Training on Synthetic Noise Improves Robustness to Natural Noise in Machine Translation
Full text
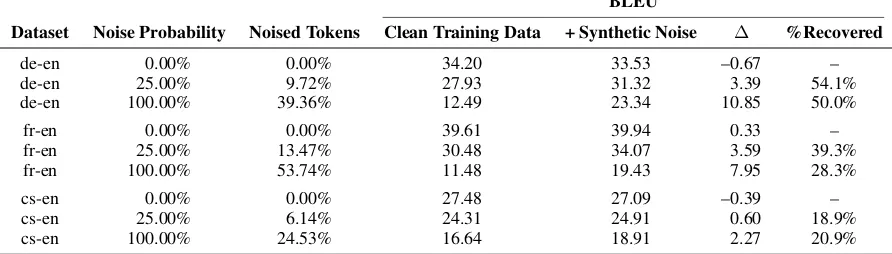
Figure
Related documents
CUNI’s submission ( Helcl et al. , 2019 ): They participated in Eng → Fra and Fra → Eng direc- tions, following a classical two stage approach, i) training of a base model using a
The basic idea is to introduce evaluation metrics as loss functions and assume that the opti- mal set of model parameters should minimize the expected loss on the training data.. Let
We use about 10K sentences (180K words) of manual word alignments which were created in house using part of the NIST MT-08 training data 3 to train our baseline reordering model and
Concept Equalization to Guide Correct Training of Neural Machine Translation Proceedings of the The 8th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, pages 302?307,
translation of the input sentence, and if the model is any good, better translations will have higher probabilities. Training models that will yield good probabilities
We then viterbi-align the part-of-speech tagged parallel corpus, using translation parameters obtained via Model 1 training of word segmented Arabic and symbol-tokenized English,
(3) We bootstrap the NN training using Viterbi word alignments obtained from the HMM and IBM model training, and use the trained neural models to generate new alignments.. The
We further develop a multi-dialectal word seg- mentation model, which we train on the Arabic side of the multi-dialectal training data, which consists of Qatari Arabic, Egyptian