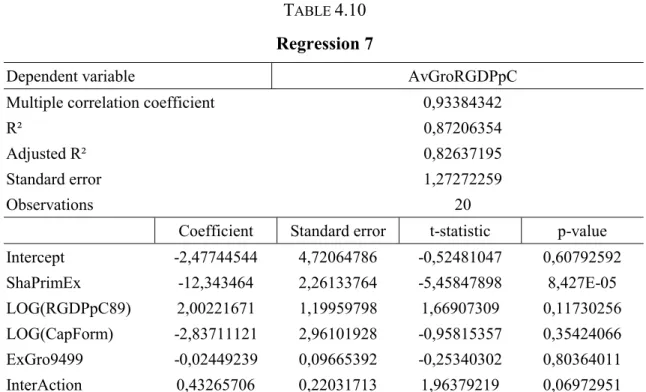
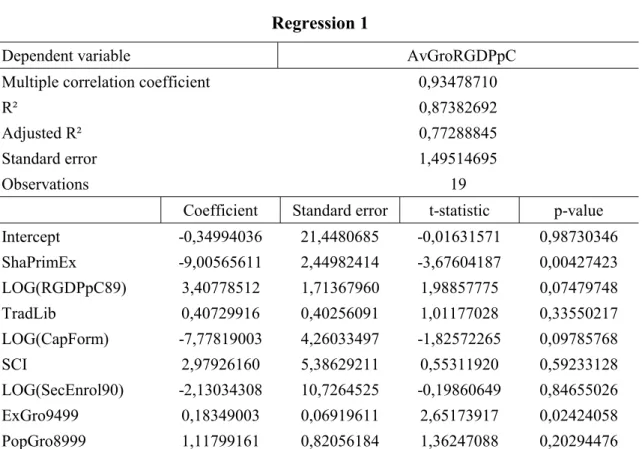
The Curse Of Natural Resources In The Transition Economies
Full text
Figure



Related documents
To address these issues we develop simple rent seeking and conflict models, and explore how resource abundance and pointiness affect the incentives of agents to divert resources
However, the more exogenous measure of resource abundance (stock of natural capital) has a significant negative effect on income per capita even after controlling for geography,
Our OLS results indicate that natural resource abundance has a positive effect on human development, since the coefficients for the net exporters of natural resources are positive and
Based on the panel data, countries exhibited conditional convergence (Table 3) implying that the annual GDP growth rates bear negative relationship with the GDP per capita of
It is evident from the third row of the Table 1 that resource abundance increases the incentives to invest in political capital, and since high investment in political capital
The figure covers 85 countries, and shows a scatterplot of economic growth per capita from 1965 to 1998 and natural resource abundance as measured by the share of natural capital
constant GDP per capita growth annual percent, is used as proxy of growth in per capita income Base Lending Rate which is the charge on the customer by banks for borrowing money
Controlling for GDP per capita, we found the share of VAA in percent of GDP to be significantly higher in transition countries than in developing countries for 1991 (+12.8