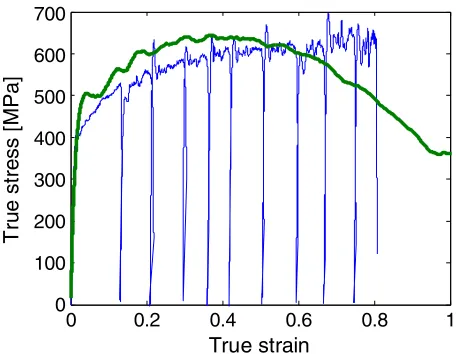
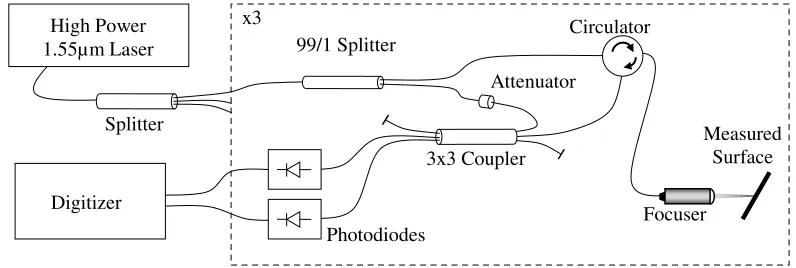
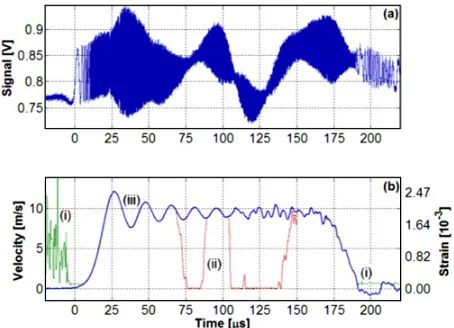
Eliminating the thermal softening of dynamically loaded specimens in the Kolsky bar system by multi-step loading
Full text
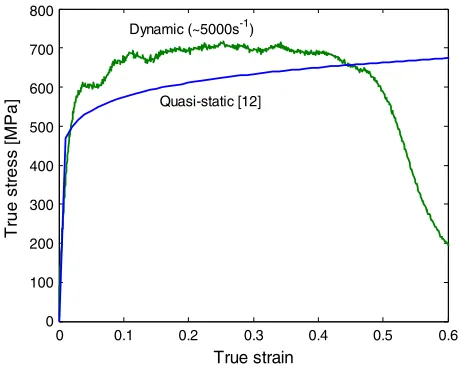
Figure
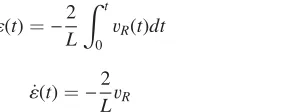
Related documents
diagnosis of heart disease in children. : The role of the pulmonary vascular. bed in congenital heart disease.. natal structural changes in intrapulmon- ary arteries and arterioles.
It was decided that with the presence of such significant red flag signs that she should undergo advanced imaging, in this case an MRI, that revealed an underlying malignancy, which
In Afghanistan, this is a qualification through either the Institute of Health Sciences or the Community Midwifery Education programme.. Skilled
Conclusion: It has been found transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) on bilateral ST36 acupoints have an effect to control plasma glucose level for type 2
You are being asked to participate in a research study titled “Exercise Identity and Self-Presentational Responses to a six-week Physical Activity plus Imagery Intervention. ” The
In this study, we investigated the impact of GFR-Matrigel from different sources and xeno-free culturing conditions (E-8 medium and Vitronectin) on BMEC differentiation
Root mean squared (RMS) differences var- ied from 4.75 m, when compared to a densely gridded air- borne dataset over the Siple Coast region of West Antarctica to 33.78 m when
Combined with phylogenetic tree reconstruction of diverse eukaryotic, archaeal and bacterial DHH subfamilies, this analysis yields a complex scenario of RecJ family evolution in