BRAND LOVE IMPACT ON THE SOCIAL MEDIA AND STAGES
OF BRAND LOYALTY
Salem S.F., Tarofder A.K., Chaichi K., Musah A.A. *
Abstract: The primary objective of the current research is to propose and investigate a conceptual model which integrates social media activities and brand love as antecedents and brand loyalty phases as an outcome of brand love. The proposed model is analysed with a sample of 240 fast fashion’s consumers by using a self -structured questionnaire survey technique. PLS -SEM applied for statistical analysis to evaluate the hypnotized linkage between the variables. The results show that social internet marketing has a tremendous impact on brand love in the fast fashion profession. Furthermore, the finding shows that social media, has an indirect constructive effect on the various phases of brand loyalty through brand love. The current research supports the crucial role of social media in marketing and advertising which will assist internet marketers to fully realize brand love and loyalty behavior. The consequence of this particular study might assist marketers to develop the successful communication approach through social networking activities to shape good attitudes and advance brand loyalty, particularly in fast fashion profession Key words: social internet marketing, brand loyalty, fast fashion, brand love
DOI: 10.17512/pjms.2019.20.1.33 Article history:
Received August 12, 2019; Revised November 7, 2019; Accepted November 20, 2019 Introduction
Social media consider a new form for building relationship between a brand and consumers. This make a company might face different challenges in building brand loyalty. Accordingly, companies are increasing investing their time and money in developing strategies that fit with social media users which might support building brand loyalty (Moro et al., 2016). Switching consumers from brand to brand cost a company more than retaining customers. According to Theng So et al., (2013), consumers continuing switching from a brand to a new brand in emerging market especially in Malaysia lead scholars to concentrate more on brand loyalty. Enhancing the value of a brand by composite a functional benefits and a symbolic benefits could support building a loyalty (Salem and Salem, 2018). Previous research already proved that brand love is a crucial element in enhancing brand attachment and help to build consumer brand relationships. Brand love could explain by liking, sharing and number of followers within a social network. Deep understanding for a brand love and how it shaped within a social media platform could be valuable to explain developing of a brand loyalty toward a fast fashion.
*
Suha Fouad Salem, Arun Kumar Tarofder, Adiza Alhassan Musah Faculty of Business Management and Professional Studies, Management & Science University, Malaysia; Kamelia Chaichi, School of Hospitality, Sunway University, Malaysia
Fast fashion emerged to respond to fast shifting consumers demands which represent with most recent fashion with a low cost (Biedenbach et al., 2015). Several companies have moved to the model of fast fashion to achieve the market trends and consumers demands. However, few empirical studies have explored and understand consumer behaviour toward a fast fashion. Therefore, it is vital to understand how companies could build brand loyalty in different stages especially in social media platform. To fill a research gap and gain deeper understanding of brand loyalty, this research seeks to investigate the role of social media activities and its indirect impact through a brand love on building a brand loyalty. The results of this study contribute to variety of literatures such as branding, consumer behaviour literature. Moreover, to raise practitioners’ knowledge about developing brand loyalty in the fast fashion industry.
Literature Review
Recently, several companies have adopted social media platform to build strong relationship with the target customers. Social media marketing is an approach that company use to connect with their target to improve brand image, brand loyalty (Salem & Salem, 2019), and brand love. According to literature using a video on the social media has positive effect on brand equity. Therefore, brands use a social media to influence on the users and then convert them to be influencers to others to build strong brand awareness and to assess them to make decision.
Positive experience could create emotional connection between an individual and a brand. Therefore, people who active on a social media may like and share their experiences with a brand. One of the reasons could make users like or share a brand through a social platform is emotional attachment. Furthermore, users become more active when they find high level of entertainment which make them get positive experience within a platform. As a result, users of a social media begin to create favourable attitude toward a brand which lead them to have strong bond with a brand. Thus, according the above argument, it is posited that:
H1. There is a positive association between social media activities and brand love.
