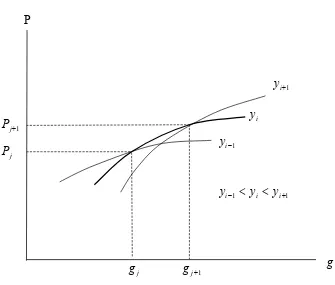
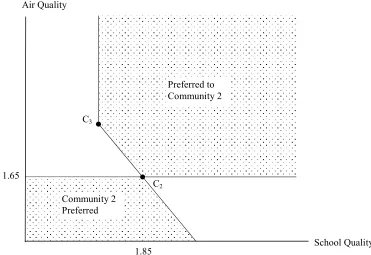
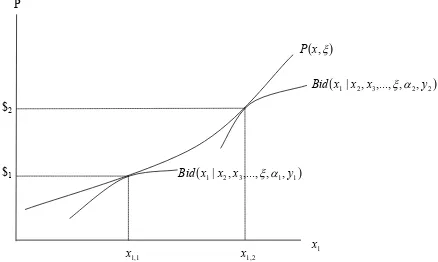
Recovering Preferences for Public Goods from a Dual-Market Locational Equilibrium
Full text
Figure


Related documents
A 180-degree offset has a pressure drop equal to about forty (40) lineal feet of flexible duct.. 2) These multipliers apply to airway sizing tools (friction chart or slide rule)
We think that the different approaches undertaken at a regional level, combined with other initiative regarding harmonization of rules (balancing, allocation of capacity,
Real nondefense spending for government, which accounts for the spending on salaries of Government employees and on administrative expenses of all Federal nondefense programs,
Among service occupations, the largest number of new jobs is expected to arise in healthcare support
The alternative source data used include data published by the Energy Information Administration ( EIA ), and data from the Consumer Price Index ( CPI ), which is produced by the
Where possible we try to repeat the pre-test at the post-test phase so that we can match pairs (i.e., the same professional) of data and calculate outcomes. Generally, the
Tato bakalářská práce se zabývá analýzou spánku pomocí telefonu a návrhem inteligentního budíku pro platformu Bada.. V úvodní části je rozebrána problematika
Comparing elements of the Workers’ Compensation database with data from the Survey of Occupational Injuries and Illnesses is a useful way to determine which types of injuries