Evaluating the Performance of Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands Using Natural Zeolite (escott)
Full text
Figure

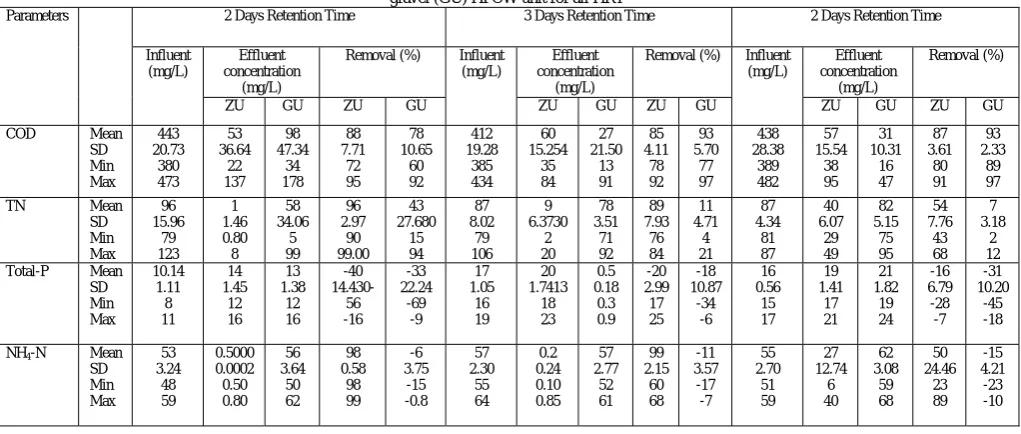

Related documents
In this paper, we extend our previous work by providing: (i) a more detailed discus- sion on the formal model to ensure the best provision of SFCs in face of dynamic changes in
Field experiments were conducted at Ebonyi State University Research Farm during 2009 and 2010 farming seasons to evaluate the effect of intercropping maize with
After classification of urban streets into number of classes, direction wise average travel speed on street segments during both peak and off peak hours were clustered using ANN
The difference between the analytical and numerical solutions using a first-order control volume (CV) discretisation and a second-order piecewise-linear Galerkin (P1) discretisation
higher temperatures than participants who drink their coffee with milk. Similarly,
To make the present CrowdSen- Sim 2.0 simulator more oriented to the algorithmic side rather than energy consumption of MCS systems, we implemented the Simulator Engine in a way
Since this area has not yet been explored with the transgender population, a qualitative study design is recommended, whereby a case study can be conducted with
For example families living on stations or in remote communities accepted that their children would have to study through some form of Distance Education, and then leave home to