International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013)
308
Survey On Cloud Computing
Heena I. Syed
1, Naghma A. Baig
21,2Jawaharlal Darda Institute of Engineering & Technology,
Yavatmal,M.S., India.
1kauser.heena853@gmail.com
2naghmabaig@gmail.com
Abstract—Cloud computing is an Internet-based computing, where resources, software and information are shared and provided to computers and devices as per their demands. Cloud computing is the use of computing resources that are delivered as a service over a network (Internet).Cloud computing allows remote services with a user's data, software and computation. It increase capacity of networks without having a new infrastructure. Cloud is made up of large numbers of servers. Cloud contains the vast amount of information. It also provides the variety of services to the peoples.
Keywords— Cloud computing, architecture, benefits, Deployment model & Service models.
I. INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing is a type of computing that relies on Sharing. In cloud computing, the word ―Cloud‖ is used as a metaphor for the internet. Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the Internet. Cloud services allow individuals and businesses to use software and hardware that are managed by third parties at remote locations.
[image:1.612.371.517.262.412.2]Cloud computing is not something that suddenly appeared overnight; in some form it may trace back to a time when computer systems remotely time-shared computing resources and applications.More currently though, cloud computing refers to the many different types of services and applications being delivered in the internet cloud, in many cases, the devices used to access these services and applications do not require any special applications.
Fig 1. Cloud computing
II. CLOUD COMPUTING ARCHITECTURE
Cloud computing architecture, is just like any other system, which is categorized into two main sections : i.e. Front End and Back End.
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013)
[image:2.612.65.268.305.447.2]309 Cloud architecture, the systems architecture of the software systems involved in the delivery of cloud computing, typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other over a loose coupling mechanism such as a messaging queue.There are several major cloud computing providers including Amazon, Google, Yahoo, Microsoft and others that are providing cloud computing services (Figure shows current cloud providers).Cloud computing providers provide a variety of services to the customers and these services include e-mails, storage, software-as-a-services, infrastructure-as-aservices etc.
Fig 2.Cloud Computing Provider
III. CLOUDCOMPUTINGCHARACTERISTICS
Cloud computing has variety of characteristics which are explain below:
• Cost: Cloud computing is cost-effective. Here, cost is
greatly reduced as initial expense and are much lower than
traditional computing.
• Virtualization: Technology allows servers and storage devices to be shared and utilization be increased.
• Reliability: It is improved if multiple redundant sites are used, which makes well-designed cloud computing suitable for business continuity.
• Security: Could improve due to centralization of data, increased security-focused resources.
• Maintenance: Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier, because they do not need to be installed on each user's computer and can be accessed from different places.
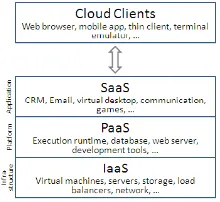
IV. CLOUD COMPUTING SERVICE MODELS
Cloud computing service models are
classified into 3 main categories: 1. Infrastructure as-a-Service(IaaS)
2. Platform as-a-Service(PaaS)
3. Software as-a-Service(SaaS)
[image:2.612.395.505.410.511.2]IaaS : In IaaS model , the cloud user patches and maintains the operating systems and the application software. IaaS offer computers - physical or virtual machines and other resources. It also offer additional resources such as file-based storage, firewalls, IP addresses, virtual local area network (VLANs), and software bundles.IaaS cloud providers supply these resources on-demand from their large pools installed in data centers.Infrastructure as a Service is sometimes referred to as Hardware as a Service (HaaS). Examples of IaaS providers include :Windows Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine, HP Cloud, iland, Joyent , Oracle Infrastructure as a Service.
Fig 3.Cloud computing service models
PaaS: In the PaaS model, cloud providers deliver a computing platform typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server.
Application developers can develop and run
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013)
310 3. SaaS: In the SaaS model, cloud providers install and operate application software in the cloud and cloud users access the software from cloud clients. The cloud users do not manage the cloud infrastructure and platform on which the application is running. This eliminates the need to install and run the application on the cloud user's own computers simplifying maintenance and support. What makes a cloud application different from other applications is its scalability. This can be achieved by cloning tasks onto multiple virtual machines at run-time to meet the changing work demand. Load balancers distribute the work over the set of virtual machines.This process is transparent to the cloud user who sees only a single access point.It is common to refer to special types of cloud based application software with a similar naming convention: desktop as a service,business process as a service, test environment as a service, communication as a service.The pricing model for SaaS applications is typically a monthly or yearly flat fee per user, so price is scalable and adjustable if users are added or removed at any point.Examples of SaaS include: Google Apps, Microsoft Office 365, Onlive, GT Nexus, Marketo, and TradeCard.
V. CLOUD COMPUTING DEPLOYMENT MODELS
Deploying cloud computing can differ depending on requirements, and the following four deployment models have been identified,each with specific characteristics that support the needs of the services and users of the clouds in particular ways (see Figure).
Private Cloud — The cloud infrastructure has been deployed, and is maintained and operated for a specific organization. The operation may be in-house or with a third party on the premises.
Community Cloud — The cloud infrastructure is shared among a number of organizations with similar interests and requirements. This may help limit the capital expenditure costs for its establishment as the costs are shared among the organizations. The operation may be in-house or with a third party on the premises.
Public Cloud — The cloud infrastructure is available to the public on a commercial basis by a cloud service provider. This enables a consumer to develop and deploy a
service in the cloud with very little financial outlay compared to the capital expenditure requirements normally associated with other deployment options.