Social media marketing used as a tool for the organizations to improve the communication with the consumers and build brand loyalty afar from traditional approaches. A research by Akar and Topçu, (2011) found that almost half of Facebook and Twitter users chat, purchase or recommend a company's products after they engaged with the company on social media. Prior studies have explored the impact of social media marketing on building brand loyalty as one construct. However, none of the studies have investigate in what way social media marketing could create brand loyalty in different stages and in which stage of brand loyalty will be using social media marketing effective strategy.
Brand loyalty is consumers’ commitments to purchase the bran. Bandyopadhyay and Martell, (2007) classified brand loyalty as behavioural and altitudinal loyalty.
According to Oliver, (1999), brand loyalty has three stages which include cognitive , affective and conative loyalty. Bandyopadhyay and Martell, (2007) argue that social media play a vital role to influence consumer perception toward a product. People have tendency to repurchase a product when they have positive attitude toward it.
One of the strategies that could shape positive perception is to use different forms of social media for instance, content communities, social networking sites, blogs, virtual worlds, microblogging sites, social bookmarking, online gaming sites, news sites, forums and more in order, to promote products and services, deliver immediate support and create an online community of brand supporters. These strategies motivate consumer to be loyal to a brand which reflect the first level of brand loyalty that named cognitive brand loyalty.
One of the essential factor in marketing construct is “Conative loyalty” since it defines a brand’s success. According to Russell-Bennett et al., (2007), conative loyalty states customers’ constant behavioural intention toward a particular brand, and is subjective by attitudinal loyalty toward the specific brand. The critical goal in relationship marketing is to generate a strong behavioural intention toward a specific brand. Consumers, who have a solid behavioural intention toward a specific brand, incline to behave constantly regardless of environmental changes and demonstrate positive longstanding relationship. King et al., (2016) argue that social media has solid impact on consumer perception toward a brand and could shape positive perception which lead them to be loyal to that brand. As a result, consumer will be satisfied for long term with a brand even when the condition and environment is changed. Consequently, according the above argument, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H2. Social media activities positively influence on cognitive brand loyalty. H3. Social media activities positively influence on affective brand loyalty. H4. Social media activities positively influence on conative brand loyalty.
In recent trends of brand relationships, “Brand love” is a novel idea that demonstrates good feelings and positive attachment towards the brand, and help to describe and forecast important post consumption manners among contented customers (Ahuvia and Carroll, 2006). Individuals constructive feelings and opinions have been linked with enhanced repurchase motives (Romero and Yagüe, 2016), lower cost sensitivity , opposition to improper data regarding the brand name as well as involvement in appropriate word-of-mouth communication. Prior research showed that when customer bond psychologically with a brand, they formed more optimistic attitude, develop more satisfaction and dedicated to the brand for the long term. Prior research has been examined the effect of brand love on brand loyalty as just one construct. As outlined by Drennan et al., (2015), a happy customer with a brand love shows a habit to produce much more effective devotion and brand loyalty in comparison with customers without brand love. Additionally, Pandir and Yasin, (2017) state that brand love accompanied by
different experiences leads to significant emotional outcomes, and subsequently leads to brand loyalty which is in line with findings of another study by Drennan et al., (2015). To the knowledge of the researchers, there was no significant study to examine the impact of brand love on the all different stages of brand loyalty. Thus, the current study proposes the following argument:
H5. Brand love positively influence on cognitive brand loyalty. H6. Brand love positively influence on affective brand loyalty. H7. Brand love positively influence on conative brand loyalty.
Brand loyalty described as a repurchase process toward a certain brand with a high level of commitment and could be behavioural or attitudinal loyalty (Aerts et al., 2017). According to Oliver, (1999), brand loyalty consists of three stages which include cognitive loyalty, affective loyalty and conative loyalty. Cognitive loyalty as a first stage is developed based on the positive perception that shaped by the information available about a brand. The affective loyalty as second stage, is shaped by the emotional connection between consumers and a brand (Oliver, 1999). This emotional attachment may create favourable attitude and experience with a brand. In the last stage which is conative loyalty where the customers keep satisfy with a brand over time (Oliver, 1999). Furthermore, previous study found that there are relationships between the stages of brand loyalty which initiate with cognitive up to conative loyalty. Therefore, the study proposes the following hypothesis:
H8. High cognitive brand loyalty impacts on affective brand loyalty. H9. High affective brand loyalty influences conative brand loyalty.
