Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Normal Pediatric Spinal Cord Using an Inner Field of View Echo Planar Imaging Sequence
Full text
Figure
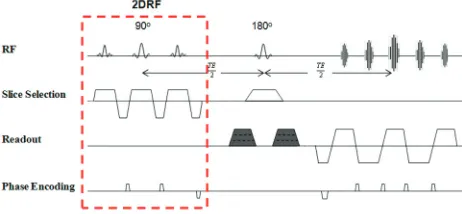



Related documents
Because there are no published reliability data on the DTI technique in children of any age with SCI and because children younger than of 6 years of age cannot participate in the
Fiber tracking performed on the spinal cord showed the main white matter tracts (posterior corticospinal tracts with nerve root visualization and posterior cordonal tracts) in
Our preliminary experience shows that limiting data acqui- sition to spinal cord quiescence increased the fraction of spinal cord voxels for which the first eigenvector of the
When a more robust protocol and thus more robust data is available, a broader comparison in grey matter to spinal cord ratio and anterior to posterior nerve root diameter
Fractional anisotropy ( A ) and mean diffusivity ( B ) values for regions of interest at different levels of the medulla oblongata and spinal cord for healthy controls and patients
Region-specific impairment of the cervical spinal cord (SC) in amyotrophic lat- eral sclerosis: A preliminary study using SC templates and quantitative MRI (diffusion tensor
