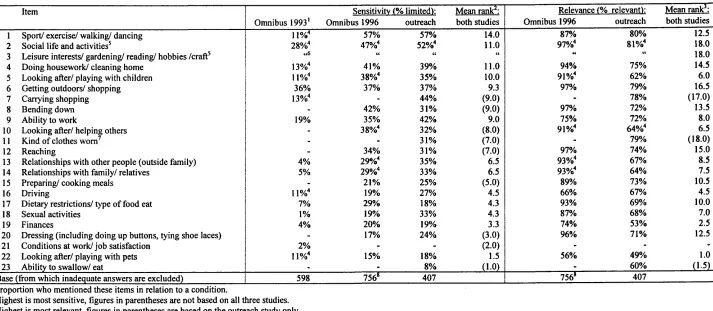
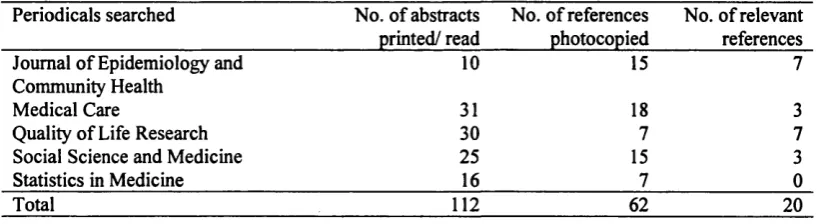
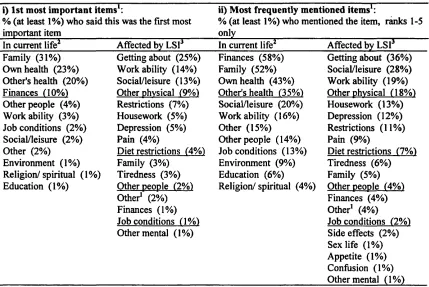
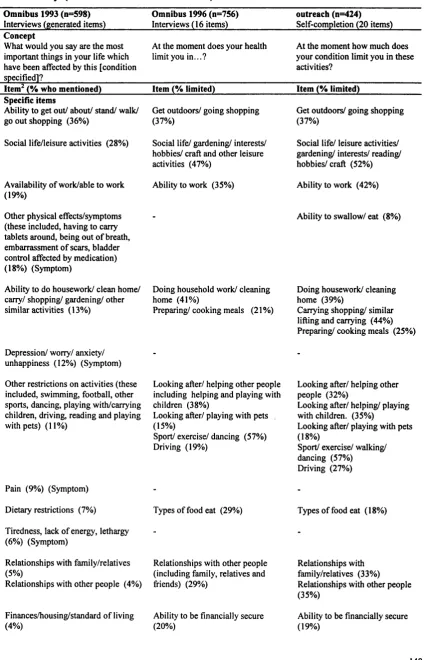
Measuring the quality of life of patients in ambulatory care, in relation to their medical condition or illness
Full text
Figure

Related documents
We show that because perception effects may have lingering long-term deleterious impacts on both the supply- cost of resources to a region and willingness to pay for regional
Recently, the interaction of a high intensity laser pulse with a nanometer thin foil has raised great interest as it promises the creation of a dense, attosecond short,
Figure 14A and B indicates that the serum ALT and AST of healthy ICR mice treated with 20,000 nmol/ kg of HMCEF are at the same level as that of healthy ICR
JEL-Classification: H2, H4. Keywords: marginal cost of public funds, Pigou effect, revenue effect, Ramsey taxation, public good. 34) claims that the social marginal cost of the
After normalization for lung size, changes in lung dimensions between inspiration and expiration were used for analysis; normalization was based on the cranial-caudal length
Graphs showing the percentage change in epithelial expression of the pro-apoptotic markers Bad and Bak; the anti-apoptotic marker Bcl-2; the death receptor Fas; the caspase
was associated with lower physical quality of life among earthquake and flood survivors in Iran and China, [26, 56] lower physical functioning in Iran, Rwanda, and Syrian refugees
The sample size calculation focused on detecting a higher incidence of complications (serious and/or postoperative) among laparoscopic sterilization patients, compared to