The mediating role of brand love on the association between social media activities and different stages of brand loyalty
Social media platform has been analyzed to take a look at just how customer develops the loyalty of theirs to a particular brand. Researchers supported the positive connection between social networking and brand loyalty. Zheng et al., (2015) argue that consumers mind is easily shaped with positive perception when they are part of social platform communities. Furthermore, the more consumers active in a social platform, the more are sharing and engaging in a brand community. As a result, strong relationship between consumers and a brand could be created. This connection will lead consumers to be happy, satisfy with a brand. According to Heinonen, (2011), social media platform plays a crucial role in enhancing consumers’ relationship with a brand through a review that users normally share about a brand, products and even a brand service. The empirical studies have also demonstrated individuals be driven to share reviews that are good once they discover values of using a brand name item which easy for businesses to placing these values by way of a social media. Consumers tend to be high commitment to buy a product from a certain brand when there is a strong emotional attachment with a brand regardless the reasons behind their committed buy a brand
continuously and their satisfaction. Since the literature reveals that both social media activities as well as brand love have influence on brand loyalty phases, brand love is actually anticipated to get an indirect effect on the association between brand loyalty stages and social media activities (Lee and Workman, 2015). Thus,
H10. Brand love mediates the relationship between social media activities and cognitive brand loyalty
H11. Brand love mediates the relationship between social media activities and affective brand loyalty.
H12. Brand love mediates the relationship between social media activities and conative brand loyalty
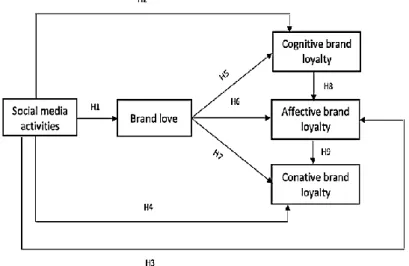
Figure 1 represent proposed relationships between antecedent variables namely social media activities and brand love with brand loyalty stages including cognitive, affective, and conative. In addition, the framework proposed the mediating role of brand love between social media activities and different stages of brand loyalty.
Figure 1: Conceptual model Research Method
This particular investigation is going to employ a questionnaire as the key information collection instrument. It consists of 6 components (i.e. social networking tasks, brad love, cognitive brand loyalty, affective brand loyalty, conative brand loyalty as well as demographics - gender, education, age, ethnicity as well as month household income).Respondents for the questionnaire have to answer two questions as a filter question which first include indicating the loved brand that offer fast fashion products in Malaysia such as Uniqlo, forever 21, Top Shop, Mango, H&M, and Zara then they answer the rest of questions based on
chosen brand. Second include question to make sure that respondents active in a social media and interact actively with a brand on a social platform. Social networking activities scale was adopted from (Kim and Ko, 2012), while brand love scope was adopted from Carroll and Ahuvia, (2006), and lastly brand loyalty phases adopted from (Oliver, 1999) . A questionnaire used 5 point Likert scale ranging between one = strongly disagree to five = strongly agree. The questionnaire was initially created in English and later converted to the Malay language which is the main language in Malaysia. Upon removing the uncompleted questionnaire, only 240 of questionnaire was eligible for analysis.
Results of the Study
Validity and Reliability of constructs: The validity of the construct analyzed by examining composite reliability, discriminant validity, and convergent validity (Aldholay et al., 2018). As mentioned earlier the value of Cronbach's alpha higher than 0.7 confirmed the reliability and internal consistency for all the constructs (Al-Jubari et al., 2018). For evaluating the convergent validity, we analyzed the mean of the average variance and outer loading. The outer loadings more than 0.5 are reflected substantial and spectacle convergence validity. Respectively, the average variance extracted (AVE) ought to be greater than 0.50 to show appropriate convergent validity. The results for reliability and AVE for the present study demonstrated satisfactory convergent validity. Results showed no collinearity issues between the variables since the values of Variance Inflation Factors (VIF) were all at the conventional level 0.2 to 5.0.
