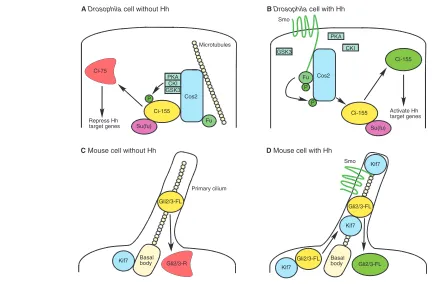
Mechanism and evolution of cytosolic Hedgehog signal transduction
Full text
Figure




Related documents
[7] Mohsen Rezvani, Student Member, IEEE, Aleksandar Ignjatovic, Elisa Bertino, Fellow, IEEE and Sanjay Jha, Senior Member, IEEE, “Secure Data Aggregation Technique for
Given this, we correlate our chest radiograph test with tests of novel object recognition and of face recognition ability (the Cambridge Face Memory Test (CFMT), Duchaine
The analysis of experimental data was performed in order to determine the effect of cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut and cutting environment on the magnitude of cutting
Purification of lipase reaches 6.9 times increase from crude lipase by using ammonium sulfate 75%.. The indication of esterification results is observed by presence of
A general transcription cofactor that transmits regulatory information to the basal transcription machinery is the large multi subunit Mediator complex that contains 22-28
45 The Lofton court read Lawrence as suggesting that the right to engage in private sexual conduct comes from the Due Process Clause’s broad concept of liberty and from
The Emergence of Anthroponotic Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Following the Earthquake in Southern Villages of Bam District, Southeastern Iran, 2010.. Mohammad Reza Aflatoonian 1 ,
EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin;