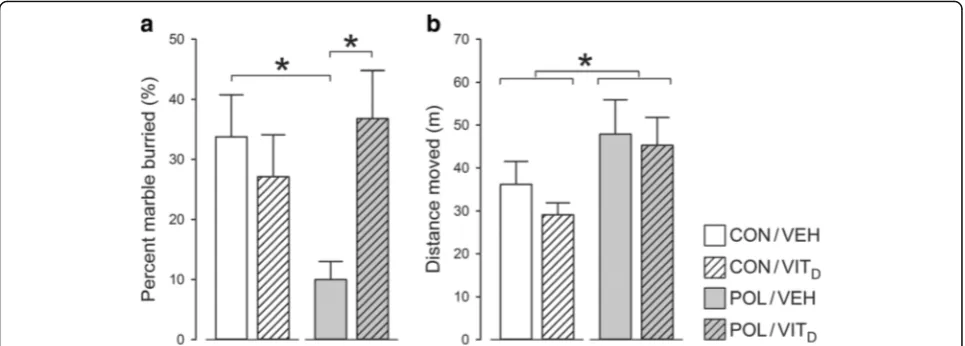
Vitamin D treatment during pregnancy prevents autism-related phenotypes in a mouse model of maternal immune activation
Full text
Figure


Related documents
StarPU and friends overview: what StarPU can do today Code and performance portability, ease of programming The Sequential Task Flow (STF) model.. Overview of some of StarPU’s usages
gigantic point cloud information preparing utilizing distributed computing innovations, particularly Apache Spark.. Filling this hole, we present our work on one of
Quality factors for fresh fruit and vegetables were defined by Kader [18] as: hygiene and quarantine factors (parasites larvae, pupae, natural toxicants, contaminants, spray
Priority to SBHA tenants; One Weeks Rent Required in advance ; close to local amenities and good transport links. Fixed term tenancy offered to
This paper explores the achievements of the Small and Medium Scale Enterprise (SME) sector in Ghana and Malawi and the role government, internal and external support institutions
We study which machine learning algorithms build a more accurate model of the behavior of the anomaly system, and focus on Linear Regression and Decision Tree algorithms..
Taking advantage of sil- icon nanowires as surface temperature nano-sensors, and using Raman Thermography, the in-plane and cross-plane components of the thermal conductivity
Conclusions: Repetitive locomotor training with an electromechanical gait trainer may improve gait velocity, endurance, spatiotemporal, and kinematic gait parameters in patients