Discriminant Validity: The results for discriminant validity of the construct demonstrated in Table 1 which is in fact the Fornell-Larcker criterion matrix. The matrix showed that validity is achieved because the measure within column is not above the square root of the AVE (Mosbah et al., 2019).
Table 1: Discriminant validity by Fornell-Larcker Criterion Matrix
Construct AL BL CgL CnL SM
Affective Brand Loyalty 0.897
Brand Love 0.786 0.837
Cognitive Brand loyalty 0.756 0.739 0.856 Conative Brand Loyalty 0.758 0.734 0.778 0.837 social media marketing activities 0.434 0.441 0.375 0.411 0.785 Outcomes of Structural Model
The results of the hypothesized associations are tabularized in Table 2. It indicates that almost all the hypothesis H1, H3, H5, H6, H7, H8, H9 are supported except for H2 and H4. The rejected hypotheses stand for the associations of social media with cognitive and conative brand loyalty. H1 and H3 which stand for the association between social media and brand love as well as affective brand loyalty are supported since statistics measure was above 1.96 (Hair et al., 2016). The
associated t-statistics measures are 7.963 and 2.263, and the associated path coefficient values are 0.443 and 0.089, respectively. H5, H6, and H7 stand for the association between brand love and the three stages of brand loyalty. The associations are supported by t-statistics of 14.129, 0.470, as well as 0.348, respectively. Finally, H8 which suggest the relationship between conative brand loyalty and affective brand loyalty and also H9 which stand for the association between affective brand loyalty and Cognitive Brand loyalty, are supported, as the t-statistics measure are 5.609 as well as 5.985, respectively.
Table 2: Hypothesis Testing and Relationships Measurement
Hypothesis Path Path
coefficient(β) T Statistics P Values Decision H1 SM BL 0.443 7.963*** 0.000 Supported H2 SM Cgl 0.064 1.118 0.264 Not Supported H3 SM AL 0.089 2.263** 0.024 Supported H4 SM CnL 0.059 1.346 0.179 Not Supported H5 BL Cgl 0.712 14.129*** 0.000 Supported H6 BL AL 0.470 7.115*** 0.000 Supported H7 BL CnL 0.348 4.735*** 0.000 Supported H8 CgL AL 0.375 5.609*** 0.000 Supported H9 AL CnL 0.459 5.985*** 0.000 Supported
Mediating impact of brand love in the relationships between social media activities and stages of brand loyalty
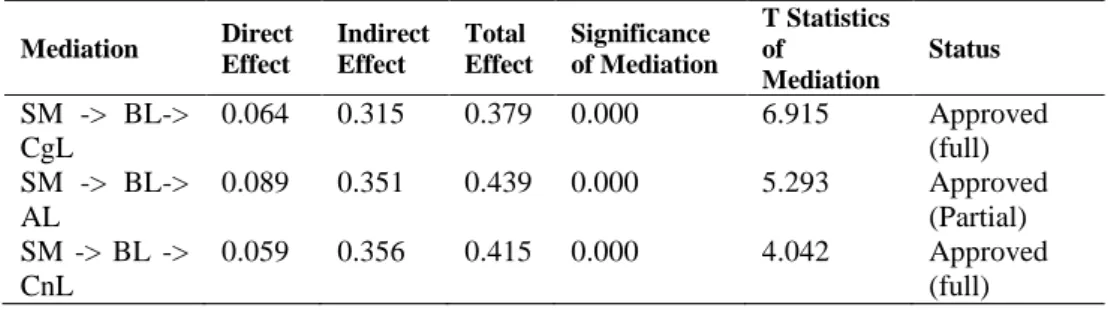
Different methods are actually offered to evaluate mediation effect; one of the widely used methods was suggested and enhanced by (Hayes and Scharkow, 2013), which are developed based on Sobel mediation process. Table 3 illustrates the results of the mediation evaluation.
