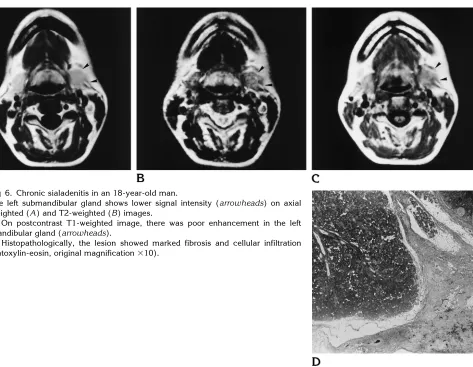
MR of the submandibular gland: normal and pathologic states
Full text
Figure



Related documents
CAPNON should be con- sidered in the imaging differential diagnosis when a heavily calcified lesion is found on CT, with hypointensity on T1- weighted and T2-weighted MR images,
A , Axial T2-weighted image shows a cobblestone cerebral cortex with hypomyelination of the white matter.. A , Axial T2-weighted image shows undersulcation of the frontal
3 Sagittal FS T1-weighted direct MR arthrographic images ( a , b ), coronal FS T1-weighted direct MR arthrographic image ( c ), and axial FS T1- weighted direct MR arthrographic
a Sagittal T2-weighted MR image demonstrates a prevertebral cystic lesion ( arrow ) b Coronal MIP image shows giant cisterna chyli at con- fluence of left and right markedly
C, T1·weighted axial MR image, SE 438/16/4, shows left frontal lobe region with central region of intermediate signal intensity and surrounding area of decreased signal
Figure 2 a-d: a-b: Axial and coronal plane T2 weighted c: axial plane T1 weighted sequence, the mass in the masseter muscles, heterogeneous signal intensity on T1 and T2
MR images in the axial plane show the fatty nature of the lesion, which is hyper-intense on T1-weighted images (a), hyper-intense on T2-weighted images (b) and hypo-intense
(C) T2 weighted fat saturation axial image showing bone oedema surrounding erosions (thin arrows) and adjacent synovitis (thick arrow).. Figure 12 (A) T1 weighted coronal image of