Fiscal and Monetary Policy Interactions in Pakistan Using a Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Framework
Full text
Figure
Related documents
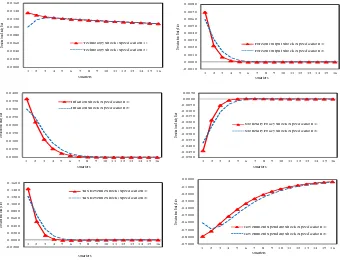
To examine the nature and the effect of fiscal and monetary policy interactions on output, the study interacted fiscal policy variable (government expenditure) and monetary
Because the committees and the Government support different target values of inflation, output and the deficit, and monetary and fiscal policy are not necessarily
Paal, on the contrary assumes that at the time of the reform the government, by com m itting to a non-contingent inflation target, leaves both the volume of
For this purpose we have included in our reaction function: the output gap, inflation, lagged interest rate, exchange rate and trade deficit as monetary policy objectives, while
Under aggressive inflation targeting regime (like in monetary unions), the policy combination of active monetary policy and passive fiscal policy (depicting monetary dominance)
If the monetary authority internalizes government misbehavior, the optimal policy rule involves the targeting of union-wide fiscal stance, on top of inflation and output gap..
Specifically, it will be tested whether output growth and inflation declines following a contractionary monetary policy shock, whether the reaction of output growth to
Whether this estimated DSGE model approximately accounts for the empirical evidence concerning the monetary transmission mechanism in a small open economy is determined by