Table 3. Mediation analysis results
Mediation Direct Effect Indirect Effect Total Effect Significance of Mediation T Statistics of Mediation Status SM -> BL-> CgL 0.064 0.315 0.379 0.000 6.915 Approved (full) SM -> BL-> AL 0.089 0.351 0.439 0.000 5.293 Approved (Partial) SM -> BL -> CnL 0.059 0.356 0.415 0.000 4.042 Approved (full)
As observed in the table, brand love mediates the relationships between social media activities and three constructs of cognitive brand loyalty. The three indirect relations are significant at level 1% (Sig = 0.000) with proper t statistic scores above 1.96. The mediation of BL between SM and CgL is accepted with indirect
effect of 0.315 and the mediation is full as the direct relation is not significant. The mediation of BL between SM and AL is accepted with indirect effect of 0.351 and the mediation is partial as the direct relation is not significant. The mediation of BL between SM and CnL is accepted with indirect effect of 0.356 and the mediation is full as the direct relation is not significant.
Concluding Remarks and Managerial Implications
The significant goal of the present study is to scrutinize the antecedences of three stages of brand loyalty toward fast fashion. In addition, to investigate the indirect impact of social media activities on the stages of brand loyalty through a mediating role of brand love. The current research supports the crucial role of social media in marketing and advertising which will assist internet marketers to fully realize brand love, and the loyalty behavior. The consequence of this particular study might assist marketers to develop the successful communication approach through social networking activities to shape good attitudes toward the brand. Present study contributes to the brand managing literature in different ways. First, the study develops promising information on the antecedents and outcomes of brand love. Next, it shows the concurrent effect of social media activities on a brand love and its impacts on a different stages of brand loyalty. Lastly, it shows the important role of brand love between social media activities and stages of brand loyalty. This result emphasize that social media marketing strategies have strong impact on users to fall in love with a particular brand which lead them to a different phases of brand loyalty.
The findings confirmed that social marketing activities have effect on brand love.Though the results showed that, the association between social network activities and cognitive brand loyalty and conative brand loyalty were rejected, which is inconsistent with the results of Ismail, (2017) that discovered that social network activities has impact on brand loyalty. However, in the previous studies, brand loyalty was considered as one construct, as well as the evaluation was on social media users without concentrating on any particular business. In contrast, the current study concentrates on the fast fashion industry and on active users on a social media which keenly using various information regarding the brands. The results indicate that consumers of fast fashion become loyal in case they have strong emotional connection with a brand. Marketing managers can create a brand community through social media. Social media users can share their brand experiences and confirm the values and establish their friendly relationships to brand with other members.
The present study has outstanding implications for managers. At the outset, the positive impact of social media activities on brand love, specifies that marketing managers should focus more on using social media marketing as a leading strategy to develop strong relationship with brand customers and convert this relationship to the brand love. Managers may device strategies by creating an interactive content in social media that engage the customers with a brand to build the love between
consumers and a brand. Moreover, it is crucial that managers maintain the consistency of their messages through a social media as well as updating the social media content which may lead to more customer’s engagement and more feeling of love to the brand.
The results indicate that consumers which express their love to the brands have more tendencies to be loyal to the brands. Based on this finding, it can be state that managers may improve strategies to develop the relationship with the customers by different methods for instance, appreciation and offering special gift, vouchers, and discount coupons for the brand customers. These kinds of activities develop more feeling of love towards the brand and therefore, a customers’ intention to be loyal to the brand may increase. There are many methods that help marketing managers to improve brand love and maintain the love feeling for the customer over long time. For instance, researchers suggest that marketing managers need to pay attention to use design and packaging techniques that have been shown to create a strong sense of desire. Marketers can create positive emotional associates with the brand which includes a feeling of rightness about the brand. This may be attained by providing the brand with a sense of its history, founders, and corporate culture, so that customers feel a sense of connection about it. Marketing managers need to develop more connection with consumers through social media, and getting customers feedback and opinions. The excessive customer’s engagement with the brand developed more trust and this make social media platform as an appreciated and trusted resources, of advice and opinions for the brands.
