Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and HOMO–LUMO analysis of (E) N′ (3 hydroxy 4 methoxybenzylidene)nicotinohydrazide monohydrate
Full text
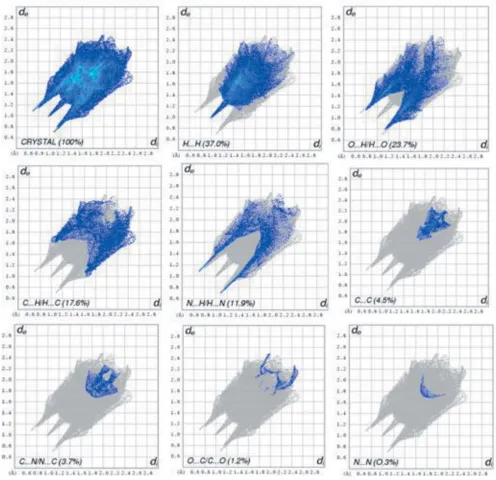
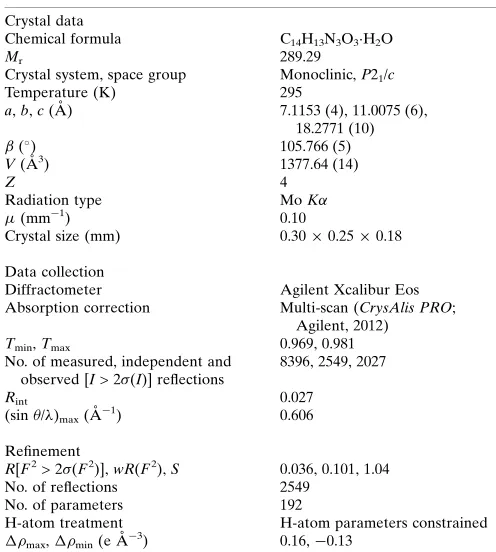
Figure
Related documents
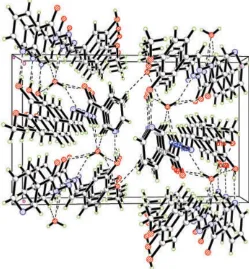
The hydroxy group forms the usual S(5) hydrogen bond with the central carboxylate group, and the water molecule acts as a donor in two strong hydrogen bonds (2.686 and 2.662 A ˚ )..
The amine-N4—H atoms form a hydrogen bond to a carboxylate-O1 atom and to a water molecule and at the same time accept a hydrogen bond from an amino-H atom, this being the only N—H
The crystal structure is stabilized by intermolecular hydrogen bonds involving the cyclam N—H groups and water O—H groups as donor groups, and the O atoms of the Cr2O7 2 anion
O—H O hydrogen bonds involving the coordinating O W 1 water molecule as donor group and the solvent O W 2 molecule as both acceptor and donor groups consolidate the anionic
Both amine donor functions as well as both H atoms of the water molecule are involved in hydrogen bonds with the two pyridine ring N atoms and the water molecule acting as
The packing in the crystal structure of (I) involves not only hydrogen bonds of the type N—H O between urea amino donor groups and the O acceptor atoms of carbonyl groups, the
The water molecule serves both as acceptor and donor for efficient hydrogen bonds involving N—H and C O functional groups as donor and acceptor groups, respectively.. As a result,
Each cation acts as a threefold donor using all its NÐH bonds, each anion acts as a fourfold acceptor with atom O1 accepting two hydrogen bonds and atoms O2 and N1 accepting one