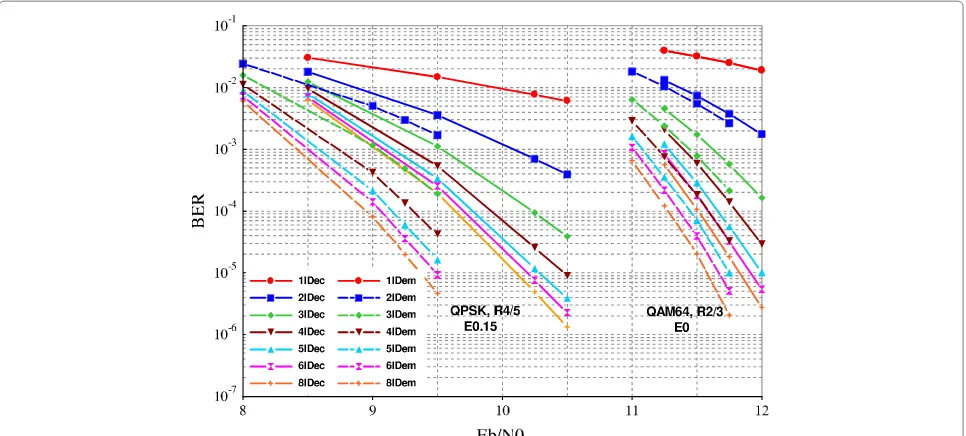
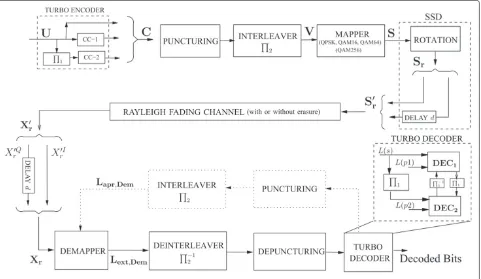
Complexity adaptive iterative receiver performing TBICM-ID-SSD
Full text
Figure



Related documents
The above flowchart shows the general approach to seismic trace inversion, which involves a geological model, a seismic volume and an inversion algorithm.. We can apply the method
(Only required if the drive installation bracket requires relocating) Remove the screw holding the bracket in place on the reverse side using a Philips head screw driver
Use IOmeter and configure a 64KB random read to test the SAMBA read performance. The average read is 11.4MB/s without the SSD cache; and the average read with the SSD cache enabled
SSD as a Read Cache Layer allows for the combined use of HDD and SSD technology to service the same block of data depending on the pattern of access?. Targeted usage allows
270 MB/s Read - Sequential Transfer MB/s @ 128K blocks 260 MB/s Write - Sequential Transfer MB/s @ 128K blocks Random Read IOPS @ 4K blocks: up to 30K. Random Write IOPS @ 4K blocks:
key expressions: expr: _col1 type: int sort order: - tag: -1 value expressions: expr: _col0 type: string expr: _col1 type: int expr: _col2 type: int Reduce Operator Tree:.
Data Polling container writes to MongoDB New data automatically synced to ES Space Client writes new data to the space.. Christos Erotocritou
By leveraging the superior random access performance of Solid State Drives (SSD), Synology SSD Cache technology provides a solution to enterprise challenges which boosts read and