The last finding of the study the effective mediating role of brand love between social media activities and different brand loyalty stages. Therefore, mangers are required to emphasize on maintaining strong emotional relationship with customers through social media platform, since continuing emotional connection with customers have a crucial role on the link between social media and brand loyalty. Different social media strategies accompanied by effective customer relationship management may help managers to maintain strong relationship with customers which in turn, concludes in stronger brand love. Customers who fall in love with a brand are more likely to be loyal to the brand which in long run has an impact on a company images to sustain competitive advantage in the fast fashion industry and growing marketplace.
Declaration of conflicting interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding
The authors received financial support for the research and publication from management and science university through research management centre (RMC) under the project code of SG-027-022018-FBMP-20180710001.
References
Adler, N.J. (1983). A typology of management studies involving culture. Journal of International Business Studies, 14(2), 29-47.
Aerts, G., Smits, T., & Verlegh, P.W.J. (2017). The platform shapes the message: How website design affects abstraction and valence of online consumer reviews. Decision Support Systems, 104, 104-112.
Akar, E., Topçu, B. (2011). An examination of the factors influencing consumers’ attitudes toward social media marketing. Journal of Internet Commerce, 10(1), 35-67.
Al-Jubari, I., Hassan, A., & Liñán, F. (2018). Entrepreneurial intention among University students in Malaysia: integrating self-determination theory and the theory of planned behavior. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 1-20.
Aldholay, A.H., Isaac, O., Abdullah, Z., & Ramayah, T. (2018). The role of transformational leadership as a mediating variable in DeLone and McLean information system success model: The context of online learning usage in Yemen. Telematics and Informatics, 35(5), 1421-1437.
Bandyopadhyay, S., Martell, M. (2007). Does attitudinal loyalty influence behavioral loyalty? A theoretical and empirical study. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 14(1), 35-44.
Biedenbach, G., Bengtsson, M., & Marell, A. (2015). Brand equity, satisfaction, and switching costs: An examination of effects in the business-to-business setting. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 33(2), 164-178.
Carroll, B.A., Ahuvia, A.C. (2006). Some antecedents and outcomes of brand love. Marketing Letters, 17(2), 79-89.
Drennan, J., Bianchi, C., Cacho-Elizondo, S., Louriero, S., Guibert, N., & Proud, W. (2015). Examining the role of wine brand love on brand loyalty: A multi-country comparison. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 49, 47-55.
Hair Jr,J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage Publications.
Hayes, A.F., Scharkow, M. (2013). The relative trustworthiness of inferential tests of the indirect effect in statistical mediation analysis: Does method really matter? Psychological Science, 24(10), 1918-1927.
Heinonen, K. (2011). Consumer activity in social media: Managerial approaches to consumers’ social media behavior. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 10(6), 356-364. Ismail, A.R. (2017). The influence of perceived social media marketing activities on brand
loyalty The mediation effect of brand. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 29(1), 129-144.
Kim, A.J., Ko, E. (2012). Do social media marketing activities enhance customer equity? An empirical study of luxury fashion brand. Journal of Business Research, 65(10), 1480-1486.
King, R.C., Schilhavy, R.A.M., Chowa, C., & Chin, W.W. (2016). Do customers identify with our website? The effects of website identification on repeat purchase intention. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 20(3), 319-354.
Lee, S.H., Workman, J.E. (2015). Determinants of brand loyalty: construal, self-expressive brands, and brand attachment. International Journal of Fashion Design, Technology and Education, 8(1), 12-20.
Moro, S., Rita, P., & Vala, B. (2016). Predicting social media performance metrics and evaluation of the impact on brand building: A data mining approach. Journal of Business Research, 69(9), 3341-3351.
Mosbah, A., Ali, M.A.M., Hizam Aljubari, I., Talib, Z.M., & Rehman Sherief, S. (2019). Migrants in the High-Tech and Engineering Sectors: An Emerging Research Area. Proceedings - 2018 IEEE Conference on Systems, Process and Control, ICSPC 2018, (December), 234-237.
