) implementation/responsiveness to information. It can be presumed that information acquisition and responsiveness are vital for implementing of the marketing concept.
Market Orientation and Business Performance
In their empirical study, they hypothesized innovation as mediating variable between market orientation and business performance. The results of the study indicated that technical and administrative innovation lead to superior organizational performance. The impact of market orientation was also stated by Balanabis, Stables and Phillips (1997) in charity organizations. Theyalso found that the more efficient the charitable trustwas, the moremoney donations it was able to raise.Avlonitisand Gounaris (1997) compared 444 industrial and consumer-goods and industrial goods producing companies. It was revealed in their study was that company performance was positively affected by adoption of market orientation and support the view that developing a marketingorientation leads to performance improvements. Kumar, Subramanian and Yauger (1998); Woods, Bhuian and Kiecker (2000);Narver and Slater (2000); Rose and Shoham (2002) also found a positive relationship between market orientation and company performance.
Linkage among market orientation and performance
developing economy’s small and medium scale organization lead to innovation, thus resulting in improved economic and non-economic performance. The literature suggests three elements of market orientation may be interrelated. In spite of JaworskianfKohli’s (1990) assumption that effect of market orientation on performance is positive was proved to be correct in later studies (Fritz &Mundof, 1996; Avlonitis&Gounaris, 1997; Zebal& Goodwin, 2012). In different backdrops.
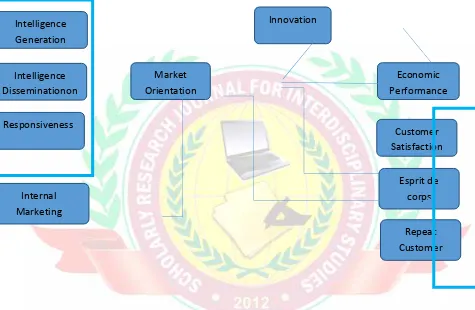
Figure 1: Model for Market orientation
Narver and Slater (1990) also purported and empirically proved the positive relationship between market orientation and business performance. They concluded that higher the degree of market orientation higher/enhanced will be the business performance. From the given discussions it can be inferred that business performance is result of market orientation (refer to figure 1).
Research Gap
Thorough research had been done in the past on the inter relationship on market orientation and its impact on business performance. One of the key determinant has been identified as competition. Earlier researches has pointed out a positive association of competition with market orientation and business performance. But no attempts have been made to study effect of market orientation on business performance under different types of competitions i.e. perfect competition, imperfect competition, monopoly, oligopolistic etc. this is one the key areas untouched by the researchers in the past.
Market Orientation
Innovation
Economic Performance
Responsiveness Intelligence Disseminationon
Intelligence Generation
Customer Satisfaction
Internal Marketing
Esprit de corps
Conclusion
Though market orientation is most likely to be related with business performance under certain conditions it may not be critical (Kohli&Jaworski, 1990). From the figure 1 it can be inferred that, market orientation is result ofpractice of internal marketing and information generation, dissemination and responsiveness exhibited by an organization. Market oriented behavior of an organization leads to innovation in organization which in turn act as predictor to improved economic and non-economic performance.This research also provides the very specifications about market orientation. It gives valuable insights about factors which act as moderator for market orientation and resulting in enhanced business performance.
References
Atuahene-Gima, K. (1996). Market orientation and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 35(2), 93-103.
Avlonitis, G. J., &Gounaris, S. P. (1997). Marketing orientation and company performance: industrial vs. consumer goods companies. Industrial Marketing Management, 26(5), 385-402.
Balabanis, G., Stables, R. E., & Phillips, H. C. (1997). Market orientation in the top 200 British charity organizations and its impact on their performance. European Journal of Marketing, 31(8), 583-603.
Dawes, J. (1999). The relationship between subjective and objective company performance measures in market orientation research: Further empirical evidence. Marketing bulletin-Department of Marketing Massey University, 10, 65-75.
Demirbag, M., Koh, S. L., Tatoglu, E., &Zaim, S. (2006). TQM and market orientation's impact on SMEs' performance. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 106(8), 1206-1228.
