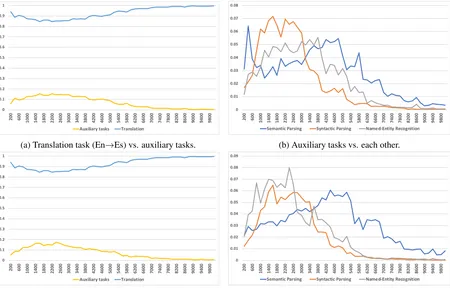
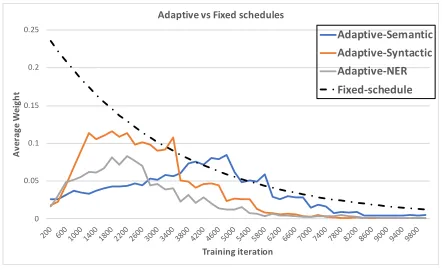
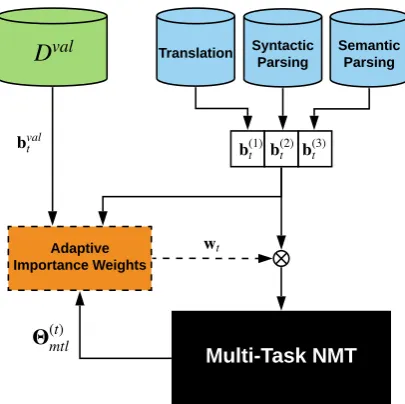
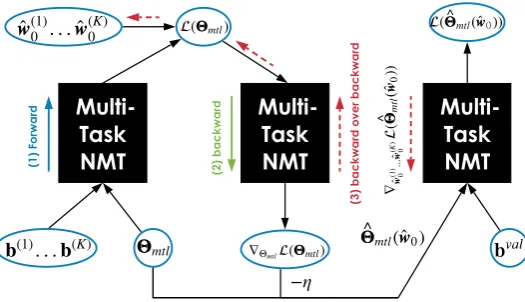
Adaptively Scheduled Multitask Learning: The Case of Low Resource Neural Machine Translation
Full text
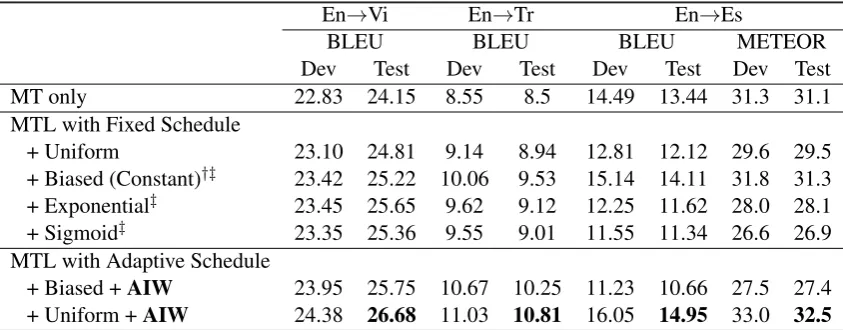
Figure
Related documents
In evaluating the effectiveness of Springboard’s provision, the research team attempted to ascertain the views of teaching staff in the client schools (including
Regulation 07(1) The person in charge shall ensure that staff have up to date knowledge and skills, appropriate to their role, to respond to behaviour that is challenging
Branagan (Secretary of the Dublin Branch of the Irish Industrial Development Association) said the objects of the Association, amongst other things, were persistently to urge upon
Propositional Satisfiability is a well-known NP-complete problem, with extensive applications in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Electronic Design Automation (EDA), and many other
This publication contains the indices of industrial production, turnover, orders received, number of employees, gross wages and salaries by branch of industry as well as indices of
Pressure coefficients (C P ) plotted as a function of location (pressure port) along dorsal antero-posterior transects (A,C) and ventral antero-posterior transects (B,D) on the
METHODS: Two neuroradiologists independently reviewed initial and follow-up MR ex- aminations of 14 patients with a clinical diagnosis of acute, symptomatic thoracolumbar SNs
The rate-limiting step in the catalytic cycle of this mutant may be the transition from open form 1 to the closed form, and the transition energy for this mutant is the same as that