Oliver, R.L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? The Journal of Marketing, 63(Special Issue), 33-44.
Pandir, B., Yasin, B. (2017). Brand love and customer engagement’s role over brand loyalty. Journal of Management, Marketing and Logistics (JMML), 4(4), 359-365. Romero, J., Yagüe, M.J. (2016). Marketing assets: Relating brand equity and customer
equity. Intangible Capital, 12(2), 591-618.
Salem, S.F., Salem, S.O. (2018). Self-Identity And Social Identity As Drivers Of Consumers ’ Purchase Intention Towards Luxury Fashion Goods And Willingness To Pay Premium Price. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 23(2), 161-184.
Salem, S.F., Salem, S.O. (2019). Effects of Social Media Marketing and Selected Marketing Constructs on Stages of Brand Loyalty. Global Business Review, 0972150919830863.
Theng So, J., Grant Parsons, A., & Yap, S.-F. (2013). Corporate branding, emotional attachment and brand loyalty: the case of luxury fashion branding. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal, 17(4), 403-423.
Zheng, X., Cheung, C.M.K., Lee, M.K.O., & Liang, L. (2015). Building brand loyalty through user engagement in online brand communities in social networking sites. Information Technology & People, 28(1), 90-106.
WPŁYW POLUBIENIA MARKI NA MEDIA SPOŁECZNE I ETAPY LOJALNOŚCI MARKI
Streszczenie: Głównym celem badań zaprezentowanych w artykule jest zaproponowanie i zbadanie modelu koncepcyjnego, który integruje działania w mediach społecznościowych w zakresie przywiązania do marki i lojalności wobec marki. Proponowany model został przeanalizowany na próbie 240 konsumentów przy użyciu samoorganizującej się ankiety. PLS -SEM zastosowano do analizy statystycznej, aby ocenić „zauroczenie” w obszarze powiązania między zmiennymi. Wyniki pokazują, że marketing społecznościowy ma ogromny wpływ na przywiązanie do marki w odniesieniu do szybko zmieniającej się mody. Co więcej, odkrycie pokazuje, że media społecznościowe mają pośredni wpływ na kształtowanie różnych fazy lojalności wobec marki poprzez przywiązanie do marki. Przedstawione badania potwierdzają kluczową rolę mediów społecznościowych w marketingu i reklamie, która pomoże sprzedawcom internetowym w pełni wykorzystywać przywiązanie do marki i pogłebiać zachowania lojalnościowe. Wynik tego badania może pomóc marketingowcom w opracowaniu skutecznego podejścia do komunikacji poprzez działania w sieciach społecznościowych w celu kształtowania dobrych postaw i promowania lojalności wobec marki, szczególnie w obszarze szybko zmieniającej się mody.
Słowa kluczowe: społeczny marketing internetowy, lojalność wobec marki, szybka moda, polubienie marki
品牌爱对社交媒体和品牌忠诚度的影响 抽象。当前研究的主要目的是提出和研究一个概念模型,该模型将社交媒体活动和品 牌热作为先验,并将品牌忠诚阶段作为品牌热的结果进行整合。通过使用自组织问卷 调查技术,对240个快时尚消费者的样本进 行了分析。PLS-SEM用于统计分析,以评估变量之间的催眠联系。结果表明,社交网络营销对快时尚 行业的品牌热爱产生巨大影响。此外,研究结果表明,社交媒体通过品牌热爱对品牌 忠诚度的各个阶段具有间接的建设性作用。当前的研究支持社交媒体在营销和广告中 的关键作用,这将有助于互联网营销人员充分实现品牌爱和忠诚行为。这项特殊研究 的结果可能会帮助营销人员通过社交活动发展成功的沟通方法,以塑造良好的态度并 提高品牌忠诚度,特别是在快时尚行业。 关键字:社交网络营销,品牌忠诚度,快速时尚,品牌热爱