Deshpandé, R., Farley, J. U., & Webster Jr, F. E. (1993). Corporate culture, customer orientation, and innovativeness in Japanese firms: A quadrad analysis. The journal of Marketing, 23-37.
Fritz, W. &Mundorf, N. (1996). Market orientation and corporate success: Findings from Germany. European Journal of Marketing,30(8), 59-74.
Han, J. K., Kim, N., & Srivastava, R. K. (1998). Market orientation and organizational performance: Is innovation a missing link?.The Journal of marketing, 30-45.
Ho, V. B., Niden, P., &Johneny, S. Market orientation of individuals: A study on the remisiers in Malaysia.
Hult, G. T. M., Ketchen, D. J., & Slater, S. F. (2005). Market orientation and performance: an integration of disparate approaches. Strategic Management Journal, 26(12), 1173-1181.
Jaworski, B. J., &Kohli, A. K. (1993). Market orientation: Antecedents and consequences. The Journal of marketing, 53-70.
Kohli, A. K., &Jaworski, B. J. (1990). Market orientation: The construct, research propositions, and managerial implications. The Journal of Marketing, 1-18.
Kohli, A. K., Jaworski, B. J., & Kumar, A. (1993). MARKOR: A measure of market orientation. Journal of Marketing research, 467-477.
Kumar, K., Subramanian, R., &Yauger, C. (1998). Examining the market orientation-performance relationship: A context-specific study. Journal of Management, 24(2), 201-233.
Langerak, F. (2001). Effects of market orientation on the behaviors of salespersons and purchasers, channel relationships, and performance of manufacturers. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 18(3), 221-234.
Lings, I. N., &Greenley, G. E. (2009). The impact of internal and external market orientations on firm performance. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 17(1), 41-53.
McKitterick, J. B. (1957). What is the marketing management concept (pp. pp-71). Chicago, IL.
Narver, J. C., & Slater, S. F. (1990). The effect of a market orientation on business profitability. The Journal of Marketing, 20-35.
Narver, J., & Slater, S. (1993). Market orientation and customer service: The implications for business performance. European Advances in Consumer Research, 1, 317-321.
Norburn, D., Birley, S., Dunn, M., & Payne, A. (1990). A four nation study of the relationship between marketing effectiveness, corporate culture, corporate values, and market orientation. Journal of International Business Studies, 451-468.
Payne, A. F. (1988). Developing a marketing-oriented organization. Business Horizons, 31(3), 46-53.
Rose, G. M., &Shoham, A. (2002). Export performance and market orientation: establishing an empirical link. Journal of Business Research, 55(3), 217-225.
Ruekert, R. W. (1992). Developing a market orientation: An organizational strategy perspective. International journal of research in marketing, 9(3), 225-245.
Schlosser, F. K., & McNaughton, R. B. (2007). Individual-level antecedents to market-oriented actions. Journal of Business Research, 60(5), 438-446.
Sciascia, S., Naldi, L., & Hunter, E. (2006). Market orientation as determinant of entrepreneurship: An empirical investigation on SMEs. The international entrepreneurship and management journal, 2(1), 21-38.
Shapiro, B. P. (1988). What the hell is market oriented?.HBR Reprints.
Siguaw, J. A., Brown, G., &Widing, R. E. (1994). The influence of the market orientation of the firm on sales force behavior and attitudes. Journal of Marketing research, 106-116.
Slater, S. F., &Narver, J. C. (1995). Market orientation and the learning organization. The Journal of Marketing, 63-74.
Slater, S. F., &Narver, J. C. (2000). The positive effect of a market orientation on business profitability: A balanced replication. Journal of business research, 48(1), 69-73.
Soreze, F., &Bunić, Ž. (2007). Influence of Market Orientation on Business Performance Case: Croatian Manufacturing Companies.16th EDAMBA Summer Academy, France.
Verhees, F. (1999). Market Orientation, Product Innovation and Market Performance:
the Case of Small Independent Companies.
TijdschriftvoorSociaalwetenschappelijkOnderzoek van de Landbouw, 14, 19-35.
Wood, V. R., Bhuian, S., &Kiecker, P. (2000). Market orientation and organizational performance in not-for-profit hospitals. Journal of Business Research, 48(3), 213-226.