[image:3.612.378.507.304.380.2]Hybrid Cloud — The cloud infrastructure consists of a number of clouds of any type, but the clouds have the ability through their interfaces to allow data and/or applications to be moved from one cloud to another. This can be a combination of private and public clouds that support the requirement to retain some data in an organization, and also the need to offer services in the cloud.
Fig 4.Cloud computing types.
VI. BENEFITS
The following are some of the possible benefits for those
who offer cloud computing-based services and
applications:
Cost Savings — Companies can reduce their capital expenditures and use operational expenditures for increasing their computing capabilities. This is a lower barrier to entry and also requires fewer in-house IT resources to provide system support.
Scalability/Flexibility — Companies can start with a small deployment and grow to a large deployment fairly rapidly, and then scale back if necessary. Also, the flexibility of cloud computing allows companies to use extra resources at peak times, enabling them to satisfy consumer demands.
Reliability — Services using multiple redundant sites can support business continuity and disaster recovery.
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013)
311
Mobile Accessible — Mobile workers have increased productivity due to systems accessible in an infrastructure available from anywhere.
VII. APPLICATIONS
Google — Has a private cloud that it uses Google — Has a private cloud that it uses for delivering many different services to its users, including email access, document applications, text translations, maps, web analytics, and much more.
Microsoft — Has Microsoft® Sharepoint® online service that allows for content and business intelligence tools to be moved into the cloud, and Microsoft currently makes its office applications available in a cloud.
Salesforce.com — Runs its application set for its customers in a cloud, and its Force.com and Vmforce.com products provide developers with platforms to build customized cloud services.many different services to its users, including email access, document applications, text translations, maps, web analytics, and much more.
Microsoft — Has Microsoft® Sharepoint® online service that allows for content and business intelligence tools to be moved into the cloud, and Microsoft currently makes its office applications available in a cloud.
[image:4.612.57.279.558.671.2]Salesforce.com — Runs its application set for its customers in a cloud, and its Force.com and Vmforce.com products provide developers with platforms to build customized cloud services.
Fig 5.Cloud computing applications
VIII. CONCLUSION
In this paper the cloud computing architecture contains the cloud computing providers, which provide cloud computing services. In future these cloud provider will offer s the security for cloud. We believe the Cloud offers Small and Medium Businesses major potential security benefits. Frequently SMBs struggle with limited or non-existent in-house INFOSEC resources and budgets. Cloud computing is a combination of several key technologies that have evolved and matured over the years. Cloud computing has a potential for cost savings to the enterprises but the security risk are also enormous. Although Cloud computing can be seen as a new phenomenon which is set to revolutionize the way we use the Internet, there is much to be cautious about. There are many new technologies emerging at a rapid rate, each with technological advancements and with the potential of making human’s lives easier in which cloud computing is one of them. Everyone in the IT sector speaks about cloud computing however this concept is still unclear to many. In this paper we have made efforts to clear the basic concepts of cloud computing. We have brought some light on the applications, characteristics, and deployments models of cloud computing. Further future reading of cloud computing will give us some more light on security and its implementation issues.
REFERENCES
[1] Monaco, Ania (7 June 2012 [last update]). "A View Inside the Cloud" (http:/ / theinstitute. ieee. org/ technology-focus/ technology-topic/a-view-inside-the-cloud). theinstitute.ieee.org (IEEE).. Retrieved August 21, 2012.
[2] "Baburajan, Rajani, "The Rising Cloud Storage Market Opportunity Strengthens Vendors," infoTECH, August 24, 2011" (http:/ / it. tmcnet.com/ channels/ cloud-storage/ articles/ 211183-rising-cloud-storage-market-opportunity-strengthens-vendors. htm). It.tmcnet.com.2011-08-24. . Retrieved 2011-12-02.
[3] "Oestreich, Ken, "Converged Infrastructure," CTO Forum, November 15, 2010" (http:/ / www. thectoforum. com/content/converged-infrastructure-0).Thectoforum.com. 2010-11-15. . Retrieved 2011-12-02.
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013)
312
[5] "Defining "Cloud Services" and "Cloud Computing"" (http:/ / blogs. idc. com/ ie/ ?p=190). IDC. 2008-09-23. . Retrieved 2010-08-22. [6] "Is a Private Cloud Really More Secure?" (http:/ / www. dell. com/
Learn/ us/ en/ rc956904/ large-business/ private-cloud-more-secure).Dell.com. . Retrieved 07-11-12.
[7] "VMware Launches Open Source PaaS Cloud Foundry" (http:/ / www. cmswire. com/ cms/ information-management/vmware-launches-open-source-paas-cloud-foundry-010941. php). Simpler Media Group, Inc.. 2011-04-21. . Retrieved 2012-12-14.
[8] Armbrust, M; Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A., Katz, R., Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D., Rabkin, A., Zaharia, (2010). "A view of cloud computing". Communication of the ACM 53 (4): 50–58. doi:10.1145/1721654.1721672.
AUTHOR’S PROFILE
Heena I. Syed is a Candidate of Bachelor of Engineering (BE.) of the Department Of Computer Science(3rd Year), Jawaharlal Darda
Institute Of Engineering &Technology, Yavatmal,Maharashtra,India She Received Diploma Of Computer Engineering in 2011 From Agnihotri School of Technology,Wardha,M.S,India.She is especially interested in Cloud Computing.