Path Union and Double Path Union of Cordialgraphs
Full text
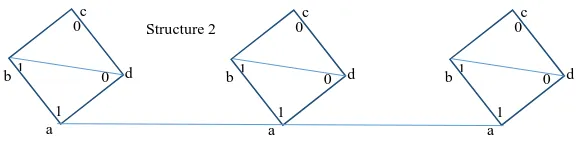
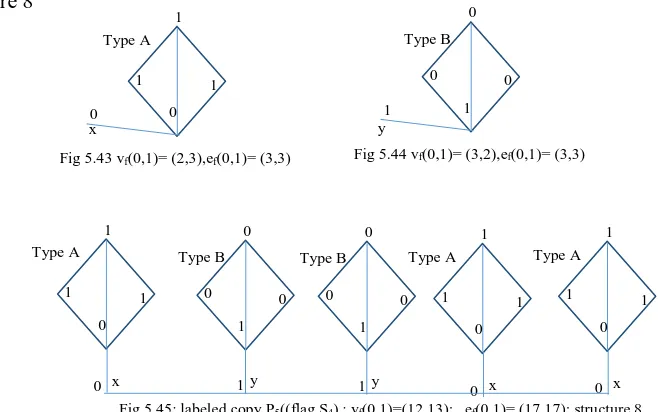
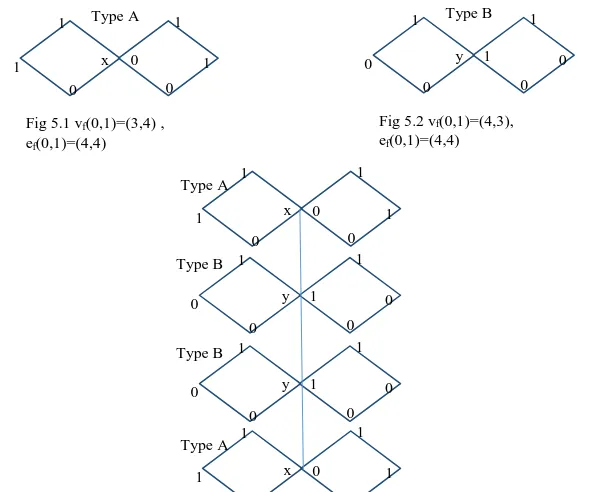
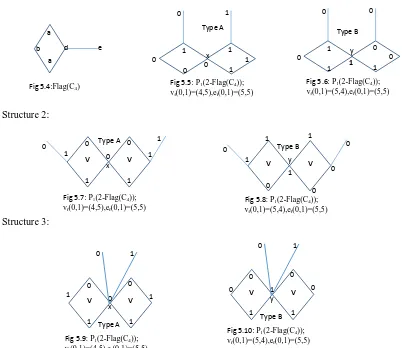
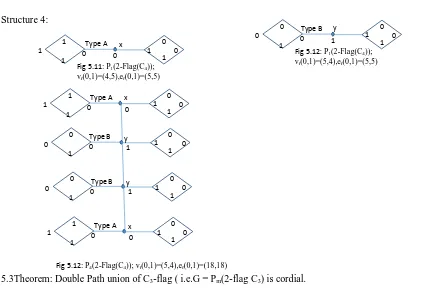
Figure

Related documents
Field of Action „Intellectual Capital“ – Human Potential as Innovation Factor – Overview. Members of Field of Action Approach – Cause for Interest Analyses
A graph Γ is G -vertex-transitive (G -edge-transitive, G -arc-transitive, respectively) if it admits G as a group of automorphisms such that G is transitive on the set of
A line graph L(G) (also called an interchange graph or edge graph) of a simple graph G is obtained by associating a vertex with each edge of the graph and connecting two vertices
• This method is used most frequently in the Indonesia because much of the coal resource base is near the surface and it is Less expensive than underground mining •
The blocktransformation graph of a graph G is the graph, whose vertex set is the union of vertices and blocks of G, in which two vertices are adjacent whenever the
In 1 , Cvetkocic defined the subdivision graph S(G) is the graph obtained from G by replacing each of its edge by a path of length 2, or equivalently by inserting an additional
The edge semientire block graph of a graph G denoted by E b (G) is the plane graph G whose vertex set is the union of set of edges, set of blocks and set of regions of G in which
An orthogonal drawing of a plane graph G is a planar drawing of G, denoted by D(G), such that each vertex of G is drawn as a point on the plane, and each edge of G is drawn as